Howto: Clustering with JOnAS
This guide describes how to configure Apache, Tomcat, and JOnAS to install a
cluster.
This configuration uses the Apache/Tomcat plug-in mod_jk. This plug-in
allows use of the Apache HTTP server in front of one or several Tomcat
JSP/Servlet engines, and provides the capability of forwarding some of the
HTTP requests (typically those concerning the dynamic pages, i.e. JSP and
Servlet requests) to Tomcat instances.
It also uses the In-Memory-Session-Replication technique based on the
group communication protocol JavaGroups to provide failover at servlet/JSP
level.
For the load balancing at EJB level, a clustered JNDI called cmi is
used.
This document describes one architecture with all the clustering
functionalities available in JOnAS, the configuration of architectures
integrating one of those functionalities, and other possible
configurations.
The content of this guide is the following:
Architecture
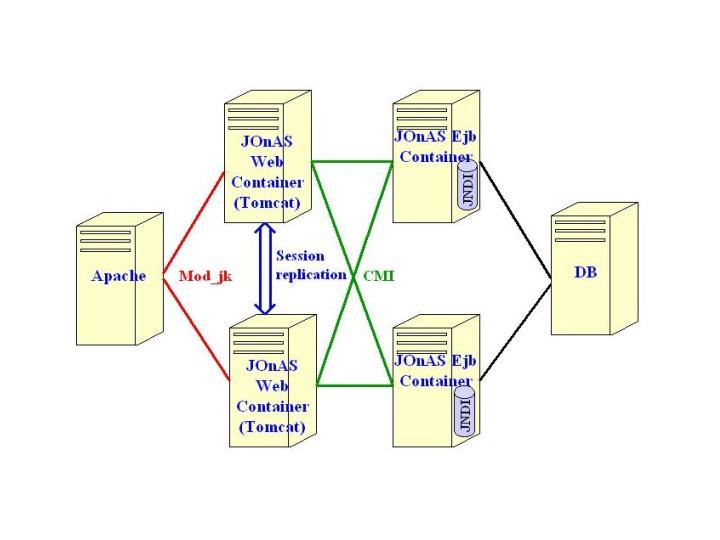
The architecture with all the clustering functionality available in JOnAS is:
Apache as the front-end HTTP server, JOnAS/Tomcat as J2EE Container, and a
shared database.
At the Servlet / JSP level, the mod_jk plug-in provides
Load Balancing / High Availability and the Tomcat-Replication module provides
Failover.
At the EJB level, the clustered JNDI cmi provides Load
Balancing / High Availability.
The database is shared by the JOnAS servers.
The versions assumed here are: Apache 2.0, JOnAS 3.1.x/Tomcat 4.1.x
package.
The architecture presented in this document is shown in the following
illustration:
This architecture provides:
- Load balancing: Requests can be dispatched over a set of servers
to distribute the load. This improves the "scalability" by allowing more
requests to be processed concurrently.
- High Availability (HA): having several servers able to fulfill a
request makes it possible to ensure that, if a server dies, the request
can be sent to an available server (thus the load-balancing algorithm
ensures that the server to which the request will be sent is available).
Therefore, "Service Availability" is achieved.
- Failover at Servlet / JSP Level: This feature ensures that, if
one JSP/servlet server goes down, another server is able to transparently
take over, i.e. the request will be switched to another server without
service disruption. This means that it will not be necessary to start
over, thus achieving Continuity.
However, failover at EJB level is not available. This means that no
State Replication is provided. The mechanism to provide failover at EJB level
is under development and will be available in a coming version of JOnAS.
Products Installation
This chapter provides information about installing Apache and JOnAS / Tomcat.
The versions assumed here are: Apache 2.0 and the package JOnAS 3.1.x /Tomcat
4.1.x.
Installing Apache
- Download Apache HTTP server source code from the Apache site.
- Extract the source code.
gunzip httpd-2_0_XX.tar.gz
tar xvf httpd-2_0_XX.tar
- Compile and Install.
./configure
make
make install
A binary version is also available for installation at the Apache site.
Installing the package JOnAS / Tomcat
Refer to Installing JOnAS with a web
container from scratch.
Load balancing at web level with
mod_jk
This chapter describes how to configure Apache, Tomcat, and JOnAS to run the
architecture shown in the following illustration:
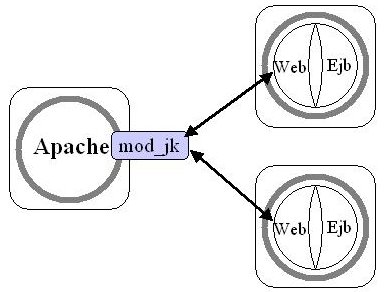
Configuring the JK Module
JK module principles
Mod_jk is a plug-in that handles the communication between Apache and Tomcat.
