Copyright © 2000-2014 The FreeBSD Documentation Project
Copyright
Redistribution and use in source (XML DocBook) and 'compiled' forms (XML, HTML, PDF, PostScript, RTF and so forth) with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code (XML DocBook) must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer as the first lines of this file unmodified.
Redistributions in compiled form (transformed to other DTDs, converted to PDF, PostScript, RTF and other formats) must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Important:
THIS DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED BY THE FREEBSD DOCUMENTATION PROJECT "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE FREEBSD DOCUMENTATION PROJECT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
FreeBSD is a registered trademark of the FreeBSD Foundation.
Apple, AirPort, FireWire, iMac, iPhone, iPad, Mac, Macintosh, Mac OS, Quicktime, and TrueType are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
IBM, AIX, OS/2, PowerPC, PS/2, S/390, and ThinkPad are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
IEEE, POSIX, and 802 are registered trademarks of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. in the United States.
Intel, Celeron, Centrino, Core, EtherExpress, i386, i486, Itanium, Pentium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft, IntelliMouse, MS-DOS, Outlook, Windows, Windows Media and Windows NT are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Motif, OSF/1, and UNIX are registered trademarks and IT DialTone and The Open Group are trademarks of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
Sun, Sun Microsystems, Java, Java Virtual Machine, JDK, JRE, JSP, JVM, Netra, OpenJDK, Solaris, StarOffice, SunOS and VirtualBox are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Many of the designations used by manufacturers and sellers to distinguish their products are claimed as trademarks. Where those designations appear in this document, and the FreeBSD Project was aware of the trademark claim, the designations have been followed by the “™” or the “®” symbol.
Welcome to the Developers' Handbook. This manual is a work in progress and is the work of many individuals. Many sections do not yet exist and some of those that do exist need to be updated. If you are interested in helping with this project, send email to the FreeBSD documentation project mailing list.
The latest version of this document is always available from the FreeBSD World Wide Web server. It may also be downloaded in a variety of formats and compression options from the FreeBSD FTP server or one of the numerous mirror sites.
- I. Basics
- II. Interprocess Communication
- III. Kernel
- 9. Building and Installing a FreeBSD Kernel
- 10. Kernel Debugging
- 10.1. Obtaining a Kernel Crash Dump
- 10.2. Debugging a Kernel Crash Dump with
kgdb - 10.3. Debugging a Crash Dump with DDD
- 10.4. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using DDB
- 10.5. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using Remote GDB
- 10.6. Debugging a Console Driver
- 10.7. Debugging Deadlocks
- 10.8. Kernel debugging with Dcons
- 10.9. Glossary of Kernel Options for Debugging
- IV. Architectures
- 11. x86 Assembly Language Programming
- 11.1. Synopsis
- 11.2. The Tools
- 11.3. System Calls
- 11.4. Return Values
- 11.5. Creating Portable Code
- 11.6. Our First Program
- 11.7. Writing UNIX® Filters
- 11.8. Buffered Input and Output
- 11.9. Command Line Arguments
- 11.10. UNIX® Environment
- 11.11. Working with Files
- 11.12. One-Pointed Mind
- 11.13. Using the FPU
- 11.14. Caveats
- 11.15. Acknowledgements
- V. Appendices
- Index
- 2.1. A sample
.emacsfile
So here we are. System all installed and you are ready to start programming. But where to start? What does FreeBSD provide? What can it do for me, as a programmer?
These are some questions which this chapter tries to answer. Of course, programming has different levels of proficiency like any other trade. For some it is a hobby, for others it is their profession. The information in this chapter might be aimed toward the beginning programmer; indeed, it could serve useful for the programmer unfamiliar with the FreeBSD platform.
To produce the best UNIX® like operating system package possible, with due respect to the original software tools ideology as well as usability, performance and stability.
Our ideology can be described by the following guidelines
Do not add new functionality unless an implementor cannot complete a real application without it.
It is as important to decide what a system is not as to decide what it is. Do not serve all the world's needs; rather, make the system extensible so that additional needs can be met in an upwardly compatible fashion.
The only thing worse than generalizing from one example is generalizing from no examples at all.
If a problem is not completely understood, it is probably best to provide no solution at all.
If you can get 90 percent of the desired effect for 10 percent of the work, use the simpler solution.
Isolate complexity as much as possible.
Provide mechanism, rather than policy. In particular, place user interface policy in the client's hands.
