ArangoDB on Apache Mesos using Marathon and Docker
Problem
I want to use ArangoDB in Apache Mesos with Docker containers.
Solution
Mesos in its newest version makes it very easy to use ArangoDB, because Mesos has added support for docker containers. Together with Marathon to start the front-end and back-end parts of an application, installation is straight forward.
My colleague Max has written a guesser game with various front-ends and ArangoDB as backend. In order to get the feeling of being part of the Mesosphere, I have started to set up this game in an DigitalOcean environment.
First Steps
The guesser game consists of a front-end written as express application in node and a storage back-end using ArangoDB and a small API developed with the Foxx microservices framework.
The front-end application is available as image
arangodb/example-guesser
and the ArangoDB back-end with the Foxx API as
arangodb/example-guesser-db
The dockerfiles used to create the images are available from github
https://github.com/arangodb/guesser
Set Up the Environment
Follow the instructions on Mesosphere to setup an environment with docker support. You should end up with ssh access to the Mesos master.
Set Up the Application
For this tutorial we bind the database to a fixed port on the Mesos environment. Please note, that the mesosphere uses HAproxy to map the global port to the real host and port. The servers created by Mesosphere will have a HAproxy defined on all masters and slaves.
That means, if we chose 32333 as
service port for the
database, it will be reachable on this port on all masters and slaves. The app
definition for the database looks like
{
"id": "/guesser/database",
"apps": [
{
"id": "/guesser/database/arangodb",
"container": {
"docker": {
"image": "arangodb/example-guesser-db",
"network": "BRIDGE",
"portMappings": [
{ "containerPort": 8529, "hostPort": 0, "servicePort": 32222, "protocol": "tcp" }
]
}
},
"cpus": 0.2,
"mem": 512.0,
"instances": 1
}
]
}
This will start the docker image for the back-end and binds the port to 32222.
Inside the docker container an environment variable HOST is set be the mesos slave
to point to the slave. The front-end can therefore access port 32222 on this host
to contact the HAproxy, gaining access to the database.
The app definition for the front-end looks like
{
"id": "/guesser/frontend",
"apps": [
{
"id": "/guesser/frontend/node",
"container": {
"docker": {
"image": "arangodb/example-guesser",
"network": "BRIDGE",
"portMappings": [
{ "containerPort": 8000, "hostPort": 0, "servicePort": 32221, "protocol": "tcp" }
]
}
},
"cpus": 0.2,
"mem": 256.0,
"instances": 1
}
]
}
Marathon allows to define a group of applications with dependencies between the components. The front-end depends on the back-end, therefore the complete group definitions looks like
{
"id": "/guesser",
"groups": [
{
"id": "/guesser/database",
"apps": [
{
"id": "/guesser/database/arangodb",
"container": {
"docker": {
"image": "arangodb/example-guesser-db",
"network": "BRIDGE",
"portMappings": [
{ "containerPort": 8529, "hostPort": 0, "servicePort": 32222, "protocol": "tcp" }
]
}
},
"cpus": 0.2,
"mem": 512.0,
"instances": 1
}
]
},
{
"id": "/guesser/frontend",
"dependencies": ["/guesser/database"],
"apps": [
{
"id": "/guesser/frontend/node",
"container": {
"docker": {
"image": "arangodb/example-guesser",
"network": "BRIDGE",
"portMappings": [
{ "containerPort": 8000, "hostPort": 0, "servicePort": 32221, "protocol": "tcp" }
]
}
},
"cpus": 0.2,
"mem": 256.0,
"instances": 1
}
]
}
]
}
This starts one instance of the back-end called /guesser/database/arangodb and one
instance of the front-end called /guesser/frontend/node. The front-end depends on
the back-end.
In order to fire up the guesser game save the above definition in a file
guesser.json and execute
curl -X PUT -H "Accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" 127.0.0.1:8080/v2/groups -d "`cat guesser.json`"
on the mesos master.
