Denormalizer
Not available in Community Designer
| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| Denormalizer Attributes |
| Details |
| CTL Interface |
| Java Interface |
| Examples |
| Best Practices |
| See also |
Short Description
Denormalizer creates single output record from one or more input records. Input records should be sorted.
| Component | Same input metadata | Sorted inputs | Inputs | Outputs | Java | CTL | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denormalizer | - |  | 1 | 1 |  |  |  |
Icon

Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 |  | for input data records | any |
| Output | 0 |  | for denormalized data records | any |
Metadata
Denormalizer does not propagate metadata.
Denormalizer does not have metadata templates.
Denormalizer does not require any specific metadata fields.
Denormalizer Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| Key | [1] | Key that creates groups of input data records according to its value. Adjacent input records with the same value of Key are considered to be members of one group. One output record is composed from members of such group. See Key for more information. | |
| Group size | [1] | Group may be defined by exact number of its members.
E.g. each five records form a single group.
The input record count MUST be
a multiple of group size (see Allow incomplete last group).
This is mutually exclusive with key attribute. | a number |
| Denormalize | [2] | Definition of how to denormalize records, written in the graph in CTL or Java. | |
| Denormalize URL | [2] | Name of external file, including path, containing the definition of how to denormalize records, written in CTL or Java. | |
| Denormalize class | [2] | Name of external class defining the way how records should be normalized. | |
| Equal NULL | By default, records with null values of key fields are
considered to be equal. If false,
they are considered to be different. | true (default) | false | |
| Denormalize source charset |
Encoding of external file defining the transformation. The default encoding depends on DEFAULT_SOURCE_CODE_CHARSET in defaultProperties. | E.g. UTF-8 | |
| Advanced | |||
| Allow incomplete last group | In case input records grouping is specified by Group size attribute, number of input records must be a multiple of group size. Using this attribute this condition can be suppressed. The last group does not need to be complete. | true | false (default) | |
| Deprecated | |||
| Sort order | Order in which groups of input records are expected to be sorted. See Sort order | Auto (default) | Ascending | Descending | Ignore | |
| Error actions | Definition of the action that should be performed when the specified transformation returns some Error code. See Return Values of Transformations. | ||
| Error log | URL of the file to which error messages for specified Error actions should be written. If not set, they are written to Console. | ||
[1] [2] One of them must specified. | |||
Details
Denormalizer receives sorted data through single input port, checks Key values, creates one output record from one or more adjacent input records with the same Key value.
Denormalizer requires transformation.
The transformation can be defined in CTL (see CTL Interface)
or in Java (see Java Interface)
or using existing .class file (Normalize class attribute).
To define transformation use one of the three transformation attributes: Denormalize, Denormalize URL or Denormalize class.
Diagram below describes flow of function calls in Denormalizer.
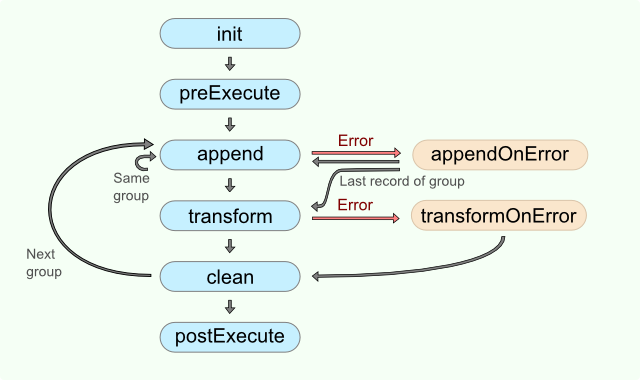
Figure 50.1. Denormalizer code workflow
The function append() is called with each input record.
The function transform() is called once for each group of input records.
If you do not define any of the optional functions init(), preExecute(),
clean() or postExecute(),
the execution flow continues with the next function according to the diagram.
If you do not specify appendOnError() or transformOnError() functions and error occurs,
the execution of graph fails.
The transformation uses a CTL template for Denormalizer,
implements a RecordDenormalize interface
or inherits from a DataRecordDenormalize superclass.
The interface methods are listed in CTL Interface
and Java Interface.
Key
Key is expressed as a sequence of field names separated from each other by semicolon, colon, or pipe.