Mod_jk uses the concept of worker. A worker is a Tomcat instance that is
running to perform servlet requests coming from the web server. Each worker
is identified to the web server by the host on which it is located, the port
where it listens, and the communication protocol used to exchange messages.
In this configuration there is one worker for each Tomcat instance and one
worker that will handle the load balancing (this is a specific worker with no
host and no port number). All workers are defined in a file called
worker.properties.
Note: this module can also be used for site partitioning.
install Mod_jk
The easiest way to obtain this plug-in is to download the binary from the Tomcat
Site and place it in the directory libexec (for unix) or modules (for
windows or Mandrake) of the Apache installation directory.
Configure Apache
- httpd.conf
Create a file tomcat_jk.conf, which must be included in
$APACHE_HOME/conf/httpd.conf.
This file should load the module mod_jk:
LoadModule jk_module modules/mod_jk.so (for windows)
LoadModule jk_module libexec/mod_jk.so (for Unix)
AddModule mod_jk.c
And configure mod_jk:
# Location of the worker file
JkWorkersFile "/etc/httpd/conf/jk/workers.properties"
# Location of the log file
JkLogFile "/etc/httpd/jk/logs/mod_jk.log"
# Log level : debug, info, error or emerg
JkLogLevel emerg
# Assign specific URL to Tomcat workers
JkMount /admin loadbalancer
JkMount /admin/* loadbalancer
JkMount /examples loadbalancer
JkMount /examples/* loadbalancer
- worker.properties
This file should contain the list of workers first:
worker.list=<a comma separated list of worker names>
then the properties of each worker:
worker.<worker name>.<property>=<property
value>
The following is an example of a worker.properties file:
# List the workers name
worker.list=worker1,worker2,loadbalancer
# ----------------
# First worker
# ----------------
worker.worker1.port=8009
worker.worker1.host=server1
worker.worker1.type=ajp13
# Load balance factor
worker.worker1.lbfactor=1
# ----------------
# Second worker
# ----------------
worker.worker2.port=8009
worker.worker2.host=server2
worker.worker2.type=ajp13
worker.worker2.lbfactor=1
# ----------------------
# Load Balancer worker
# ----------------------
worker.loadbalancer.type=lb
worker.loadbalancer.balanced_workers=worker1,worker2
Configure Tomcat
To configure Tomcat, perform the following configuration steps for each
Tomcat server.
- Configure Tomcat for the connector AJP13. In the file conf/server.xml
of the JOnAS installation directory, add (if not already there):
<!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 -->
<Connector className="org.apache.ajp.tomcat4.Ajp13Connector"
port="8009" minProcessors="5"
maxProcessors="75"
acceptCount="10" debug="20"/>
- Define the jvmRoute.
In the file conf/server.xml of the JOnAS installation directory, add a
unique route to the Catalina engine.
Replace the line:
<Engine name="Standalone" defaultHost="localhost"
debug="0">
with:
<Engine jvmRoute="worker1" name="Standalone"
defaultHost="localhost" debug="0">
Note: The jvmRoute name should be the same as the name of the
associated worker defined in worker.properties. This will ensure the
Session affinity.
Configuring JOnAS
In the JOnAS-specific deployment descriptor, add the tag shared for
the entity beans involved and set it to true. When this flag is set
to true, multiple instances of the same entity bean in different JOnAS
servers can access a common database concurrently.
The following is an example of a deployment descriptor with the flag
shared:
<jonas-ejb-jar>
<jonas-entity>
<ejb-name>Id_1</ejb-name>
<jndi-name>clusterId_1</jndi-name>
<shared>true</shared>
<jdbc-mapping>
<jndi-name>jdbc_1</jndi-name>
<jdbc-table-name>clusterIdentityEC</jdbc-table-name>
<cmp-field-jdbc-mapping>
<field-name>name</field-name>
<jdbc-field-name>c_name</jdbc-field-name>
</cmp-field-jdbc-mapping>
<cmp-field-jdbc-mapping>
<field-name>number</field-name>
<jdbc-field-name>c_number</jdbc-field-name>
</cmp-field-jdbc-mapping>
<finder-method-jdbc-mapping>
<jonas-method>
<method-name>findByNumber</method-name>
</jonas-method>
<jdbc-where-clause>where
c_number = ?</jdbc-where-clause>
</finder-method-jdbc-mapping>
<finder-method-jdbc-mapping>
<jonas-method>
<method-name>findAll</method-name>
</jonas-method>
<jdbc-where-clause></jdbc-where-clause>
</finder-method-jdbc-mapping>
</jdbc-mapping>
</jonas-entity>
</jonas-ejb-jar>
Running a Web Application
The web application is now ready to run:
- Start the jonas servers: jonas start.
