What are records
This topic describes the structure of record. A record is an item that can be stored in the Comms Database.
A record is a container and an element. A record refers to a set of fields in a defined order. A set or records that has the same fields in the same order can be called a recordset or a table. Fields in a given position make a column. A column is conceptual. The CommsDat API has no C++ item defined as a column.
There are two types of record:
records defined at system compile time - these records have named fields and are defined by Symbian platform.
records defined by the user - these records are defined at run time - they are not known to Symbian platform when Symbian platform is built.
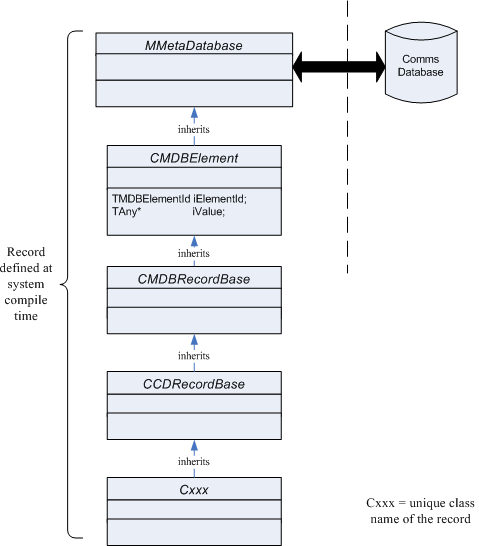
Records defined at system compile time
The class CCDRecordBase represents a Symbian platform defined record. All Symbian platform defined records inherit from CCDRecordBase. An individual named record is an instance of a class derived from CCDRecordBase. Symbian platform creates an individual named record and assigns a unique numeric Id. Symbian platform defines the class and the unique Id before the system is built.
The class defines a schema for the record. A schema is a pattern for the record that all records of this type follow. The class contains a set of fields and links to other records.
For example, Symbian platform defines the class CCDIAPRecord. The class represents an Internet Access Point (IAP) record. A set of IAP records form an IAP table. Symbian platform assigns the unique numeric Id KCDTIdIAPRecord to a record of this type.
The public data members of this class are the fields and links that make the record. The following code shows part of the class definition. Some parts are omitted - this is not the complete class definition.
class CCDIAPRecord : public CCDRecordBase { public: CMDBField<TDesC> iServiceType; CMDBRecordLink<CCDServiceRecordBase> iService; CMDBField<TDesC> iBearerType; CMDBRecordLink<CCDBearerRecordBase> iBearer; CMDBRecordLink<CCDNetworkRecord> iNetwork; CMDBField<TUint32> iNetworkWeighting; CMDBRecordLink<CCDLocationRecord> iLocation; ... }
To create an instance of a Symbian platform defined record in memory, use the factory function: CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::RecordFactoryL().
Tools and applications can also create an instance of a Symbian platform defined record in memory, and copy it from another record. Use the factory function: CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::CreateCopyRecord().
Fields are public data members of a Symbian platform defined record. Tools and applications access the fields directly.
Tools and applications can use the CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::GetFieldByNameL() or CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::GetFieldByIdL() functions to find fields in a Symbian platform defined record. These methods are not recommended. It is more efficient to access the fields directly.
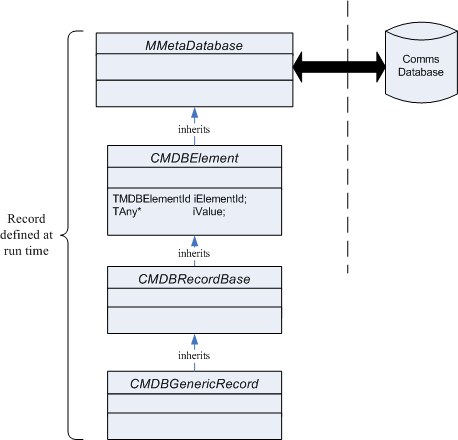
Records defined by the user
The class CMDBGenericRecord represents a user defined record. All user defined records inherit from CMDBGenericRecord. User defined records do not have named fields. A tool or application supplies a schema at run time. The schema defines the structure of the record.
A schema is an array of SGenericRecordTypeInfo objects. Each item in the array defines the fields in the record in order.
Tools and applications can use the CommsDat::CMDBGenericRecord::InitializeL() function to initialise a record in memory. Tools and Applications can also get use the LoadL() and FindL() functions to get the the table schema from the Comms Database.
You use the same methods to create, store and access user defined records that Symbian platform defined records use. Symbian platform backs up user defined data and secures user defined data with Platform Security. Symbian platform does not maintain user defined data formats.
Tools and applications must use the CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::GetFieldByNameL() or CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::GetFieldByIdL() functions to find fields in a user defined record. It is more efficient to use CommsDat::CCDRecordBase::GetFieldByIdL().