Example 50.2. Key for Denormalizer
first_name;last_name
In this Key,
first_name and last_name are
fields of metadata on input port.
Sort order
If the records are denormalized by the Key, i.e., not by the Group size, the input records must be grouped according to the Key field value. Then, depending on the sorting order of the groups, select the proper Sort order:
Auto - the sorting order of the groups of input records is guessed from the first two records with different value in the key field, i.e., from the first records of the first two groups.
Ascending - if the groups of input records with the same key field value(s) are sorted in ascending order
Descending - if the groups of input records with the same key field value(s) are sorted in descending order
Ignore - if the groups of input records with the same key field value(s) are not sorted
CTL Interface
| CTL Templates |
| Access to input and output fields |
The transformation written in CTL uses a CTL template for Denormalizer.
Only the functions count() and transform() are mandatory.
Once you have written your transformation, you can also convert it to Java language code by clicking corresponding button at the upper right corner of the tab.
You can open the transformation definition as another tab of the graph (in addition to the Graph and Source tabs of Graph Editor) by clicking corresponding button at the upper right corner of the tab.
CTL Templates
Table 50.3. Functions in Denormalizer
| CTL Template Functions | |
|---|---|
| boolean init() | |
| Required | No |
| Description | Initializes the component, sets up the environment and global variables. |
| Invocation | Called before processing the first record |
| Returns | true | false (in
case of false graph fails) |
| integer append() | |
| Required | yes |
| Input Parameters | none |
| Returns | Integer numbers. Negative value lower than -1 aborts processing. Any non-negative value means successful pass. |
| Invocation | Called repeatedly, once for each input record |
| Description |
For the group of adjacent input records with the same Key values it appends the information from which composes the resulting output record.
If
If any of the input records causes fail of the |
| Example |
function integer append() {
CustomersInGroup++;
myLength = length(errorCustomers);
if(!isInteger($in.0.OneCustomer)) {
errorCustomers = errorCustomers + iif(myLength > 0 ," - ","") + $in.0.OneCustomer;
}
customers = customers + iif(length(customers) > 0 ," - ","") + $in.0.OneCustomer;
groupNo = $in.0.GroupNo;
return OK;
} |
| integer transform() | |
| Required | yes |
| Input Parameters | none |
| Returns | Integer numbers. See Return Values of Transformations for detailed information. |
| Invocation | Called repeatedly, once for each output record. |
| Description |
It creates output records.
If
If any part of the
The |
| Example | function integer transform() {
$out.0.CustomersInGroup = CustomersInGroup;
$out.0.CustomersOnError = errorCustomers;
$out.0.Customers = customers;
$out.0.GroupNo = groupNo;
return OK;
} |
| void clean() | |
| Required | no |
| Input Parameters | none |
| Returns | void |
| Invocation |
Called repeatedly, once for each output record. The |
| Description | Returns the component to the initial settings |
| Example | function void clean(){
customers = "";
errorCustomers = "";
groupNo = 0;
CustomersInGroup = 0;
} |
| integer appendOnError(string errorMessage, string stackTrace) | |
| Required | no |
| Input Parameters | string errorMessage |
string stackTrace | |
| Returns | Integer numbers. Positive integer numbers are ignored, meaning of 0 and negative values is described in Return Values of Transformations |
| Invocation | Called if append() throws an exception.
|
| Description |
The function handles error which occurred in
If any of the input records causes fail of the
The |
| Example |
function integer appendOnError(string errorMessage, string stackTrace) {
printErr(errorMessage);
return CustomersInGroup;
} |
| integer transformOnError(Exception exception, stackTrace) | |
| Required | no |
| Input Parameters | string errorMessage |
string stackTrace | |
| Returns | Integer numbers. See Return Values of Transformations for detailed information. |
| Invocation | Called if transform() throws an exception. |
| Description |
The function handles error which occurred in
If any part of the
The the function |
| Example | function integer transformOnError(
string errorMessage,
string stackTrace) {
$out.0.CustomersInGroup = CustomersInGroup;
$out.0.ErrorFieldForTransform = errorCustomers;
$out.0.CustomersOnError = errorCustomers;
$out.0.Customers = customers;
$out.0.GroupNo = groupNo;
return OK;
} |
| string getMessage() | |
| Required | No |
| Description | Prints error message specified and invoked by user |
| Invocation | Called in any time specified by user
(called only when either append(), transform(), appendOnError(), or transformOnError() returns value less than or equal to -2). |
| Returns | string |
| void preExecute() | |
| Required | No |
| Input parameters | None |
| Returns | void |
| Description |
May be used to allocate and initialize resources required by the transform. All resources allocated within this function should be released by the |
| Invocation | Called during each graph run before the transform is executed. |
| void postExecute() | |
| Required | No |
| Input parameters | None |
| Returns | void |
| Description | Should be used to free any resources allocated within the preExecute() function. |
| Invocation | Called during each graph run after the entire transform was executed. |
Access to input and output fields
Input records or fields
Input records or fields are accessible within the append() and appendOnError() functions only.
