Area Effector 2D
Switch to ScriptingThe Area Effector 2D applies forces within an area defined by the attached colliders when another (target) collider comes into contact with the effector. The force can be configured at any angle with a specific magnitude and random variation on that magnitude. Also available is the ability the apply both linear and angular drag forces to slow rigidbodies down.
Colliders that you use with the effector would typically be set as triggers so that other colliders can overlap with it to have forces applied however, non-triggers will still work but forces will only be applied when colliders come into contact with it.
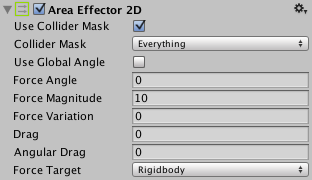
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Use Collider Mask | Should the ‘Collider Mask’ property be used? If not then the global collision matrix will be used as is the default for all colliders. |
| Collider Mask | The mask used to select specific layers allowed to interact with the effector. |
| Use Global Angle | Is the ‘Force Angle’ a global (world-space) angle or a local angle? |
| Force Angle | The angle of the force to be applied. |
| Force Magnitude | The magnitude of the force to be applied. |
| Force Variation | The variation of the magnitude of the force to be applied. |
| Drag | The linear drag to apply to rigid-bodies. |
| Angular Drag | The angular drag to apply to rigid-bodies. |
| Force Target | The force target is the point on a target object where the effector applies any force. |
| Collider | The target point is defined as the current position of the collider. Applying force here can generate torque (cause the target to rotate) if the collider isn’t positioned at the center-of-mass. |
| Rigidbody | The target point is defined as the current center-of-mass of the rigidbody. Applying force here will never generate torque (cause the target to rotate). |