Diagram showing the three boxes, of which one is anonymous, for the example above.
Contents
This chapter and the next describe the visual formatting model: how user agents process the document tree for visual media.
In the visual formatting model, each element in the document tree generates zero or more boxes according to the box model. The layout of these boxes is governed by:
The properties defined in this chapter and the next apply to both continuous media and paged media. However, the meanings of the margin properties vary when applied to paged media (see the page model for details).
The visual formatting model does not specify all aspects of formatting (e.g., it does not specify a letter-spacing algorithm). Conforming user agents may behave differently for those formatting issues not covered by this specification.
User agents for continuous media generally offer users a viewport (a window or other viewing area on the screen) through which users consult a document. User agents may change the document's layout when the viewport is resized (see the initial containing block).
When the viewport is smaller than the area of the canvas on which the document is rendered, the user agent should offer a scrolling mechanism. There is at most one viewport per canvas, but user agents may render to more than one canvas (i.e., provide different views of the same document).
In CSS 2.1, many box positions and sizes are calculated with respect to the edges of a rectangular box called a containing block. In general, generated boxes act as containing blocks for descendant boxes; we say that a box "establishes" the containing block for its descendants. The phrase "a box's containing block" means "the containing block in which the box lives," not the one it generates.
Each box is given a position with respect to its containing block, but it is not confined by this containing block; it may overflow.
The details of how a containing block's dimensions are calculated are described in the next chapter.
The following sections describe the types of boxes that may be generated in CSS 2.1. A box's type affects, in part, its behavior in the visual formatting model. The 'display' property, described below, specifies a box's type.
Block-level elements are those elements of the source document that are formatted visually as blocks (e.g., paragraphs). Several values of the 'display' property make an element block-level: 'block', 'list-item', and 'run-in' (part of the time; see run-in boxes), and 'table'.
Block-level elements (except for display 'table' elements, which are described in a later chapter) generate a principal block box that contains either only block boxes or only inline boxes. The principal block box establishes the containing block for descendant boxes and generated content and is also the box involved in any positioning scheme. Principal block boxes participate in a block formatting context.
Some block-level elements generate additional boxes outside of the principal box: 'list-item' elements. These additional boxes are placed with respect to the principal box.
In a document like this:
<DIV>
Some text
<P>More text
</DIV>
(and assuming the DIV and the P both have 'display: block'), the DIV appears to have both inline content and block content. To make it easier to define the formatting, we assume that there is an anonymous block box around "Some text".
Diagram showing the three boxes, of which one is anonymous, for the example above.
In other words: if a block box (such as that generated for the DIV above) has another block box or run-in box inside it (such as the P above), then we force it to have only block boxes and run-in boxes inside it.
When an inline box contains a block box, the inline box (and its inline ancestors within the same line box) are broken around the block. The line boxes before the break and after the break are enclosed in anonymous boxes, and the block box becomes a sibling of those anonymous boxes.
This model would apply in the following example if the following rules:
body { display: inline }
p { display: block }
were used with this HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Anonymous text interrupted by a block</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
This is anonymous text before the P.
<P>This is the content of P.</P>
This is anonymous text after the P.
</BODY>
The BODY element contains a chunk (C1) of anonymous text followed by a block-level element followed by another chunk (C2) of anonymous text. The resulting boxes would be an anonymous block box around the BODY, containing an anonymous block box around C1, the P block box, and another anonymous block box around C2.
The properties of anonymous boxes are inherited from the enclosing non-anonymous box (e.g. in the example just below the subsection heading "Anonymous block boxes", the one for DIV). Non-inherited properties have their initial value. For example, the font of the anonymous box is inherited from the DIV, but the margins will be 0.
Properties set on elements that cause anonymous block boxes to be generated still apply to the boxes and content of that element. For example, if a border had been set on the BODY element in the above example, the border would be drawn around C1 (open at the end of the line) and C2 (open at the start of the line).
Some user agents have implemented borders on inlines containing blocks in other ways, e.g. by wrapping such nested blocks inside "anonymous line boxes" and thus drawing inline borders around such boxes. As CSS1 and CSS2 did not define this behavior, CSS1-only and CSS2-only user agents may implement this alternative model and still claim conformance to this part of CSS 2.1. This does not apply to UAs developed after this specification was released.
Inline-level elements are those elements of the source document that do not form new blocks of content; the content is distributed in lines (e.g., emphasized pieces of text within a paragraph, inline images, etc.). Several values of the 'display' property make an element inline: 'inline', 'inline-table', and 'run-in' (part of the time; see run-in boxes). Inline-level elements generate inline boxes.
In a document with HTML markup like this:
<p>Some <em>emphasized</em> text</p>
The <p> generates a block box, with several inline boxes inside
it. The box for "emphasized" is an inline box generated by an inline
element (<em>), but the other boxes ("Some" and "text") are inline boxes generated by a block-level element (<p>). The latter are called anonymous inline
boxes, because they don't have an associated inline-level element.
