Shared thread pool
A shared thread pool is a collection of threads which are shared across multiple buckets.
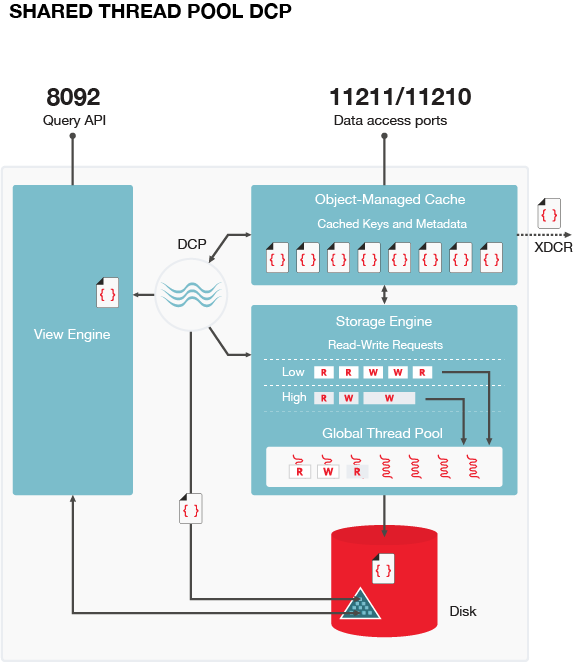
A thread pool is a collection of threads used to perform similar jobs. Each server node has a thread pool that is shared across multiple buckets. Shared thread pool optimizes dispatch tasks by decoupling buckets from thread allocation.
Threads are spawned at initial startup of a server node instance and are based on the number of CPU cores.
With the shared thread pool associated with each node, threads and buckets are decoupled. By decoupling threads from specific buckets, threads can run tasks for any bucket. Since the global thread pool permits for bucket priority levels, a separate I/O queue is available with the reader and writer workers at every priority level. This provides improved task queueing. For example, when a thread is assigned to running a task from an I/O queue and a second task is requested, another thread is assigned to pick up the second task.
Shared thread pool management promotes:
- Better parallelism for thread workers with more efficient I/O resource management.
- Better system scalability with more buckets being serviced with fewer worker threads.
- Availability of task priority if the disk bucket I/O priority setting is implemented.
The following circumstances describes how threads are scheduled to dispatch tasks:
- If all buckets have the same priority (default setting), each thread evenly round-robins over all the task queues of the buckets.
- If buckets have different priorities, the threads spend an appropriate fraction of time (scheduling frequency) dispatching tasks from queues of these bucket.
- If a bucket is being compacted, threads are not allocated to dispatch tasks for that bucket.
- If all buckets are either empty or being serviced by other threads, the thread goes to sleep.
Viewing thread status
The cbstats raw workload is used to view the status of the threads. The following is example code and results.
# cbstats 10.5.2.54:11210 -b default raw workload
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_AuxIO:InQsize: 3
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_AuxIO:OutQsize: 0
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_NonIO:InQsize: 33
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_NonIO:OutQsize: 0
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_Reader:InQsize: 12
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_Reader:OutQsize: 0
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_Writer:InQsize: 15
ep_workload:LowPrioQ_Writer:OutQsize: 0
ep_workload:num_auxio: 1
ep_workload:num_nonio: 1
ep_workload:num_readers: 1
ep_workload:num_shards: 4
ep_workload:num_sleepers: 4
ep_workload:num_writers: 1
ep_workload:ready_tasks: 0
ep_workload:shard0_locked: false
ep_workload:shard0_pendingTasks: 0
ep_workload:shard1_locked: false
ep_workload:shard1_pendingTasks: 0
ep_workload:shard2_locked: false
ep_workload:shard2_pendingTasks: 0
ep_workload:shard3_locked: false
ep_workload:shard3_pendingTasks: 0