


Code in Pid1
Pid2 = spawn(Mod, Func, Args)
After

Pid2 is process identifier of the new process - this is known only to process Pid1.
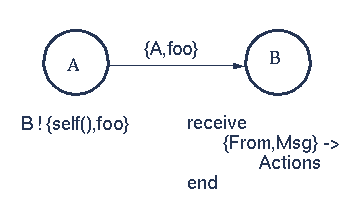
self() - returns the Process Identity (Pid) of the process executing this function.
From and Msg become bound when the message is received. Messages can carry data.
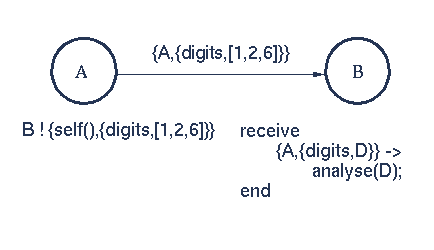
-module(echo).
-export([go/0, loop/0]).
go() ->
Pid2 = spawn(echo, loop, []),
Pid2 ! {self(), hello},
receive
{Pid2, Msg} ->
io:format("P1 ~w~n",[Msg])
end,
Pid2 ! stop.
loop() ->
receive
{From, Msg} ->
From ! {self(), Msg},
loop();
stop ->
true
end.
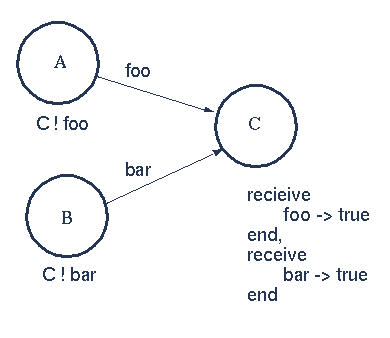
The message foo is received - then the message bar - irrespective of the order in which they were sent.
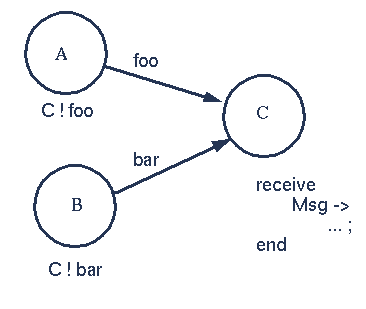
The first message to arrive at the process C will be processed - the variable Msg in the process C will be bound to one of the atoms foo or bar depending on which arrives first.
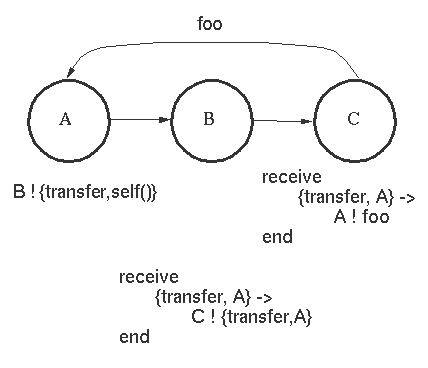
ringing_a(A, B) ->
receive
{A, on_hook} ->
A ! {stop_tone, ring},
B ! terminate,
idle(A);
{B, answered} ->
A ! {stop_tone, ring},
switch ! {connect, A, B},
conversation_a(A, B)
end.
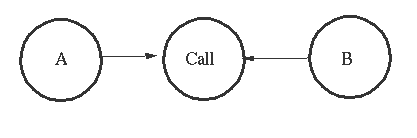
This is the code in the process `Call. A and
B are local bound variables in the process Call.
start() ->
Pid = spawn(num_anal, server, [])
register(analyser, Pid).
analyse(Seq) ->
analyser ! {self(),{analyse,Seq}},
receive
{analysis_result,R} ->
R
end.
Any process can send a message to a registered process.
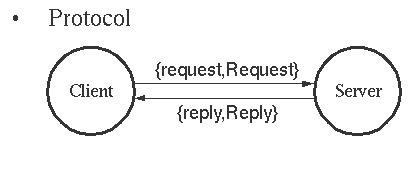
Protocol
-module(myserver).
server(Data) ->
receive
{From,{request,X}} ->
{R, Data1} = fn(X, Data),
From ! {myserver,{reply, R}},
server(Data1)
end.
-export([request/1]).
request(Req) ->
myserver ! {self(),{request,Req}},
receive
{myserver,{reply,Rep}} ->
Rep
end.
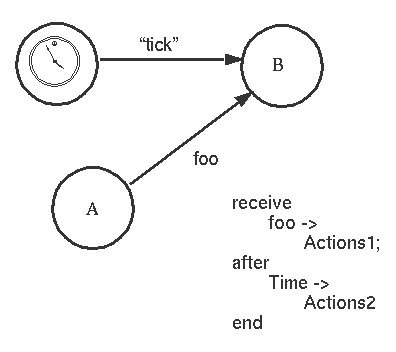
If the message foo is received from A within the time Time perform Actions1 otherwise perform Actions2.
sleep(T) -> receive after T -> true end.suspend() - process suspends indefinitely.
suspend() -> receive after infinity -> true end.alarm(T, What) - The message What is sent to the current process iin T miliseconds from now
set_alarm(T, What) -> spawn(timer, set, [self(),T,What]). set(Pid, T, Alarm) -> receive after T -> Pid ! Alarm end. receive Msg -> ... ; endflush() - flushes the message buffer
flush() -> receive Any -> flush() after 0 -> true end.A value of 0 in the timeout means check the message buffer first and if it is empty execute the following code.