Such anonymous inline boxes inherit inheritable properties from their block parent box. Non-inherited properties have their initial value. In the example, the color of the anonymous inline boxes is inherited from the P, but the background is transparent.
Whitespace content that would subsequently be collapsed away according to the 'white-space' property does not generate any anonymous inline boxes.
If it is clear from the context which type of anonymous box is meant, both anonymous inline boxes and anonymous block boxes are simply called anonymous boxes in this specification.
There are more types of anonymous boxes that arise when formatting tables.
A run-in box behaves as follows:
A 'run-in' box is useful for run-in headers, as in this example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>A run-in box example</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css">
H3 { display: run-in }
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H3>A run-in heading.</H3>
<P>And a paragraph of text that
follows it.
</BODY>
</HTML>
This example might be formatted as:
A run-in heading. And a paragraph of text that follows it.
Despite appearing visually part of the following block box, a run-in element still inherits properties from its parent in the source tree.
Please consult the section on generated content for information about how run-in boxes interact with generated content.
| Value: | inline | block | list-item | run-in | inline-block | table | inline-table | table-row-group | table-header-group | table-footer-group | table-row | table-column-group | table-column | table-cell | table-caption | none | inherit |
| Initial: | inline |
| Applies to: | all elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Media: | all |
| Computed value: | see text |
The values of this property have the following meanings:
Please note that a display of 'none' does not create an invisible box; it creates no box at all. CSS includes mechanisms that enable an element to generate boxes in the formatting structure that affect formatting but are not visible themselves. Please consult the section on visibility for details.
The computed value is the same as the specified value, except for positioned and floating elements (see Relationships between 'display', 'position', and 'float') and for the root element. For the root element, the computed value is changed as described in the section on the relationships between 'display', 'position', and 'float'.
Note that although the initial value of 'display' is 'inline', rules in the user agent's default style sheet may override this value. See the sample style sheet for HTML 4 in the appendix.
Here are some examples of the 'display' property:
p { display: block }
em { display: inline }
li { display: list-item }
img { display: none } /* Don't display images */
In CSS 2.1, a box may be laid out according to three positioning schemes:
The 'position' and 'float' properties determine which of the CSS 2.1 positioning algorithms is used to calculate the position of a box.
| Value: | static | relative | absolute | fixed | inherit |
| Initial: | static |
| Applies to: | all elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | as specified |
The values of this property have the following meanings:
@media screen {
h1#first { position: fixed }
}
@media print {
h1#first { position: static }
}
UAs must not paginate the content of fixed boxes. Note that UAs may print invisible content in other ways. See "Content outside the page box" in chapter 13.
User agents may treat position as 'static' on the root element.
An element is said to be positioned if its 'position' property has a value other than 'static'. Positioned elements generate positioned boxes, laid out according to four properties:
| Value: | <length> | <percentage> | auto | inherit |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | positioned elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | refer to height of containing block |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | for 'position:relative', see section Relative Positioning. For 'position:static', 'auto'. Otherwise: if specified as a length, the corresponding absolute length; if specified as a percentage, the specified value; otherwise, 'auto'. |
This property specifies how far an absolutely positioned box's top margin edge is offset below the top edge of the box's containing block. For relatively positioned boxes, the offset is with respect to the top edges of the box itself (i.e., the box is given a position in the normal flow, then offset from that position according to these properties). Note: For absolutely positioned elements whose containing block is based on a block-level element, this property is an offset from the padding edge of that element.
| Value: | <length> | <percentage> | auto | inherit |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | positioned elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | refer to width of containing block |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | for 'position:relative', see section Relative Positioning. For 'position:static', 'auto'. Otherwise: if specified as a length, the corresponding absolute length; if specified as a percentage, the specified value; otherwise, 'auto'. |
Like 'top', but specifies how far a box's right margin edge is offset to the left of the right edge of the box's containing block. For relatively positioned boxes, the offset is with respect to the right edge of the box itself. Note: For absolutely positioned elements whose containing block is based on a block-level element, this property is an offset from the padding edge of that element.
| Value: | <length> | <percentage> | auto | inherit |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | positioned elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | refer to height of containing block |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | for 'position:relative', see section Relative Positioning. For 'position:static', 'auto'. Otherwise: if specified as a length, the corresponding absolute length; if specified as a percentage, the specified value; otherwise, 'auto'. |
Like 'top', but specifies how far a box's bottom margin edge is offset above the bottom of the box's containing block. For relatively positioned boxes, the offset is with respect to the bottom edge of the box itself. Note: For absolutely positioned elements whose containing block is based on a block-level element, this property is an offset from the padding edge of that element.
| Value: | <length> | <percentage> | auto | inherit |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | positioned elements |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | refer to width of containing block |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | for 'position:relative', see section Relative Positioning. For 'position:static', 'auto'. Otherwise: if specified as a length, the corresponding absolute length; if specified as a percentage, the specified value; otherwise, 'auto'. |
Like 'top', but specifies how far a box's left margin edge is offset to the right of the left edge of the box's containing block. For relatively positioned boxes, the offset is with respect to the left edge of the box itself. Note: For absolutely positioned elements whose containing block is based on a block-level element, this property is an offset from the padding edge of that element.
