Seam is an application framework for Enterprise Java. It is inspired by the following principles:
- One kind of "stuff"
Seam defines a uniform component model for all business logic in your application. A Seam component may be stateful, with the state associated with any one of several well-defined contexts, including the long-running, persistent, business process context and the conversation context, which is preserved across multiple web requests in a user interaction.
There is no distinction between presentation tier components and business logic components in Seam. You can layer your application according to whatever architecture you devise, rather than being forced to shoehorn your application logic into an unnatural layering scheme forced upon you by whatever combination of stovepipe frameworks you're using today.
Unlike plain Java EE or J2EE components, Seam components may simultaneously access state associated with the web request and state held in transactional resources (without the need to propagate web request state manually via method parameters). You might object that the application layering imposed upon you by the old J2EE platform was a Good Thing. Well, nothing stops you creating an equivalent layered architecture using Seam—the difference is that you get to architect your own application and decide what the layers are and how they work together.
- Integrate JSF with EJB 3.0
JSF and EJB 3.0 are two of the best new features of Java EE 5. EJB3 is a brand new component model for server side business and persistence logic. Meanwhile, JSF is a great component model for the presentation tier. Unfortunately, neither component model is able to solve all problems in computing by itself. Indeed, JSF and EJB3 work best used together. But the Java EE 5 specification provides no standard way to integrate the two component models. Fortunately, the creators of both models foresaw this situation and provided standard extension points to allow extension and integration with other frameworks.
Seam unifies the component models of JSF and EJB3, eliminating glue code, and letting the developer think about the business problem.
It is possible to write Seam applications where "everything" is an EJB. This may come as a surprise if you're used to thinking of EJBs as coarse-grained, so-called "heavyweight" objects. However, version 3.0 has completely changed the nature of EJB from the point of view of the developer. An EJB is a fine-grained object—nothing more complex than an annotated JavaBean. Seam even encourages you to use session beans as JSF action listeners!
On the other hand, if you prefer not to adopt EJB 3.0 at this time, you don't have to. Virtually any Java class may be a Seam component, and Seam provides all the functionality that you expect from a "lightweight" container, and more, for any component, EJB or otherwise.
- Integrated AJAX
Seam supports the best open source JSF-based AJAX solutions: JBoss RichFaces and ICEfaces. These solutions let you add AJAX capability to your user interface without the need to write any JavaScript code.
Alternatively, Seam provides a built-in JavaScript remoting layer that lets you call components asynchronously from client-side JavaScript without the need for an intermediate action layer. You can ever subscribe to server-side JMS topics and receive messages via AJAX push.
Neither of these approaches would work well, were it not for Seam's built-in concurrency and state management, which ensures that many concurrent fine-grained, asynchronous AJAX requests are handled safely and efficiently on the server side.
- Business process as a first class construct
Optionally, Seam provides transparent business process management via jBPM. You won't believe how easy it is to implement complex workflows, collaboration and and task management using jBPM and Seam.
Seam even allows you to define presentation tier pageflow using the same language (jPDL) that jBPM uses for business process definition.
JSF provides an incredibly rich event model for the presentation tier. Seam enhances this model by exposing jBPM's business process related events via exactly the same event handling mechanism, providing a uniform event model for Seam's uniform component model.
- Declarative state management
We're all used to the concept of declarative transaction management and declarative security from the early days of EJB. EJB 3.0 even introduces declarative persistence context management. These are three examples of a broader problem of managing state that is associated with a particular context, while ensuring that all needed cleanup occurs when the context ends. Seam takes the concept of declarative state management much further and applies it to application state. Traditionally, J2EE applications implement state management manually, by getting and setting servlet session and request attributes. This approach to state management is the source of many bugs and memory leaks when applications fail to clean up session attributes, or when session data associated with different workflows collides in a multi-window application. Seam has the potential to almost entirely eliminate this class of bugs.
Declarative application state management is made possible by the richness of the context model defined by Seam. Seam extends the context model defined by the servlet spec—request, session, application—with two new contexts—conversation and business process—that are more meaningful from the point of view of the business logic.
You'll be amazed at how many things become easier once you start using conversations. Have you ever suffered pain dealing with lazy association fetching in an ORM solution like Hibernate or JPA? Seam's conversation-scoped persistence contexts mean you'll rarely have to see a LazyInitializationException. Have you ever had problems with the refresh button? The back button? With duplicate form submission? With propagating messages across a post-then-redirect? Seam's conversation management solves these problems without you even needing to really think about them. They're all symptoms of the broken state management architecture has been prevalent since the earliest days of the web.
