Resource Control Sets Associated With a Project, Processes, and Tasks
The following figure shows the resource control sets associated with tasks, processes and a project.
Figure 5-1 Resource Control Sets for Task, Project, and Process
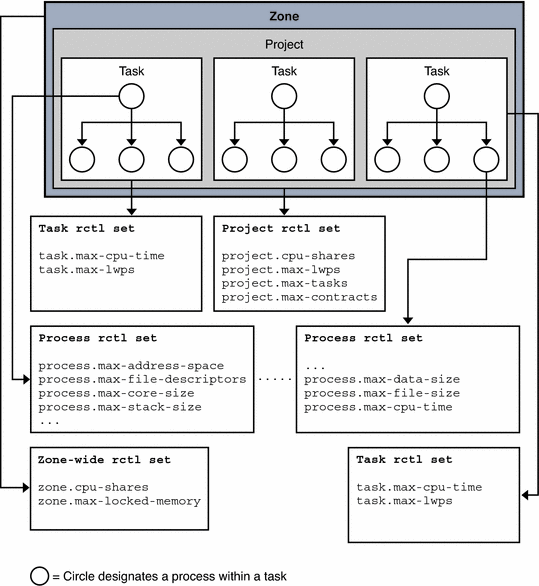
More than one resource control can exist on a resource, each resource control at a containment level in the process model. Resource controls can be active on the same resource for both a process and collective task or collective project. In this case, the action for the process takes precedence. For example, action is taken on process.max-cpu-time before task.max-cpu-time if both controls are encountered simultaneously.
Resource Controls Associated With a Project
Resource controls associated with a project include the following:
- project.cpu-shares
The number of CPU shares that are granted to this project for use with the fair share scheduler, FSS(7).
- project.max-crypto-memory
Total amount of kernel memory that can be used by libpkcs11 for hardware crypto acceleration. Allocations for kernel buffers and session-related structures are charged against this resource control.
- project.max-locked-memory
Total amount of physical locked memory allowed.
Note that this resource control replaced project.max-device-locked-memory, which has been removed.
- project.max-msg-ids
Maximum number of System V message queues allowed for a project.
- project.max-port-ids
Maximum allowable number of event ports.
- project.max-sem-ids
Maximum number of semaphore IDs allowed for a project.
- project.max-shm-ids
Maximum number of shared memory IDs allowed for this project.
- project.max-msg-ids
Maximum number of message queue IDs allowed for this project.
- project.max-shm-memory
Total amount of shared memory allowed for this project.
- project.max-lwps
Maximum number of LWPs simultaneously available to this project.
- project.max-tasks
Maximum number of tasks allowable in this project.
- project.max-contracts
Maximum number of contracts allowed in this project.
Resource Controls Associated With Tasks
Resource controls associated with tasks include the following:
- task.max-cpu-time
Maximum CPU time (seconds) available to this task's processes.
- task.max-lwps
Maximum number of LWPs simultaneously available to this task's processes.
Resource Controls Associated With Processes
Resource controls associated with processes include the following:
- process.max-address-space
Maximum amount of address space (bytes), as summed over segment sizes, available to this process.
- process.max-core-size
Maximum size (bytes) of a core file that is created by this process.
- process.max-cpu-time
Maximum CPU time (seconds) available to this process.
- process.max-file-descriptor
Maximum file descriptor index that is available to this process.
- process.max-file-size
Maximum file offset (bytes) available for writing by this process.
- process.max-msg-messages
Maximum number of messages on a message queue. This value is copied from the resource control at msgget() time.
- process.max-msg-qbytes
Maximum number (bytes) of messages on a message queue. This value is copied from the resource control at msgget() time.When you set a new project.max-msg-qbytes value, initialization occurs only on the subsequently created values. The new project.max-msg-qbytes value does not effect existing values.
- process.max-sem-nsems
Maximum number of semaphores allowed for a semaphore set.
- process.max-sem-ops
Maximum number of semaphore operations that are allowed for a semop() call. This value is copied from the resource control at msgget() time.A new project.max-sem-ops value only affects the initialization of subsequently created values and has no effect on existing values.
- process.max-port-events
Maximum number of events that are allowed per event port.
Zone-Wide Resource Controls
Zone-wide resource controls are available on a system with zones installed. Zone-wide resource controls limit the total resource usage of all process entities within a zone.
zone.cpu-shares | Limit on the number of fair share scheduler (FSS) CPU shares for a zone. CPU shares are first allocated to the zone, and then further subdivided among projects within the zone as specified in the project.cpu-shares entries. |
zone.max-locked-memory | Total amount of physical locked memory available to a zone. |
zone.max-lwps | Maximum number of LWPs simultaneously available to this zone |
zone.max-msg-ids | Maximum number of message queue IDs allowed for this zone |
zone.max-sem-ids | Maximum number of semaphore IDs allowed for this zone |
zone.max-shm-ids | Maximum number of shared memory IDs allowed for this zone |
zone.max-shm-memory | Total amount of shared memory allowed for this zone |
For information on configuring zone-wide resource controls, see Chapter 17, "Non-Global Zone Configuration (Overview)," in System Administration Guide: Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Solaris Zones and Chapter 18, "Planning and Configuring Non-Global Zones (Tasks)," in System Administration Guide: Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Solaris Zones.
Signals Used With Resource Controls
For each threshold value that is placed on a resource control, the following restricted set of signals is available:
- SIGBART
Terminate the process.
- SIGXRES
Signal generated by resource control facility when the resource control limit is exceeded.
- SIGHUP
When carrier drops on an open line, the process group that controls the terminal is sent a hangup signal, SIGHUP.
- SIGSTOP
Job control signal. Stop the process. Stop signal not from terminal.
- SIGTERM
Terminate the process. Termination signal sent by software.
- SIGKILL
Terminate the process. Kill the program.
- SIGXFSX
Terminate the process. File size limit exceeded. Available only to resource controls with the RCTL_GLOBAL_FILE_SIZE property.
- SIGXCPU
Terminate the process. CPU time limit exceeded. Available only to resource controls with the RCTL_GLOBAL_CPUTIME property.
Other signals might be permitted due to global properties of a specific control.
Note - Calls to setrctl() with illegal signals fail.
Figure 5-2 Setting Privilege Levels for Signals
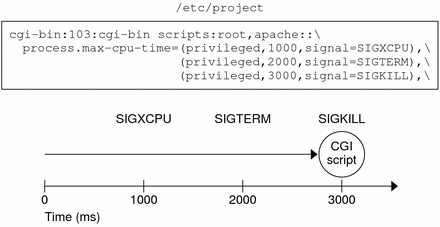

 Previous
Previous