The values for the four properties have the following meanings:
Boxes in the normal flow belong to a formatting context, which may be block or inline, but not both simultaneously. Block boxes participate in a block formatting context. Inline boxes participate in an inline formatting context.
Floats, absolutely positioned elements, inline-blocks, table-cells, and elements with 'overflow' other than 'visible' establish new block formatting contexts.
In a block formatting context, boxes are laid out one after the other, vertically, beginning at the top of a containing block. The vertical distance between two sibling boxes is determined by the 'margin' properties. Vertical margins between adjacent block boxes in a block formatting context collapse.
In a block formatting context, each box's left outer edge touches the left edge of the containing block (for right-to-left formatting, right edges touch). This is true even in the presence of floats (although a box's line boxes may shrink due to the floats), unless the box establishes a new block formatting context (in which case the box itself may become narrower due to the floats).
For information about page breaks in paged media, please consult the section on allowed page breaks.
In an inline formatting context, boxes are laid out horizontally, one after the other, beginning at the top of a containing block. Horizontal margins, borders, and padding are respected between these boxes. The boxes may be aligned vertically in different ways: their bottoms or tops may be aligned, or the baselines of text within them may be aligned. The rectangular area that contains the boxes that form a line is called a line box.
The width of a line box is determined by a containing block and the presence of floats. The height of a line box is determined by the rules given in the section on line height calculations.
A line box is always tall enough for all of the boxes it contains. However, it may be taller than the tallest box it contains (if, for example, boxes are aligned so that baselines line up). When the height of a box B is less than the height of the line box containing it, the vertical alignment of B within the line box is determined by the 'vertical-align' property. When several inline boxes cannot fit horizontally within a single line box, they are distributed among two or more vertically-stacked line boxes. Thus, a paragraph is a vertical stack of line boxes. Line boxes are stacked with no vertical separation and they never overlap.
In general, the left edge of a line box touches the left edge of its containing block and the right edge touches the right edge of its containing block. However, floating boxes may come between the containing block edge and the line box edge. Thus, although line boxes in the same inline formatting context generally have the same width (that of the containing block), they may vary in width if available horizontal space is reduced due to floats. Line boxes in the same inline formatting context generally vary in height (e.g., one line might contain a tall image while the others contain only text).
When the total width of the inline boxes on a line is less than the width of the line box containing them, their horizontal distribution within the line box is determined by the 'text-align' property. If that property has the value 'justify', the user agent may stretch the inline boxes as well.
When an inline box exceeds the width of a line box, it is split into several boxes and these boxes are distributed across several line boxes. If an inline box cannot be split (e.g. if the inline box contains a single character, or language specific word breaking rules disallow a break within the inline box, or if the inline box is affected by a white-space value of nowrap or pre), then the inline box overflows the line box.
When an inline box is split, margins, borders, and padding have no visual effect where the split occurs (or at any split, when there are several).
Inline boxes may also be split into several boxes within the same line box due to bidirectional text processing.
Here is an example of inline box construction. The following paragraph (created by the HTML block-level element P) contains anonymous text interspersed with the elements EM and STRONG:
<P>Several <EM>emphasized words</EM> appear
<STRONG>in this</STRONG> sentence, dear.</P>
The P element generates a block box that contains five inline boxes, three of which are anonymous:
To format the paragraph, the user agent flows the five boxes into line boxes. In this example, the box generated for the P element establishes the containing block for the line boxes. If the containing block is sufficiently wide, all the inline boxes will fit into a single line box:
Several emphasized words appear in this sentence, dear.
If not, the inline boxes will be split up and distributed across several line boxes. The previous paragraph might be split as follows:
Several emphasized words appear in this sentence, dear.or like this:
Several emphasized words appear in this sentence, dear.
In the previous example, the EM box was split into two EM boxes (call them "split1" and "split2"). Margins, borders, padding, or text decorations have no visible effect after split1 or before split2.
Consider the following example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Example of inline flow on several lines</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css">
EM {
padding: 2px;
margin: 1em;
border-width: medium;
border-style: dashed;
line-height: 2.4em;
}
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>Several <EM>emphasized words</EM> appear here.</P>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Depending on the width of the P, the boxes may be distributed as follows:
Once a box has been laid out according to the normal flow or floated, it may be shifted relative to this position. This is called relative positioning. Offsetting a box (B1) in this way has no effect on the box (B2) that follows: B2 is given a position as if B1 were not offset and B2 is not re-positioned after B1's offset is applied. This implies that relative positioning may cause boxes to overlap. However, if relative positioning causes an 'overflow:auto' box to have overflow, the UA must allow the user to access this content, which, through the creation of scrollbars, may affect layout.
