AIR 中的显示屏幕Adobe AIR 1.0 和更高版本 使用 Adobe® AIR® Screen 类访问关于连接到计算机或设备的显示屏幕的信息。 AIR 中的显示屏幕的基础知识屏幕 API 只包含单个 Screen 类,该类提供用于获取系统屏幕信息的静态成员以及用于描述特定屏幕的实例成员。 计算机系统可以连接多台监视器或显示器,这些监视器或显示器对应于虚拟空间中排列的多个桌面屏幕。AIR Screen 类提供有关这些屏幕、屏幕的相对排列及其可用空间的信息。如果多台监视器映射到同一屏幕,则只存在一个屏幕。如果屏幕的尺寸大于监视器的显示区域,则无法确定当前可以看到屏幕的哪个部分。 屏幕表示独立的桌面显示区域。屏幕被描述为虚拟桌面内部的矩形。被指定为主显示屏的屏幕的左上角是虚拟桌面坐标系的原点。用于描述屏幕的所有值均以像素为单位提供。 查看完全大小图形 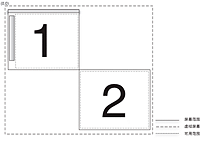 在此屏幕排列中,虚拟桌面中存在两个屏幕。主屏幕 (#1) 左上角的坐标始终是 (0,0)。如果屏幕排列更改为指定屏幕 #2 作为主屏幕,则屏幕 #1 的坐标将变为负值。报告屏幕的可用范围时将排除菜单栏、任务栏和停靠栏。 有关屏幕 API 类、方法、属性和事件的详细信息,请参阅用于 Adobe Flash Platform 的 ActionScript 3.0 参考。 枚举屏幕可以使用以下屏幕方法和属性枚举虚拟桌面的屏幕:
不要保存 Screen 类方法和属性返回的值。用户或操作系统可随时更改可用屏幕及其排列方式。 以下示例使用屏幕 API 在多个屏幕间移动窗口,以响应箭头键的按键操作。该示例获取 screens 数组并将其在垂直或水平方向排序(取决于所按的箭头键),以便将窗口移动到下一个屏幕。代码随后将遍历排序后的数组,将每个屏幕与当前屏幕的坐标进行比较。该示例调用 Screen.getScreensForRectangle(),传入窗口范围,以便识别窗口的当前屏幕。 package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.Screen;
import flash.events.KeyboardEvent;
import flash.ui.Keyboard;
import flash.display.StageAlign;
import flash.display.StageScaleMode;
public class ScreenExample extends Sprite
{
public function ScreenExample()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
stage.addEventListener(KeyboardEvent.KEY_DOWN,onKey);
}
private function onKey(event:KeyboardEvent):void{
if(Screen.screens.length > 1){
switch(event.keyCode){
case Keyboard.LEFT :
moveLeft();
break;
case Keyboard.RIGHT :
moveRight();
break;
case Keyboard.UP :
moveUp();
break;
case Keyboard.DOWN :
moveDown();
break;
}
}
}
private function moveLeft():void{
var currentScreen = getCurrentScreen();
var left:Array = Screen.screens;
left.sort(sortHorizontal);
for(var i:int = 0; i < left.length - 1; i++){
if(left[i].bounds.left < stage.nativeWindow.bounds.left){
stage.nativeWindow.x +=
left[i].bounds.left - currentScreen.bounds.left;
stage.nativeWindow.y += left[i].bounds.top - currentScreen.bounds.top;
}
}
}
private function moveRight():void{
var currentScreen:Screen = getCurrentScreen();
var left:Array = Screen.screens;
left.sort(sortHorizontal);
for(var i:int = left.length - 1; i > 0; i--){
if(left[i].bounds.left > stage.nativeWindow.bounds.left){
stage.nativeWindow.x +=
left[i].bounds.left - currentScreen.bounds.left;
stage.nativeWindow.y += left[i].bounds.top - currentScreen.bounds.top;
}
}
}
private function moveUp():void{
var currentScreen:Screen = getCurrentScreen();
var top:Array = Screen.screens;
top.sort(sortVertical);
for(var i:int = 0; i < top.length - 1; i++){
if(top[i].bounds.top < stage.nativeWindow.bounds.top){
stage.nativeWindow.x += top[i].bounds.left - currentScreen.bounds.left;
stage.nativeWindow.y += top[i].bounds.top - currentScreen.bounds.top;
break;
}
}
}
private function moveDown():void{
var currentScreen:Screen = getCurrentScreen();
var top:Array = Screen.screens;
top.sort(sortVertical);
for(var i:int = top.length - 1; i > 0; i--){
if(top[i].bounds.top > stage.nativeWindow.bounds.top){
stage.nativeWindow.x += top[i].bounds.left - currentScreen.bounds.left;
stage.nativeWindow.y += top[i].bounds.top - currentScreen.bounds.top;
break;
}
}
}
private function sortHorizontal(a:Screen,b:Screen):int{
if (a.bounds.left > b.bounds.left){
return 1;
} else if (a.bounds.left < b.bounds.left){
return -1;
} else {return 0;}
}
private function sortVertical(a:Screen,b:Screen):int{
if (a.bounds.top > b.bounds.top){
return 1;
} else if (a.bounds.top < b.bounds.top){
return -1;
} else {return 0;}
}
private function getCurrentScreen():Screen{
var current:Screen;
var screens:Array = Screen.getScreensForRectangle(stage.nativeWindow.bounds);
(screens.length > 0) ? current = screens[0] : current = Screen.mainScreen;
return current;
}
}
}
|

|