From Scheifler & Gettys: "X Window System"
The complete source code to FreeBSD is available from our
public repository. The source code is normally installed in
/usr/src which contains
the following subdirectories:
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
bin/ | Source for files in
/bin |
cddl/ | Utilities covered by the Common Development and Distribution License |
contrib/ | Source for files from contributed software. |
crypto/ | Cryptographical sources |
etc/ | Source for files in /etc |
games/ | Source for files in /usr/games |
gnu/ | Utilities covered by the GNU Public License |
include/ | Source for files in /usr/include |
kerberos5/ | Source for Kerberos version 5 |
lib/ | Source for files in /usr/lib |
libexec/ | Source for files in /usr/libexec |
release/ | Files required to produce a FreeBSD release |
rescue/ | Build system for the
/rescue
utilities |
sbin/ | Source for files in /sbin |
secure/ | FreeSec sources |
share/ | Source for files in /usr/share |
sys/ | Kernel source files |
tools/ | Tools used for maintenance and testing of FreeBSD |
usr.bin/ | Source for files in /usr/bin |
usr.sbin/ | Source for files in /usr/sbin |
This chapter is an introduction to using some of the programming tools supplied with FreeBSD, although much of it will be applicable to many other versions of UNIX®. It does not attempt to describe coding in any detail. Most of the chapter assumes little or no previous programming knowledge, although it is hoped that most programmers will find something of value in it.
FreeBSD offers an excellent development environment.
Compilers for C and C++ and an assembler come with the
basic system, not to mention classic UNIX®
tools such as sed and awk.
If that is not enough, there are many more compilers and
interpreters in the Ports collection. The following section,
Introduction to Programming,
lists some of the available options. FreeBSD is very
compatible with standards such as POSIX® and
ANSI C, as well with its own BSD heritage, so
it is possible to write applications that will compile and run
with little or no modification on a wide range of
platforms.
However, all this power can be rather overwhelming at first if you have never written programs on a UNIX® platform before. This document aims to help you get up and running, without getting too deeply into more advanced topics. The intention is that this document should give you enough of the basics to be able to make some sense of the documentation.
Most of the document requires little or no knowledge of programming, although it does assume a basic competence with using UNIX® and a willingness to learn!
A program is a set of instructions that tell the computer to do various things; sometimes the instruction it has to perform depends on what happened when it performed a previous instruction. This section gives an overview of the two main ways in which you can give these instructions, or “commands” as they are usually called. One way uses an interpreter, the other a compiler. As human languages are too difficult for a computer to understand in an unambiguous way, commands are usually written in one or other languages specially designed for the purpose.
With an interpreter, the language comes as an environment, where you type in commands at a prompt and the environment executes them for you. For more complicated programs, you can type the commands into a file and get the interpreter to load the file and execute the commands in it. If anything goes wrong, many interpreters will drop you into a debugger to help you track down the problem.
The advantage of this is that you can see the results of your commands immediately, and mistakes can be corrected readily. The biggest disadvantage comes when you want to share your programs with someone. They must have the same interpreter, or you must have some way of giving it to them, and they need to understand how to use it. Also users may not appreciate being thrown into a debugger if they press the wrong key! From a performance point of view, interpreters can use up a lot of memory, and generally do not generate code as efficiently as compilers.
In my opinion, interpreted languages are the best way to
start if you have not done any programming before. This kind
of environment is typically found with languages like Lisp,
Smalltalk, Perl and Basic. It could also be argued that the
UNIX® shell (sh, csh) is itself an
interpreter, and many people do in fact write shell
“scripts” to help with various
“housekeeping” tasks on their machine. Indeed, part
of the original UNIX® philosophy was to provide lots of small
utility programs that could be linked together in shell
scripts to perform useful tasks.
Here is a list of interpreters that are available from the FreeBSD Ports Collection, with a brief discussion of some of the more popular interpreted languages.
Instructions on how to get and install applications from the Ports Collection can be found in the Ports section of the handbook.
- BASIC
Short for Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. Developed in the 1950s for teaching University students to program and provided with every self-respecting personal computer in the 1980s, BASIC has been the first programming language for many programmers. It is also the foundation for Visual Basic.
The Bywater Basic Interpreter can be found in the Ports Collection as lang/bwbasic and the Phil Cockroft's Basic Interpreter (formerly Rabbit Basic) is available as lang/pbasic.