A relatively positioned box keeps its normal flow size, including line breaks and the space originally reserved for it. The section on containing blocks explains when a relatively positioned box establishes a new containing block.
For relatively positioned elements, 'left' and 'right' move the box(es) horizontally, without changing their size. 'left' moves the boxes to the right, and 'right' moves them to the left. Since boxes are not split or stretched as a result of 'left' or 'right', the computed values are always: left = -right.
If both 'left' and 'right' are 'auto' (their initial values), the computed values are '0' (i.e., the boxes stay in their original position).
If 'left' is 'auto', its computed value is minus the value of 'right' (i.e., the boxes move to the left by the value of 'right').
If 'right' is specified as 'auto', its computed value is minus the value of 'left'.
If neither 'left' nor 'right' is 'auto', the position is over-constrained, and one of them has to be ignored. If the 'direction' property of the containing block is 'ltr, the value of 'left' wins and 'right' becomes -'left'. If 'direction' of the containing block is 'rtl', 'right' wins and 'left' is ignored.
Example. The following three rules are equivalent:
div.a8 { position: relative; direction: ltr; left: -1em; right: auto }
div.a8 { position: relative; direction: ltr; left: auto; right: 1em }
div.a8 { position: relative; direction: ltr; left: -1em; right: 5em }
The 'top' and 'bottom' properties move relatively positioned element(s) up or down without changing their size. 'top' moves the boxes down, and 'bottom' moves them up. Since boxes are not split or stretched as a result of 'top' or 'bottom', the computed values are always: top = -bottom. If both are 'auto', their computed values are both '0'. If one of them is 'auto', it becomes the negative of the other. If neither is 'auto', 'bottom' is ignored (i.e., the computed value of 'bottom' will be minus the value of 'top').
Note. Dynamic movement of relatively positioned boxes can produce animation effects in scripting environments (see also the 'visibility' property). Although relative positioning may be used as a form of superscripting and subscripting, the line height is not automatically adjusted to take the positioning into consideration. See the description of line height calculations for more information.
Examples of relative positioning are provided in the section comparing normal flow, floats, and absolute positioning.
A float is a box that is shifted to the left or right on the current line. The most interesting characteristic of a float (or "floated" or "floating" box) is that content may flow along its side (or be prohibited from doing so by the 'clear' property). Content flows down the right side of a left-floated box and down the left side of a right-floated box. The following is an introduction to float positioning and content flow; the exact rules governing float behavior are given in the description of the 'float' property.
A floated box is shifted to the left or right until its outer edge touches the containing block edge or the outer edge of another float. If there's a line box, the top of the floated box is aligned with the top of the current line box.
If there isn't enough horizontal room for the float, it is shifted downward until either it fits or there are no more floats present.
Since a float is not in the flow, non-positioned block boxes created before and after the float box flow vertically as if the float didn't exist. However, line boxes created next to the float are shortened to make room for margin box of the float. If a shortened line box is too small to contain any further content, then it is shifted downward until either it fits or there are no more floats present. Any content in the current line before a floated box is reflowed in the first available line on the other side of the float. In other words, if inline boxes are placed on the line before a left float is encountered that fits in the remaining line box space, the left float is placed on that line, aligned with the top of the line box, and then the inline boxes already on the line are moved accordingly to the right of the float (the right being the other side of the left float) and vice versa for rtl and right floats.
The margin box of a table, a block-level replaced element, or an element in the normal flow that establishes a new block formatting context (such as an element with 'overflow' other than 'visible') must not overlap any floats in the same block formatting context as the element itself. If necessary, implementations should clear the said element by placing it below any preceding floats, but may place it adjacent to such floats if there is sufficient space.
Example. In the following document fragment, the containing block is too narrow to contain the content next to the float, so the content gets moved to below the floats where it is aligned in the line box according to the text-align property.
p { width: 10em; border: solid aqua; } span { float: left; width: 5em; height: 5em; border: solid blue; }...<p> <span> </span> Supercalifragilisticexpialidocious </p>
This fragment might look like this:
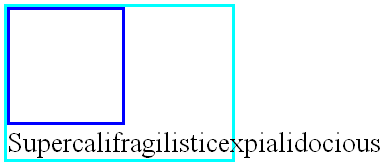
Several floats may be adjacent, and this model also applies to adjacent floats in the same line.
The following rule floats all IMG boxes with class="icon" to the left (and sets the left margin to '0'):
img.icon {
float: left;
margin-left: 0;
}
Consider the following HTML source and style sheet:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Float example</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css">
IMG { float: left }
BODY, P, IMG { margin: 2em }
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P><IMG src=img.png alt="This image will illustrate floats">
Some sample text that has no other...