- Restart Apache: /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart.
- Use a browser to access the welcome page, usually index.html.
Session Replication at web level
The intent of this chapter is to configure Apache, Tomcat, and JOnAS to run
the following architecture:
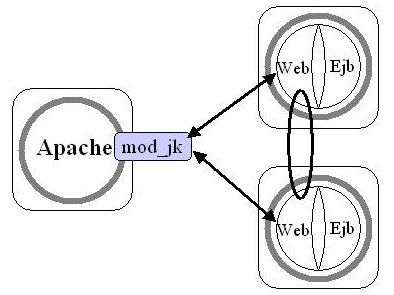
The term session replication is used when the current service state is
being replicated across multiple application instances. Session replication
occurs when the information stored in an HttpSession is replicated from, in
this example, one servlet engine instance to another. This could be data such
as items contained in a shopping cart or information being entered on an
insurance application. Anything being stored in the session must be
replicated for the service to failover without a disruption.
The solution chosen for achieving Session replication is called
in-memory-session-replication. It uses a group communication protocol written
entirely in Java, called JavaGroups. JavaGroups is a communication protocol
based on the concept of virtual synchrony and probabilistic broadcasting.
The follow describes the steps for achieving Session replication with
JOnAS.
Running your Web Application
The web application is now ready to run in the cluster:
- Start the JOnAS servers : jonas start.
- Restart Apache : /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart.
- Use a browser to access the welcome page, usually index.html.
Load Balancing at EJB level
The intent of this chapter is to configure JOnAS to run the following
architecture:
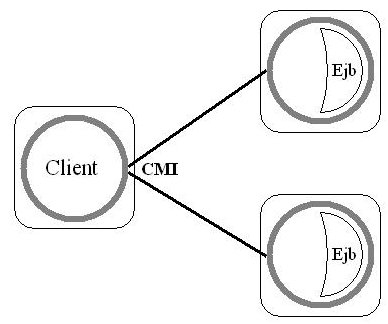
CMI Principles
CMI is a new ORB used by JOnAS to provide clustering for load balancing and
high availability. Several instances of JOnAS can be started together in a
cluster to share their EJBs. It is possible to start the same EJB on each
JOnAS, or to distribute their load. A URL referencing several JOnAS instances
can be provided to the clients. At lookup time, a client randomly chooses one
of the available servers to request the required bean. Each JOnAS instance
has the knowledge (through Javagroups) of the distribution of the Beans in
the cluster. An answer to a lookup is a special clustered stub, containing
stubs to each instance known in the cluster. Each method call on the Home of
the bean can be issued by the stub to a new instance, to balance the load on
the cluster. The default algorithm used for load distribution is currently a
weighted round robin.
CMI Configuration
In the case of EJB level clustering (CMI), the client may be either a fat
Java client (e.g. a Swing application), or a Web application (i.e.
Servlets/JSPs running within JOnAS). In the second case, the JOnAS server
running the Web client should be configured in the same way as the other
nodes of the cluster.
- In the build.properties of the application, set the protocol name to
cmi before compilation:
protocols.names=cmi
- In the file carol.properties of each server (in the directory
$JONAS_BASE/conf) and of a fat Java client, set the protocol to cmi:
carol.protocols=cmi
- In the file carol.properties of each server of the cluster, configure
the multicast address, the group name, the round-robin weight factor,
etc.
The following is a configuration example:
# java.naming.provider.url property
carol.cmi.url=cmi://localhost:2002
# Multicast address used by the registries in the cluster
carol.cmi.multicast.address=224.0.0.35:35467
# Groupname for Javagroups
carol.cmi.multicast.groupname=G1
# Factor used for this server in weighted round robin algorithms
carol.cmi.rr.factor=100
- For a fat Java client, specify the list of registries available in the
carol.properties file:
carol.cmi.url=cmi://server1:port1[,server2:port2...]
Note 1: The multicast address and group name must be the same for all
JOnAS servers in the cluster.
Note 2: If Tomcat Replication associated to cmi is used, the multicast
addresses of the two configurations must be different.
Preview of a coming version
A solution that enables failover at EJB level is currently under development.
This signifies state replication for stateful session beans and entity beans.
This will enable the following architecture:

Used symbols
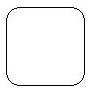 |
A node (computer) that hosts one or more servers |
|
|
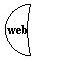 |
A web container |
 |
An ejb container |
 |
A JOnAS instance that hosts a web container |
 |
A JOnAS instance that hosts an ejb container |
 |
A JOnAS instance that hosts a web container and an ejb
container |
|
|
 |
An Apache server with the mod_jk module |
|
|
References