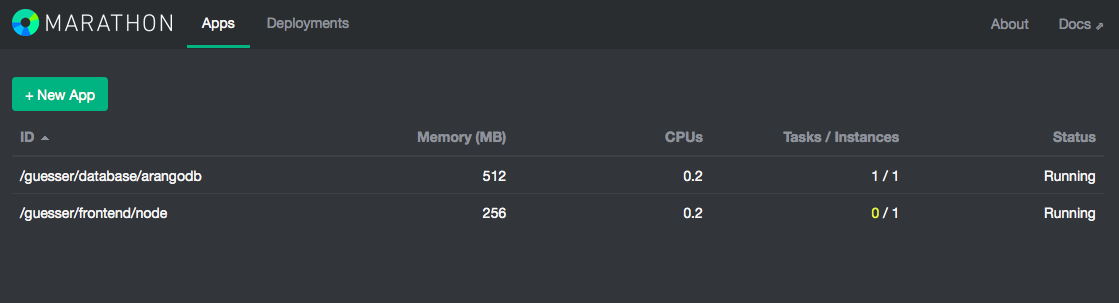
If you now switch to the Marathon console on port 8080, you should see apps, namely
/guesser/database/arangodb and /guesser/frontend/node.
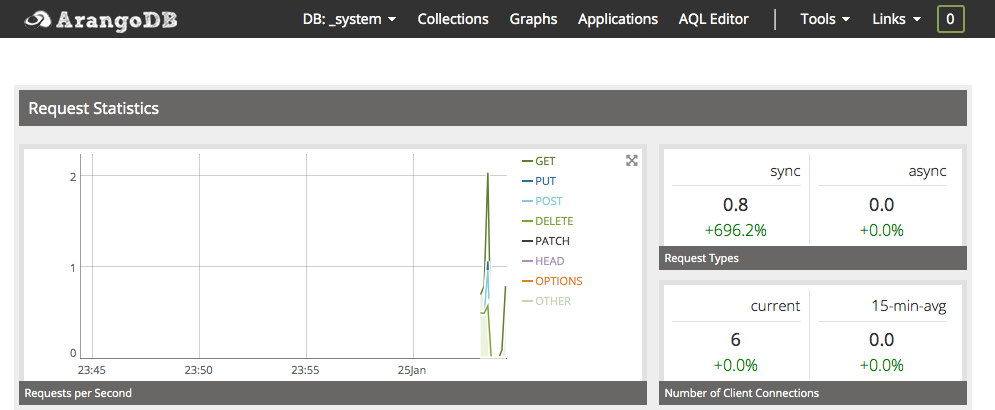
If you access port 32222, you should see the ArangoDB console.
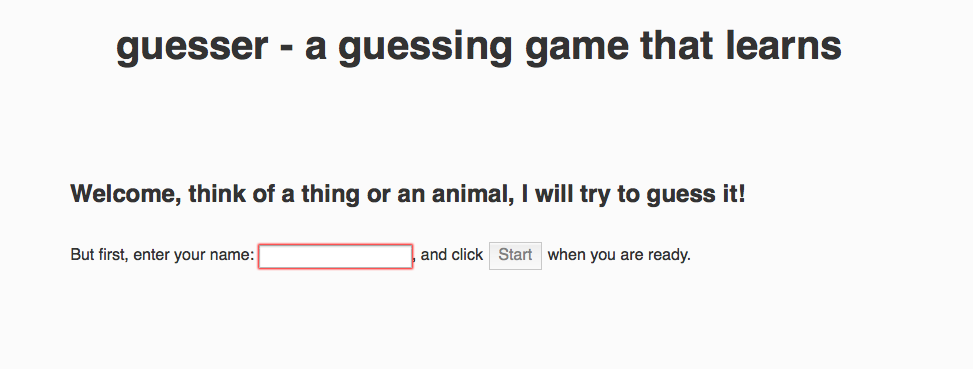
And finally, on port 32211, you can play the guesser game.
Scaling Up
Your game becomes a success. Well, scaling up the front-end is trivial. Simply, go to
the marathon page and scale up /guesser/frontend/node.
Authors: Frank Celler
Tags: #docker, #mesos, #mesosphere, #howto