</BODY>
</HTML>
The IMG box is floated to the left. The content that follows is formatted to the right of the float, starting on the same line as the float. The line boxes to the right of the float are shortened due to the float's presence, but resume their "normal" width (that of the containing block established by the P element) after the float. This document might be formatted as:
Formatting would have been exactly the same if the document had been:
<BODY>
<P>Some sample text
<IMG src=img.png alt="This image will illustrate floats">
that has no other...
</BODY>
because the content to the left of the float is displaced by the float and reflowed down its right side.
As stated in section 8.3.1, the margins of floating boxes never collapse with margins of adjacent boxes. Thus, in the previous example, vertical margins do not collapse between the P box and the floated IMG box.
The contents of floats are stacked as if floats generated new stacking contexts, except that any elements that actually create new stacking contexts take part in the float's parent's stacking context. A float can overlap other boxes in the normal flow (e.g., when a normal flow box next to a float has negative margins). When this happens, floats are rendered in front of non-positioned in-flow blocks, but behind in-flow inlines.
Here is another illustration, showing what happens when a float overlaps borders of elements in the normal flow.
A floating image obscures borders of block boxes it overlaps.
The following example illustrates the use of the 'clear' property to prevent content from flowing next to a float.
Assuming a rule such as this:
p { clear: left }
formatting might look like this:
This property specifies whether a box should float to the left, right, or not at all. It may be set for any element, but only applies to elements that generate boxes that are not absolutely positioned. The values of this property have the following meanings:
User agents may treat float as 'none' on the root element.
Here are the precise rules that govern the behavior of floats:
References to other elements in these rules refer only to other elements in the same block formatting context as the float.
This HTML fragment results in the b floating to the right.
<P>a<SPAN style="float: right">b</SPAN></P>
If the P element's width is enough, the a and the b will be side by side. It might look like this:

This property indicates which sides of an element's box(es) may not be adjacent to an earlier floating box. The 'clear' property does not consider floats inside the element itself or in other block formatting contexts.
For run-in boxes, this property applies to the final block box to which the run-in box belongs.
Clearance is introduced as spacing above the margin-top of an element. It is used to push the element vertically (typically downward), past the float.
Values have the following meanings when applied to non-floating block boxes:
Computing the clearance of an element on which 'clear' is set is done by first determining the hypothetical position of the element's top border edge within its parent block. This position is determined after the top margin of the element has been collapsed with previous adjacent margins (including the top margin of the parent block).
If the element's top border edge has not passed the relevant floats, then its clearance is set to the amount necessary to place the border edge of the block even with the bottom outer edge of the lowest float that must be cleared.
When the property is set on floating elements, it results in a modification of the rules for positioning the float. An extra constraint (#10) is added:
Note. This property applied to all elements in CSS1. Implementations may therefore have supported this property on all elements. In CSS2 and CSS 2.1 the 'clear' property only applies to block-level elements. Therefore authors should only use this property on block-level elements. If an implementation does support clear on inline elements, rather than setting a clearance as explained above, the implementation should force a break and effectively insert one or more empty line boxes (or shifting the new line box downward as described in section 9.5) to move the top of the cleared inline's line box to below the respective floating box(es).
In the absolute positioning model, a box is explicitly offset with respect to its containing block. It is removed from the normal flow entirely (it has no impact on later siblings). An absolutely positioned box establishes a new containing block for normal flow children and absolutely (but not fixed) positioned descendants. However, the contents of an absolutely positioned element do not flow around any other boxes. They may obscure the contents of another box (or be obscured themselves), depending on the stack levels of the overlapping boxes.
References in this specification to an absolutely positioned element (or its box) imply that the element's 'position' property has the value 'absolute' or 'fixed'.
Fixed positioning is a subcategory of absolute positioning. The only difference is that for a fixed positioned box, the containing block is established by the viewport. For continuous media, fixed boxes do not move when the document is scrolled. In this respect, they are similar to fixed background images. For paged media, boxes with fixed positions are repeated on every page. This is useful for placing, for instance, a signature at the bottom of each page.
Authors may use fixed positioning to create frame-like presentations. Consider the following frame layout:
This might be achieved with the following HTML document and style rules:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>A frame document with CSS 2.1</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css" media="screen">
BODY { height: 8.5in } /* Required for percentage heights below */
#header {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
height: 15%;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: auto;
left: 0;
}
#sidebar {
position: fixed;
width: 10em;
height: auto;
top: 15%;
right: auto;
bottom: 100px;
left: 0;
}
#main {
position: fixed;
width: auto;
height: auto;
top: 15%;
right: 0;
bottom: 100px;
left: 10em;
}
#footer {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
top: auto;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
}
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<DIV id="header"> ... </DIV>
<DIV id="sidebar"> ... </DIV>
<DIV id="main"> ... </DIV>
<DIV id="footer"> ... </DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The three properties that affect box generation and layout — 'display', 'position', and 'float' — interact as follows:
| Specified value | Computed value |
|---|---|
| inline-table | table |
| inline, run-in, table-row-group, table-column, table-column-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row, table-cell, table-caption, inline-block | block |
| others | same as specified |
To illustrate the differences between normal flow, relative positioning, floats, and absolute positioning, we provide a series of examples based on the following HTML:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Comparison of positioning schemes</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>Beginning of body contents.
<SPAN id="outer"> Start of outer contents.
<SPAN id="inner"> Inner contents.</SPAN>
End of outer contents.</SPAN>
End of body contents.
</P>
</BODY>
</HTML>
In this document, we assume the following rules:
body { display: block; font-size:12px; line-height: 200%;
width: 400px; height: 400px }
p { display: block }
span { display: inline }
The final positions of boxes generated by the outer and inner elements vary in each example. In each illustration, the numbers to the left of the illustration indicate the normal flow position of the double-spaced (for clarity) lines.
Note. The diagrams in this section are illustrative and not to scale. They are meant to highlight the differences between the various positioning schemes in CSS 2.1, and are not intended to be reference renderings of the examples given.
Consider the following CSS declarations for outer and inner that don't alter the normal flow of boxes:
#outer { color: red }
#inner { color: blue }
The P element contains all inline content: anonymous inline text and two SPAN elements. Therefore, all of the content will be laid out in an inline formatting context, within a containing block established by the P element, producing something like:
To see the effect of relative positioning, we specify:
#outer { position: relative; top: -12px; color: red }
#inner { position: relative; top: 12px; color: blue }
Text flows normally up to the outer element. The outer text is then flowed into its normal flow position and dimensions at the end of line 1. Then, the inline boxes containing the text (distributed over three lines) are shifted as a unit by '-12px' (upwards).
The contents of inner, as a child of outer, would normally flow immediately after the words "of outer contents" (on line 1.5). However, the inner contents are themselves offset relative to the outer contents by '12px' (downwards), back to their original position on line 2.
Note that the content following outer is not affected by the relative positioning of outer.
Note also that had the offset of outer been '-24px', the text of outer and the body text would have overlapped.
Now consider the effect of floating the inner element's text to the right by means of the following rules:
#outer { color: red }
#inner { float: right; width: 130px; color: blue }
Text flows normally up to the inner box, which is pulled out of the flow and floated to the right margin (its 'width' has been assigned explicitly). Line boxes to the left of the float are shortened, and the document's remaining text flows into them.
To show the effect of the 'clear' property, we add a sibling element to the example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Comparison of positioning schemes II</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>Beginning of body contents.
<SPAN id=outer> Start of outer contents.
<SPAN id=inner> Inner contents.</SPAN>
<SPAN id=sibling> Sibling contents.</SPAN>
End of outer contents.</SPAN>
End of body contents.
</P>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The following rules:
#inner { float: right; width: 130px; color: blue }
#sibling { color: red }
cause the inner box to float to the right as before and the document's remaining text to flow into the vacated space:
However, if the 'clear' property on the sibling element is set to 'right' (i.e., the generated sibling box will not accept a position next to floating boxes to its right), the sibling content begins to flow below the float:
#inner { float: right; width: 130px; color: blue }
#sibling { clear: right; color: red }
Finally, we consider the effect of absolute positioning. Consider the following CSS declarations for outer and inner:
#outer {
position: absolute;
top: 200px; left: 200px;
width: 200px;
color: red;
}
#inner { color: blue }
which cause the top of the outer box to be positioned with respect to its containing block. The containing block for a positioned box is established by the nearest positioned ancestor (or, if none exists, the initial containing block, as in our example). The top side of the outer box is '200px' below the top of the containing block and the left side is '200px' from the left side. The child box of outer is flowed normally with respect to its parent.
The following example shows an absolutely positioned box that is a child of a relatively positioned box. Although the parent outer box is not actually offset, setting its 'position' property to 'relative' means that its box may serve as the containing block for positioned descendants. Since the outer box is an inline box that is split across several lines, the first inline box's top and left edges (depicted by thick dashed lines in the illustration below) serve as references for 'top' and 'left' offsets.
#outer {
position: relative;
color: red
}
#inner {
position: absolute;
top: 200px; left: -100px;
height: 130px; width: 130px;
color: blue;
}
This results in something like the following:
If we do not position the outer box:
#outer { color: red }
#inner {
position: absolute;
top: 200px; left: -100px;
height: 130px; width: 130px;
color: blue;
}
the containing block for inner becomes the initial containing block (in our example). The following illustration shows where the inner box would end up in this case.
Relative and absolute positioning may be used to implement change bars, as shown in the following example. The following fragment:
<P style="position: relative; margin-right: 10px; left: 10px;">
I used two red hyphens to serve as a change bar. They
will "float" to the left of the line containing THIS
<SPAN style="position: absolute; top: auto; left: -1em; color: red;">--</SPAN>
word.</P>
might result in something like:
First, the paragraph (whose containing block sides are shown in the illustration) is flowed normally. Then it is offset '10px' from the left edge of the containing block (thus, a right margin of '10px' has been reserved in anticipation of the offset). The two hyphens acting as change bars are taken out of the flow and positioned at the current line (due to 'top: auto'), '-1em' from the left edge of its containing block (established by the P in its final position). The result is that the change bars seem to "float" to the left of the current line.
For a positioned box, the 'z-index' property specifies:
Values have the following meanings:
In this section, the expression "in front of" means closer to the user as the user faces the screen.
In CSS 2.1, each box has a position in three dimensions. In addition to their horizontal and vertical positions, boxes lie along a "z-axis" and are formatted one on top of the other. Z-axis positions are particularly relevant when boxes overlap visually. This section discusses how boxes may be positioned along the z-axis.
The order in which the rendering tree is painted onto the canvas is described in terms of stacking contexts. Stacking contexts can contain further stacking contexts. A stacking context is atomic from the point of view of its parent stacking context; boxes in other stacking contexts may not come between any of its boxes.
Each box belongs to one stacking context. Each box in a given stacking context has an integer stack level, which is its position on the z-axis relative to other boxes in the same stacking context. Boxes with greater stack levels are always formatted in front of boxes with lower stack levels. Boxes may have negative stack levels. Boxes with the same stack level in a stacking context are stacked bottom-to-top according to document tree order.
The root element forms the root stacking context. Other stacking contexts are generated by any positioned element (including relatively positioned elements) having a computed value of 'z-index' other than 'auto'. Stacking contexts are not necessarily related to containing blocks. In future levels of CSS, other properties may introduce stacking contexts, for example 'opacity'.
Each stacking context consists of the following stacking levels (from back to front):
For a more thorough explanation of the stacking order, please see Appendix E.
The contents of inline blocks and inline tables are stacked as if they generated new stacking contexts, except that any elements that actually create new stacking contexts take part in the parent stacking context. They are then painted atomically in the inline stacking level.
In the following example, the stack levels of the boxes (named with their "id" attributes) are: "text2"=0, "image"=1, "text3"=2, and "text1"=3. The "text2" stack level is inherited from the root box. The others are specified with the 'z-index' property.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN">
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Z-order positioning</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css">
.pile {
position: absolute;
left: 2in;
top: 2in;
width: 3in;
height: 3in;
}
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>
<IMG id="image" class="pile"
src="butterfly.png" alt="A butterfly image"
style="z-index: 1">
<DIV id="text1" class="pile"
style="z-index: 3">
This text will overlay the butterfly image.
</DIV>
<DIV id="text2">
This text will be beneath everything.
</DIV>
<DIV id="text3" class="pile"
style="z-index: 2">
This text will underlay text1, but overlay the butterfly image
</DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
This example demonstrates the notion of transparency. The default behavior of the background is to allow boxes behind it to be visible. In the example, each box transparently overlays the boxes below it. This behavior can be overridden by using one of the existing background properties.
Conforming user agents that do not support bidirectional text may ignore the 'direction' and 'unicode-bidi' properties described in this section.
The characters in certain scripts are written from right to left. In some documents, in particular those written with the Arabic or Hebrew script, and in some mixed-language contexts, text in a single (visually displayed) block may appear with mixed directionality. This phenomenon is called bidirectionality, or "bidi" for short.
The Unicode standard ([UNICODE], section 3.11) defines a complex algorithm for determining the proper directionality of text. The algorithm consists of an implicit part based on character properties, as well as explicit controls for embeddings and overrides. CSS 2.1 relies on this algorithm to achieve proper bidirectional rendering. The 'direction' and 'unicode-bidi' properties allow authors to specify how the elements and attributes of a document language map to this algorithm.
If the rendered content contains right-to-left characters, and if the user agent displays these characters in right-to-left order, the user agent must apply the bidirectional algorithm. (UAs that render right-to-left characters simply because a font on the system contains them but do not support the concept of right-to-left text direction are exempt from this requirement.)
Because the directionality of a text depends on the structure and semantics of the document language, these properties should in most cases be used only by designers of document type descriptions (DTDs), or authors of special documents. If a default style sheet specifies these properties, authors and users should not specify rules to override them.