- Bijection
The notion of Inversion of Control or dependency injection exists in both JSF and EJB3, as well as in numerous so-called "lightweight containers". Most of these containers emphasize injection of components that implement stateless services. Even when injection of stateful components is supported (such as in JSF), it is virtually useless for handling application state because the scope of the stateful component cannot be defined with sufficient flexibility, and because components belonging to wider scopes may not be injected into components belonging to narrower scopes.
Bijection differs from IoC in that it is dynamic, contextual, and bidirectional. You can think of it as a mechanism for aliasing contextual variables (names in the various contexts bound to the current thread) to attributes of the component. Bijection allows auto-assembly of stateful components by the container. It even allows a component to safely and easily manipulate the value of a context variable, just by assigning to an attribute of the component.
- Workspace management and multi-window browsing
Seam applications let the user freely switch between multiple browser tabs, each associated with a different, safely isolated, conversation. Applications may even take advantage of workspace management, allowing the user to switch between conversations (workspaces) in a single browser tab. Seam provides not only correct multi-window operation, but also multi-window-like operation in a single window!
- Prefer annotations to XML
Traditionally, the Java community has been in a state of deep confusion about precisely what kinds of meta-information counts as configuration. J2EE and popular "lightweight" containers have provided XML-based deployment descriptors both for things which are truly configurable between different deployments of the system, and for any other kinds or declaration which can not easily be expressed in Java. Java 5 annotations changed all this.
EJB 3.0 embraces annotations and "configuration by exception" as the easiest way to provide information to the container in a declarative form. Unfortunately, JSF is still heavily dependent on verbose XML configuration files. Seam extends the annotations provided by EJB 3.0 with a set of annotations for declarative state management and declarative context demarcation. This lets you eliminate the noisy JSF managed bean declarations and reduce the required XML to just that information which truly belongs in XML (the JSF navigation rules).
- Integration testing is easy
Seam components, being plain Java classes, are by nature unit testable. But for complex applications, unit testing alone is insufficient. Integration testing has traditionally been a messy and difficult task for Java web applications. Therefore, Seam provides for testability of Seam applications as a core feature of the framework. You can easily write JUnit or TestNG tests that reproduce a whole interaction with a user, exercising all components of the system apart from the view (the JSP or Facelets page). You can run these tests directly inside your IDE, where Seam will automatically deploy EJB components using JBoss Embedded.
- The specs ain't perfect
We think the latest incarnation of Java EE is great. But we know it's never going to be perfect. Where there are holes in the specifications (for example, limitations in the JSF lifecycle for GET requests), Seam fixes them. And the authors of Seam are working with the JCP expert groups to make sure those fixes make their way back into the next revision of the standards.
- There's more to a web application than serving HTML pages
Today's web frameworks think too small. They let you get user input off a form and into your Java objects. And then they leave you hanging. A truly complete web application framework should address problems like persistence, concurrency, asynchronicity, state management, security, email, messaging, PDF and chart generation, workflow, wikitext rendering, webservices, caching and more. Once you scratch the surface of Seam, you'll be amazed at how many problems become simpler...
Seam integrates JPA and Hibernate3 for persistence, the EJB Timer Service and Quartz for lightweight asychronicity, jBPM for workflow, JBoss Rules for business rules, Meldware Mail for email, Hibernate Search and Lucene for full text search, JMS for messaging and JBoss Cache for page fragment caching. Seam layers an innovative rule-based security framework over JAAS and JBoss Rules. There's even JSF tag libraries for rendering PDF, outgoing email, charts and wikitext. Seam components may be called synchronously as a Web Service, asynchronously from client-side JavaScript or Google Web Toolkit or, of course, directly from JSF.
- Get started now!
Seam works in any Java EE application server, and even works in Tomcat. If your environment supports EJB 3.0, great! If it doesn't, no problem, you can use Seam's built-in transaction management with JPA or Hibernate3 for persistence. Or, you can deploy JBoss Embedded in Tomcat, and get full support for EJB 3.0.
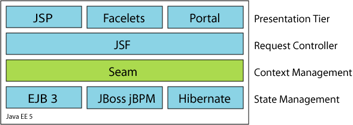
It turns out that the combination of Seam, JSF and EJB3 is the simplest way to write a complex web application in Java. You won't believe how little code is required!