Qt Widgets Examples
Qt comes with a large range of standard widgets that users of modern applications have come to expect.
You can also develop your own custom widgets and controls, and use them alongside standard widgets.
It is even possible to provide custom styles and themes for widgets that can be used to change the appearance of standard widgets and appropriately written custom widgets.
The Analog Clock example shows how to draw the contents of a custom widget. | |
The example shows how to use signals and slots to implement the functionality of a calculator widget, and how to use QGridLayout to place child widgets in a grid. | |
The Calendar Widget example shows use of QCalendarWidget. | |
The Character Map example shows how to create a custom widget that can both display its own content and respond to user input. | |
The Digital Clock example shows how to use QLCDNumber to display a number with LCD-like digits. | |
A Widgets application to display and print Json, text and PDF files. Demonstrates various features to use in widget applications: Using QSettings, query and save user preferences, manage file histories and control cursor behavior when hovering over widgets | |
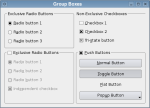
The Group Box example shows how to use the different kinds of group boxes in Qt. | |
The Icons example shows how QIcon can generate pixmaps reflecting an icon's state, mode and size. | |
The example shows how to combine QLabel and QScrollArea to display an image. | |
The Line Edits example demonstrates the many ways that QLineEdit can be used, and shows the effects of various properties and validators on the input and output supplied by the user. | |
The Movie example demonstrates how to use QMovie and QLabel to display animations. | |
The Scribble example shows how to reimplement some of QWidget's event handlers to receive the events generated for the application's widgets. | |
The Shortcut Editor example shows how to create a basic, read-write hierarchical model to use with Qt's standard view and QKeySequenceEdit classes. For a description of Model/View Programming, see the Model/View Programming overview. | |
The Sliders example shows how to use the different types of sliders available in Qt: QSlider, QScrollBar and QDial. | |
The Spin Boxes example shows how to use the many different types of spin boxes available in Qt, from a simple QSpinBox widget to more complex editors like the QDateTimeEdit widget. | |
The Style Sheet Example shows how to use style sheets. | |
The Styles example illustrates how to create custom widget drawing styles using Qt, and demonstrates Qt's predefined styles. | |
The System Tray Icon example shows how to add an icon with a menu and popup messages to a desktop environment's system tray. | |
This example shows how to use a Wacom tablet in Qt applications. | |
The Tetrix example is a Qt version of the classic Tetrix game. | |
The Tool Tips example shows how to provide static and dynamic tool tips for an application's widgets. | |
The example shows how to make a round window with a translucent background. | |
The Widgets Gallery example shows widgets relevant for designing UIs. | |
The Window Flags example shows how to use the window flags available in Qt. |
© 2023 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.