Architecture
This topic describes the Network Interface Manager (NifMan) architecture.
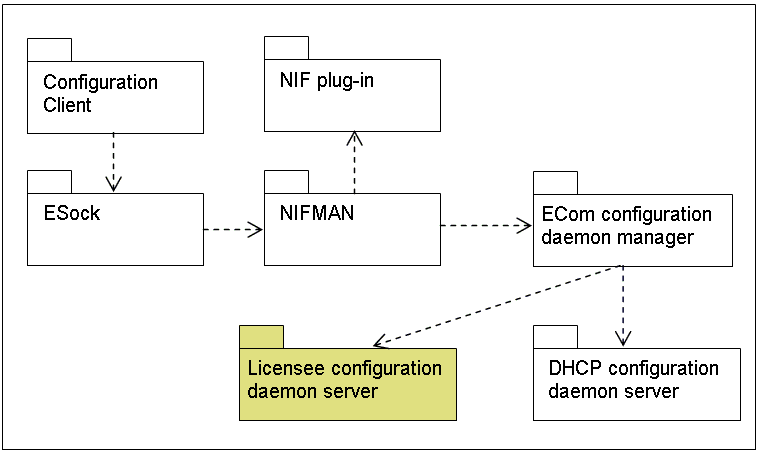
NifMan Architecture
The following diagram outlines the main components in the NifMan architecture:
As shown, the NIFMAN configuration daemon architecture consists of two parts:
An ECom plug-in for NIFMAN
The ECom plug-in manages the interface between NIFMAN and the configuration daemon. The ECom plug-in is referred to as the configuration daemon manager.
The configuration daemon
The configuration daemon is a Symbian platform server that runs in its own process. It does not run in the NIFMAN thread. Licensees can write new configuration daemons.
The framework for configuration daemons support the following:
Deregistration events
Deregistration events notify the daemon when the interface is shutting down. For Mobile IP, the phone can deregister its foreign agent address with the home agent.
Alternatively, the daemon can instruct NIFMAN to maintain the logical state of a user session and release the resources associated with the wireless connection. This is called fast dormant mode.
Progress notifications
Mobile IP reports progress notifications when it registers and deregisters with the foreign agent. The notifications are passed by NIFMAN to the sockets client using RConnection::ProgressNotification(), for the current interface.
The configuration daemon manager handles one outstanding daemon request at a time. If a request is already being processed, NIFMAN queues a deregistration request which is processed when the previous request is complete. Other types of request are not queued. This permits the handling of the following scenarios: