Chapter 14. Runtime Configuration
CloverETL Runtime is one of architectural layers of CloverETL Designer. It takes care of running graphs and subgraphs.
Current state of CloverELT Runtime can be seen in the right bottom corner of perspective.
The CloverETL Runtime is configured in Preferences dialog: open → and choose → .
The CloverETL Runtime Configuration serves to set up:
Temporary Disk Space Settings
The temporary disk space is necessary for debug files. You can store temporary files either into a temporary directory within the workspace directory or into a user-defined directory.
Engine Configuration
Change max record size etc. See Engine Configuration.
Java Runtime Environment to be Used
You may define an alternative JRE to be used.
Amount of Memory for Java Heap Size
It is important to define some memory size because Java Virtual Machine needs this memory capacity to run the graphs.
Additional Virtual Machine Parameters
Additional libraries can be added to the classpath.
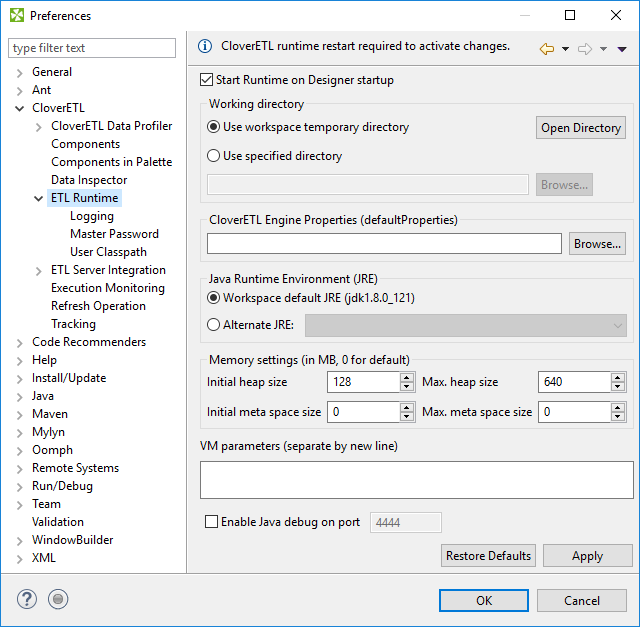 |
Figure 14.1. CloverETL Runtime
To take effect of the changes in runtime configuration restart of CloverETL Runtime is needed. The runtime menu is accessible in the right bottom corner of CloverETL window.
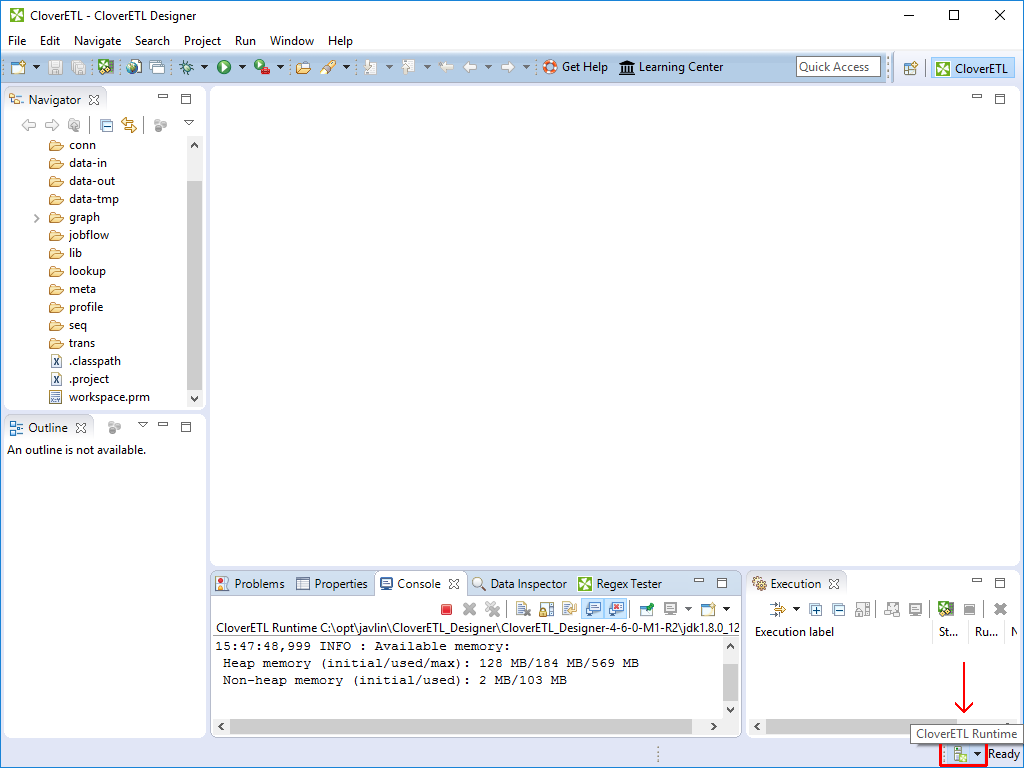 |
Figure 14.2. Accessing CloverETL Runtime menu
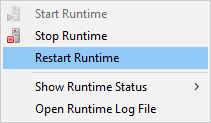
Figure 14.3. Restarting CloverETL Runtime
Example 14.1. Adding an External Library to Classpath
To add an external library to the CloverETL runtime's classpath
the -Djava.library.path=path/to/library option should be used.
To add libraries located in C:/addressDoctor/lib type -Djava.library.path=C:\addressDoctor\lib
into VM parameters textarea.
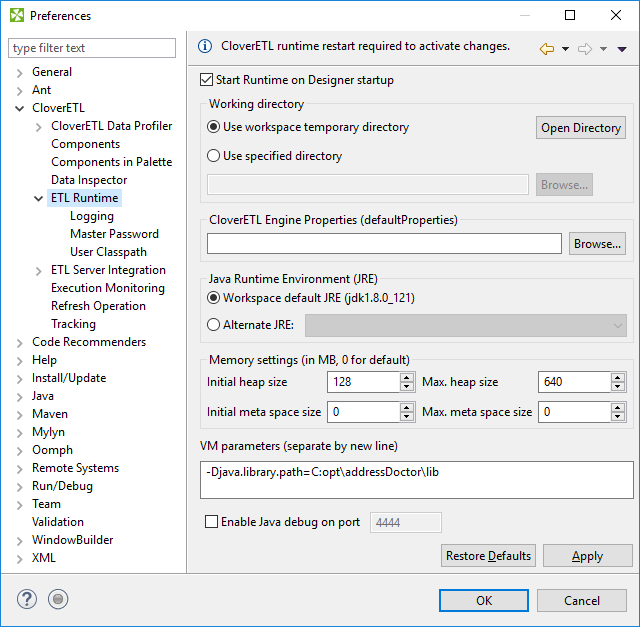 |
Figure 14.4. Adding library to classpath using VM parameters
Additional VM Parameter
Server mode (-server)
There are two flavours of JVM: client and server. The client system (default) is optimal for applications which need fast start-up times or small footprints. Switching to server mode is advantageous to long-running applications, for which reaching the maximum program execution speed is generally more important than having the fastest possible start-up time. To run the server system, Java Development Kit (JDK) needs to be downloaded.