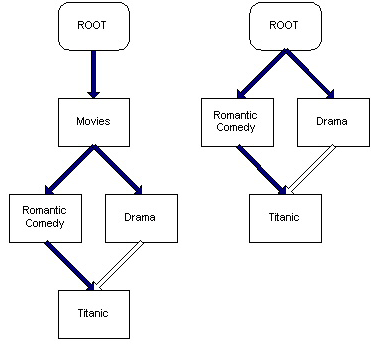
11.2. Categorization Scenarios
11.2.1. Creating a new Category
// Creates the Movies category at the top level with a description
Category movies = new Category("Movies", "long television shows");
// Create the Romantic Comedies category under the Movies category.
Category romance = new Category("Romantic Comedies",
"Comedies with love stories");
romance.setDefaultParentCategory(movies);
// Create the Titanic category under the Romantic Comedies category.
Category titanic = new Category("Titanic", "A category for large movies");
// set this as the default category
titanic.setDefaultParentCategory(romance);
// Create the Drama category under the Movies category.
Category drama = new Category("Drama", "long, not funny stories");
// Make Drama a parent category (but not the default parent) of Titanic.
drama.addChild(titanic);
// Finally, make movies a parent of Drama
drama.setDefaultParentCategory(movies); |
Example 11-1. Creating a new category
Adding the "Titanic" category to two categories looks the same as adding it to a single category. The first category to which an item (category or other ACSObject) is added is explicitly added as the default category. If a category/item only has one parent, that parent is implicitly the default.
11.2.2. Deleting a Category
// Fetch the Movies category from the database, assuming its id is 123 Category category = new Category(new BigDecimal(123)); // Delete the Movies category. category.deleteCategoryAndRemap(); |
Example 11-2. Category deletion
You can delete a category in the following ways:
Deleting Leaf Category — If the category is a leaf, call Category.delete().
Remapping Child Categories — If you want to remove the current category and make all categories that were pointing to it point to its default parent (as in the example), call Category.deleteCategoryAndRemap().
Orphaning Children — If you want to delete the category without remapping any of the child categories, call Category.deleteCategoryAndOrphan(). Note that there is no way to navigate from the root to orphaned categories. Effectively, the orphaned categories are no longer part of the categorization schemes, unless they have non-default parents.
Deleting Category Subtree — If you want to delete the entire subtree, including the passed-in category and all categories below it whose default ancestry can be traced to the root, call Category.deleteCategorySubtree().
11.2.3. Adding more Parent Categories
Category a = new Category(new OID(123));
Category b = new Category(new OID(124));
Category c = new Category(new OID(125));
if ( a != null && b != null && c != null ) {
// Makes Category B the parent of Category A
b.addChild(a);
// Makes Category C the parent of Category A
c.addChild(a);
// Sets Category B as the default parent of Category A
a.setDefaultParentCategory(b);
} |
Example 11-3. Adding more parent categories
11.2.4. Removing Parent Categories
11.2.6. Retrieving all child objects of a given Category
// assume that we have the Category OID
// (call it categoryOID)
Category category = new Category(categoryOID);
// the Collection will be a Collection of
// CategorizedObjects
Collection childObjects = category.getObjects();
// print out the toString for each object
// and its parents
Iterator childIterator = childObjects.iterator();
while (childIterator.hasNext()) {
CategorizedObject object =
(CategorizedObject) childIterator.next();
System.out.println("object = " + object.getObject());
Iterator parents = object.getParentCategories().iterator();
while(parents.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("parent = " +
((Category) parents.next()).toString());
}
} |
Example 11-6. Retrieving child objects of a given Category