The HTML 4 specification ([HTML4], section 8.2) defines bidirectionality behavior for HTML elements. The style sheet rules that would achieve the bidi behavior specified in [HTML4] are given in the sample style sheet. The HTML 4 specification also contains more information on bidirectionality issues.
| Value: | ltr | rtl | inherit |
| Initial: | ltr |
| Applies to: | all elements, but see prose |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | as specified |
This property specifies the base writing direction of blocks and the direction of embeddings and overrides (see 'unicode-bidi') for the Unicode bidirectional algorithm. In addition, it specifies the direction of table column layout, the direction of horizontal overflow, and the position of an incomplete last line in a block in case of 'text-align: justify'.
Values for this property have the following meanings:
For the 'direction' property to affect reordering in inline-level elements, the 'unicode-bidi' property's value must be 'embed' or 'override'.
Note. The 'direction' property, when specified for table column elements, is not inherited by cells in the column since columns are not the ancestors of the cells in the document tree. Thus, CSS cannot easily capture the "dir" attribute inheritance rules described in [HTML4], section 11.3.2.1.
| Value: | normal | embed | bidi-override | inherit |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | all elements, but see prose |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Media: | visual |
| Computed value: | as specified |
Values for this property have the following meanings:
The final order of characters in each block-level element is the same as if the bidi control codes had been added as described above, markup had been stripped, and the resulting character sequence had been passed to an implementation of the Unicode bidirectional algorithm for plain text that produced the same line-breaks as the styled text. In this process, non-textual entities such as images are treated as neutral characters, unless their 'unicode-bidi' property has a value other than 'normal', in which case they are treated as strong characters in the 'direction' specified for the element.
Please note that in order to be able to flow inline boxes in a uniform direction (either entirely left-to-right or entirely right-to-left), more inline boxes (including anonymous inline boxes) may have to be created, and some inline boxes may have to be split up and reordered before flowing.
Because the Unicode algorithm has a limit of 61 levels of embedding, care should be taken not to use 'unicode-bidi' with a value other than 'normal' unless appropriate. In particular, a value of 'inherit' should be used with extreme caution. However, for elements that are, in general, intended to be displayed as blocks, a setting of 'unicode-bidi: embed' is preferred to keep the element together in case display is changed to inline (see example below).
The following example shows an XML document with bidirectional text. It illustrates an important design principle: DTD designers should take bidi into account both in the language proper (elements and attributes) and in any accompanying style sheets. The style sheets should be designed so that bidi rules are separate from other style rules. The bidi rules should not be overridden by other style sheets so that the document language's or DTD's bidi behavior is preserved.
In this example, lowercase letters stand for inherently left-to-right characters and uppercase letters represent inherently right-to-left characters:
<HEBREW>
<PAR>HEBREW1 HEBREW2 english3 HEBREW4 HEBREW5</PAR>
<PAR>HEBREW6 <EMPH>HEBREW7</EMPH> HEBREW8</PAR>
</HEBREW>
<ENGLISH>
<PAR>english9 english10 english11 HEBREW12 HEBREW13</PAR>
<PAR>english14 english15 english16</PAR>
<PAR>english17 <HE-QUO>HEBREW18 english19 HEBREW20</HE-QUO></PAR>
</ENGLISH>
Since this is XML, the style sheet is responsible for setting the writing direction. This is the style sheet:
/* Rules for bidi */
HEBREW, HE-QUO {direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: embed}
ENGLISH {direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: embed}
/* Rules for presentation */
HEBREW, ENGLISH, PAR {display: block}
EMPH {font-weight: bold}
The HEBREW element is a block with a right-to-left base direction, the ENGLISH element is a block with a left-to-right base direction. The PARs are blocks that inherit the base direction from their parents. Thus, the first two PARs are read starting at the top right, the final three are read starting at the top left. Please note that HEBREW and ENGLISH are chosen as element names for explicitness only; in general, element names should convey structure without reference to language.
The EMPH element is inline-level, and since its value for 'unicode-bidi' is 'normal' (the initial value), it has no effect on the ordering of the text. The HE-QUO element, on the other hand, creates an embedding.
The formatting of this text might look like this if the line length is long:
5WERBEH 4WERBEH english3 2WERBEH 1WERBEH
8WERBEH 7WERBEH 6WERBEH
english9 english10 english11 13WERBEH 12WERBEH
english14 english15 english16
english17 20WERBEH english19 18WERBEH
Note that the HE-QUO embedding causes HEBREW18 to be to the right of english19.
If lines have to be broken, it might be more like this:
2WERBEH 1WERBEH
-EH 4WERBEH english3
5WERB
-EH 7WERBEH 6WERBEH
8WERB
english9 english10 en-
glish11 12WERBEH
13WERBEH
english14 english15
english16
english17 18WERBEH
20WERBEH english19
Because HEBREW18 must be read before english19, it is on the line above english19. Just breaking the long line from the earlier formatting would not have worked. Note also that the first syllable from english19 might have fit on the previous line, but hyphenation of left-to-right words in a right-to-left context, and vice versa, is usually suppressed to avoid having to display a hyphen in the middle of a line.