Output records or fields
Output records or fields are accessible within the transform() and transformOnError() functions only.
![[Warning]](figures/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
All of the other CTL template functions allow to access neither inputs nor outputs. Remember that if you do not hold these rules, NPE will be thrown! |
Java Interface
The transformation implements methods of the RecordDenormalize interface
and inherits other common methods from the Transform interface.
See Common Java Interfaces.
See Public Clover API.
Following are the methods of the
RecordDenormalize interface:
boolean init(Properties parameters, DataRecordMetadata sourceMetadata, DataRecordMetadata targetMetadata)Initializes denormalize class/function. This method is called only once at the beginning of denormalization process. Any object allocation/initialization should happen here.
int append(DataRecord inRecord)Passes one input record to the composing class.
int appendOnError(Exception exception, DataRecord inRecord)Passes one input record to the composing class. Called only if
append(DataRecord)throws an exception.
int transform(DataRecord outRecord)Retrieves composed output record. See Return Values of Transformations for detailed information about return values and their meaning. In Denormalizer, only
ALL,0,SKIP, and Error codes have some meaning.
int transformOnError(Exception exception, DataRecord outRecord)Retrieves composed output record. Called only if
transform(DataRecord)throws an exception.
void clean()Finalizes current round/clean after current round - called after the transform method was called for the input record.
Examples
| Converting multiple having same key records to one |
| Converting fixed number of records to one records |
Converting multiple having same key records to one
Input records acquired from relational database contain fields companyName and product.
Denormalizer Limited |chocolate Denormalizer Limited |coffee Denormalizer Limited |pizza ZXCV International |coffee
Convert the records to following form: companyName is followed by list of products separated by comma.
Solution
Use Key and Normalize attributes.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Key | companyName |
| Normalize | See the code below |
//#CTL2
string[] products;
string companyName;
function integer append() {
append(products, $in.0.product);
companyName = $in.0.companyName;
return OK;
}
function integer transform() {
$out.0.companyName = companyName;
$out.0.products = join(",", products);
return OK;
}
function void clean() {
clear(products);
}Denormalizer returns following records:
Denormalizer Limited |chocolate,coffee,pizza ZXCV International |coffee
![[Important]](figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Records having the same Key have to be available in input data all at once. Otherwise you will get a new output record for each several subsequent records having the same key. The best solution is to have input records sorted by Key. |
Converting fixed number of records to one records
Given a list of students.
Charlie Daniel Agatha Henry Oscar Kate Romeo Jane
Convert the list to groups of 3. Each group (one output record) has a number and names of it's members. The names are separated by comma.
Each output record contains groupNumber and members.
Solution
Use attributes Group size and Normalize. The be able to process number of record not being divisible by 3 you need Allow incomplete last group attribute.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Group size | 3 |
| Normalize | See the code below |
| Allow incomplete last group | true |
//#CTL2
integer groupNumber;
string[] names;
function integer append() {
append(names, $in.0.name);
return OK;
}
function integer transform() {
$out.0.groupNo = groupNumber;
$out.0.members = join(",", names);
groupNumber++;
return OK;
}
function boolean init() {
groupNumber = 1;
return true;
}
function void clean() {
clear(names);
}Denormalizer returns following records:
1|Charlie,Daniel,Agatha 2|Henry,Oscar,Kate 3|Romeo,Jane
Best Practices
If the transformation is specified in an external file (with Denormalize URL), we recommend users to explicitly specify Denormalize source charset.