readfile
(PHP 4, PHP 5)
readfile — Outputs a file
Description
Reads a file and writes it to the output buffer.
Parameters
- filename
-
The filename being read.
- use_include_path
-
You can use the optional second parameter and set it to TRUE, if you want to search for the file in the include_path, too.
- context
-
A context stream resource .
Return Values
Returns the number of bytes read from the file. If an error occurs, FALSE is returned and unless the function was called as @readfile(), an error message is printed.
Examples
Example #1 Forcing a download using readfile()
<?php
$file = 'monkey.gif';
if (file_exists($file)) {
header('Content-Description: File Transfer');
header('Content-Type: application/octet-stream');
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename='.basename($file));
header('Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary');
header('Expires: 0');
header('Cache-Control: must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0');
header('Pragma: public');
header('Content-Length: ' . filesize($file));
ob_clean();
flush();
readfile($file);
exit;
}
?>
The above example will output something similar to:
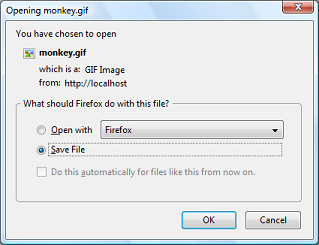
Notes
A URL can be used as a filename with this function if the fopen wrappers have been enabled. See fopen() for more details on how to specify the filename. See the List of Supported Protocols/Wrappers for links to information about what abilities the various wrappers have, notes on their usage, and information on any predefined variables they may provide.
Note: Context support was added with PHP 5.0.0. For a description of contexts, refer to Stream Functions.
See Also
- fpassthru() - Output all remaining data on a file pointer
- file() - Reads entire file into an array
- fopen() - Opens file or URL
- include() - include
- require() - require
- virtual() - Perform an Apache sub-request
- file_get_contents() - Reads entire file into a string
- List of Supported Protocols/Wrappers