6.6 Configuring the cron Utility
Contributed by Tom Rhodes.One of the most useful utilities in DragonFly is cron(8). The cron utility runs in the background and constantly checks the /etc/crontab file. The cron utility also checks the /var/cron/tabs directory, in search of new crontab files. These crontab files store information about specific functions which cron is supposed to perform at certain times.
The cron utility uses two different types of configuration files, the system crontab and user crontabs. The only difference between these two formats is the sixth field. In the system crontab, the sixth field is the name of a user for the command to run as. This gives the system crontab the ability to run commands as any user. In a user crontab, the sixth field is the command to run, and all commands run as the user who created the crontab; this is an important security feature.
Note: User crontabs allow individual users to schedule tasks without the need for root privileges. Commands in a user's crontab run with the permissions of the user who owns the crontab.
The root user can have a user crontab just like any other user. This one is different from /etc/crontab (the system crontab). Because of the system crontab, there's usually no need to create a user crontab for root.
Let us take a look at the /etc/crontab file (the system crontab):
# /etc/crontab - root's crontab for DragonFly # ## SHELL=/bin/sh PATH=/etc:/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin
HOME=/var/log # # #minute hour mday month wday who command
# # */5 * * * * root /usr/libexec/atrun

- Like most DragonFly configuration files, the # character represents a comment. A comment can be placed in the file as a reminder of what and why a desired action is performed. Comments cannot be on the same line as a command or else they will be interpreted as part of the command; they must be on a new line. Blank lines are ignored.
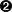
- First, the environment must be defined. The equals (=) character is used to define any environment settings, as with this example where it is used for the SHELL, PATH, and HOME options. If the shell line is omitted, cron will use the default, which is sh. If the PATH variable is omitted, no default will be used and file locations will need to be absolute. If HOME is omitted, cron will use the invoking users home directory.

- This line defines a total of seven fields. Listed here are the values minute, hour, mday, month, wday, who, and command. These are almost all self explanatory. minute is the time in minutes the command will be run. hour is similar to the minute option, just in hours. mday stands for day of the month. month is similar to hour and minute, as it designates the month. The wday option stands for day of the week. All these fields must be numeric values, and follow the twenty-four hour clock. The who field is special, and only exists in the /etc/crontab file. This field specifies which user the command should be run as. When a user installs his or her crontab file, they will not have this option. Finally, the command option is listed. This is the last field, so naturally it should designate the command to be executed.

- This last line will define the values discussed above. Notice here we have a */5 listing, followed by several more * characters. These * characters mean ``first-last'', and can be interpreted as every time. So, judging by this line, it is apparent that the atrun command is to be invoked by root every five minutes regardless of what day or month it is. For more information on the atrun command, see the atrun(8) manual page.
Commands can have any number of flags passed to them; however, commands which extend to multiple lines need to be broken with the backslash ``\'' continuation character.
This is the basic set up for every crontab file, although there is one thing different about this one. Field number six, where we specified the username, only exists in the system /etc/crontab file. This field should be omitted for individual user crontab files.
6.6.1 Installing a Crontab
Important: You must not use the procedure described here to edit/install the system crontab. Simply use your favorite editor: the cron utility will notice that the file has changed and immediately begin using the updated version. If you use crontab to load the /etc/crontab file you may get an error like ``root: not found'' because of the system crontab's additional user field.
To install a freshly written user crontab, first use your favorite editor to create a file in the proper format, and then use the crontab utility. The most common usage is:
% crontab crontab-file
In this example, crontab-file is the filename of a crontab that was previously created.
There is also an option to list installed
crontab files: just pass the
-l option to crontab and look
over the output.
For users who wish to begin their own crontab file from scratch, without the use of a template, the crontab -e option is available. This will invoke the selected editor with an empty file. When the file is saved, it will be automatically installed by the crontab command.
If you later want to remove your user crontab
completely, use crontab with the -r
option.