| Documentation |
|---|---|
25.14. Using REF CURSOR in a .NET ApplicationA REF CURSOR is a cursor variable that contains a pointer to a query result set. The result set is determined by the execution of the OPEN FOR statement using the cursor variable. A cursor variable is not tied to a particular query like a static cursor. The same cursor variable may be opened a number of times with the OPEN FOR statement containing different queries and each time, a new result set will be created for that query and made available via the cursor variable. EnterpriseDB supports the declaration of a cursor variable using both the SYS_REFCURSOR built-in data type as well as creating a type of REF CURSOR and then declaring a variable of that type. SYS_REFCURSOR is a REF CURSOR type that allows any result set to be associated with it. This is known as a weakly-typed REF CURSOR. Following is the declaration of a weakly typed SYS_REFCURSOR: name SYS_REFCURSOR; Following is the example of a strongly-typed REF CURSOR: TYPE cursor_type_name IS REF CURSOR RETURN return_type; Read,more about REF CURSORS and what you can use them for in REF CURSORS and Cursor Variables. Let us proceed with learning about using REF CURSORS in .NET with an example. 25.14.1. ExampleBefore we jump into the .NET code making use of REF CURSORS, we will create a stored procedure called "refcur_inout_callee(v_refcur IN OUT SYS_REFCURSOR)" which will be used in our .NET code. The following code listing shows the declaration of this stored procedure: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE refcur_inout_callee(v_refcur IN OUT SYS_REFCURSOR) IS BEGIN OPEN v_refcur FOR SELECT ename FROM emp; END;
The above stored procedure can be created using EnterpriseDB Developer Studio. To use the above defined procedure from our .NET code, we must specify the datatype of the REF CURSOR being passed as an IN parameter, as shown in the above script. Following is the C# code which will use the above declared stored procedure to retrieve employee names from the table emp:
using System;
using System.Data;
using EnterpriseDB.EDBClient;
namespace EDBRefCursor
{
class EmpRefcursor
{
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
EDBConnection conn = new EDBConnection("server=localhost;port=5444;username=ussama;
password=1234;database=edb");
conn.Open();
EDBTransaction tran = conn.BeginTransaction();
try
{
EDBCommand command = new EDBCommand("refcur_inout_callee (:refCursor)", conn);
command.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
command.Transaction = tran;
command.Parameters.Add(new EDBParameter("refCursor",EDBTypes.EDBDbType.RefCursor,10,"refCursor",
ParameterDirection.InputOutput,false,2,2,System.Data.DataRowVersion.Current,null));
command.Prepare();
command.Parameters[0].Value = null;
EDBDataReader result = command.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.SequentialAccess);
EDBDataReader reader = (EDBDataReader)command.Parameters[0].Value;
int fc=reader.FieldCount;
while(reader.Read())
{
for(int i=0;i<fc;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(reader.GetString(i));
}
}
result.Close();
Console.ReadLine();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
}
}
}
First of all a connection is established with the database, this is done by specifying the server name, port number, user ID, password and database name. The following section of the .NET sample code performs this operation: EDBConnection conn = new EDBConnection("server=localhost;port=5444;username=ussama;password=1234;database=edb");
conn.Open();
The following segment of .NET code will display the result on the console.
for(int i=0;i<fc;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(reader.GetString(i));
}
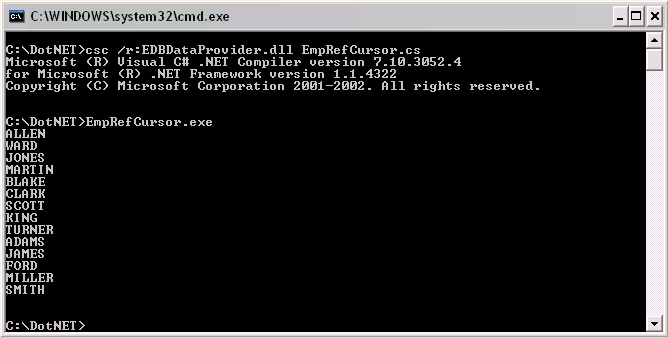
When the above .NET code is executed, it will display the names of the employees from the emp table. The following image shows the result.
|