Types of Edges
There are four types of edges, three of them have an internal buffer. You can select type of the edge with right clicking on the edge, then and choosing from the option.
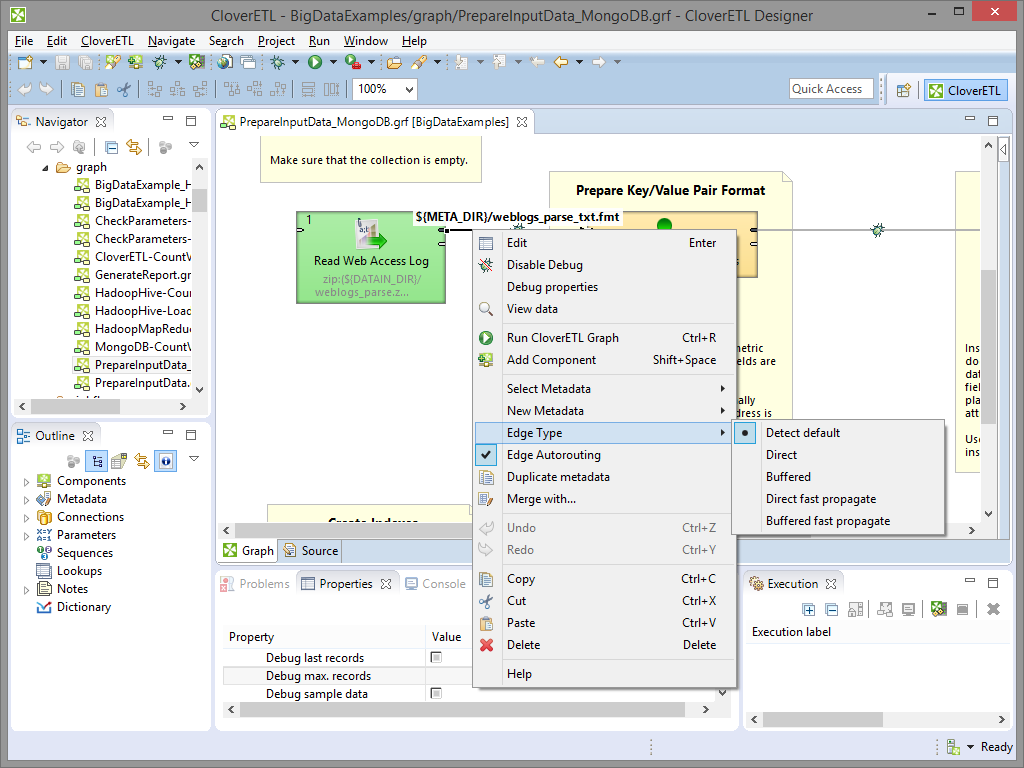 |
Figure 31.1. Selecting the Edge Type
Edges can be set to any of the following types:
Direct Edge
Direct edge has a buffer in memory, which helps data to flow faster. This is the default edge type for ETL graphs.
In 4.5.0-M1, a timeout was introduced, therefore the edge can send records in smaller chunks. This can improve the throughput in graphs with high-latency data sources.
Buffered Edge
The buffered edge has also a buffer in memory, but, if necessary, it can store data on disk as well. Thus the buffer size is unlimited. It has two buffers, one for reading and one for writing.
Direct Fast Propagate Edge
The direct fast propagate edge is an alternative implementation of the Direct edge. This edge type has no buffer but it still provides a fast data flow. It sends each data record to the target of this edge as soon as it receives it. This is the default edge type for jobflows.
Buffered Fast Propagate Edge
The buffered fast propagate edge is an alternative implementation of the Buffered edge. This type of edge has a memory buffer, but, if necessary, it can store data on disk as well. Thus the buffer size is unlimited. Moreover, data records written to this edge are immediately available to the target of this edge as soon as it receives it.
Phase Connection Edge
The phase connection edge type cannot be selected, it is created automatically between two components with different phase numbers.
If you do not want to specify an explicit edge type, you can let Clover decide by selecting the option Detect default.