- Lisp
A language that was developed in the late 1950s as an alternative to the “number-crunching” languages that were popular at the time. Instead of being based on numbers, Lisp is based on lists; in fact the name is short for “List Processing”. Very popular in AI (Artificial Intelligence) circles.
Lisp is an extremely powerful and sophisticated language, but can be rather large and unwieldy.
Various implementations of Lisp that can run on UNIX® systems are available in the Ports Collection for FreeBSD. GNU Common Lisp can be found as lang/gcl. CLISP by Bruno Haible and Michael Stoll is available as lang/clisp. For CMUCL, which includes a highly-optimizing compiler too, or simpler Lisp implementations like SLisp, which implements most of the Common Lisp constructs in a few hundred lines of C code, lang/cmucl and lang/slisp are available respectively.
- Perl
Very popular with system administrators for writing scripts; also often used on World Wide Web servers for writing CGI scripts.
Perl is available in the Ports Collection as lang/perl5.16 for all FreeBSD releases.
- Scheme
A dialect of Lisp that is rather more compact and cleaner than Common Lisp. Popular in Universities as it is simple enough to teach to undergraduates as a first language, while it has a high enough level of abstraction to be used in research work.
Scheme is available from the Ports Collection as lang/elk for the Elk Scheme Interpreter. The MIT Scheme Interpreter can be found in lang/mit-scheme and the SCM Scheme Interpreter in lang/scm.
- Icon
Icon is a high-level language with extensive facilities for processing strings and structures. The version of Icon for FreeBSD can be found in the Ports Collection as lang/icon.
- Logo
Logo is a language that is easy to learn, and has been used as an introductory programming language in various courses. It is an excellent tool to work with when teaching programming in small ages, as it makes the creation of elaborate geometric shapes an easy task even for very small children.
The latest version of Logo for FreeBSD is available from the Ports Collection in lang/logo.
- Python
Python is an Object-Oriented, interpreted language. Its advocates argue that it is one of the best languages to start programming with, since it is relatively easy to start with, but is not limited in comparison to other popular interpreted languages that are used for the development of large, complex applications (Perl and Tcl are two other languages that are popular for such tasks).
The latest version of Python is available from the Ports Collection in lang/python.
- Ruby
Ruby is an interpreter, pure object-oriented programming language. It has become widely popular because of its easy to understand syntax, flexibility when writing code, and the ability to easily develop and maintain large, complex programs.
Ruby is available from the Ports Collection as lang/ruby18.
- Tcl and Tk
Tcl is an embeddable, interpreted language, that has become widely used and became popular mostly because of its portability to many platforms. It can be used both for quickly writing small, prototype applications, or (when combined with Tk, a GUI toolkit) fully-fledged, featureful programs.
Various versions of Tcl are available as ports for FreeBSD. The latest version, Tcl 8.5, can be found in lang/tcl85.
Compilers are rather different. First of all, you write your code in a file (or files) using an editor. You then run the compiler and see if it accepts your program. If it did not compile, grit your teeth and go back to the editor; if it did compile and gave you a program, you can run it either at a shell command prompt or in a debugger to see if it works properly. [1]
Obviously, this is not quite as direct as using an interpreter. However it allows you to do a lot of things which are very difficult or even impossible with an interpreter, such as writing code which interacts closely with the operating system—or even writing your own operating system! It is also useful if you need to write very efficient code, as the compiler can take its time and optimize the code, which would not be acceptable in an interpreter. Moreover, distributing a program written for a compiler is usually more straightforward than one written for an interpreter—you can just give them a copy of the executable, assuming they have the same operating system as you.
As the edit-compile-run-debug cycle is rather tedious when using separate programs, many commercial compiler makers have produced Integrated Development Environments (IDEs for short). FreeBSD does not include an IDE in the base system, but devel/kdevelop is available in the Ports Collection and many use Emacs for this purpose. Using Emacs as an IDE is discussed in Section 2.7, “Using Emacs as a Development Environment”.
This section deals with the gcc
and clang compilers for C and C++,
since they come with the FreeBSD base system. Starting with
FreeBSD 10.X clang is installed as
cc. The
details of producing a program with an interpreter vary
considerably between interpreters, and are usually well covered
in the documentation and on-line help for the
interpreter.
Once you have written your masterpiece, the next step is to convert it into something that will (hopefully!) run on FreeBSD. This usually involves several steps, each of which is done by a separate program.
Pre-process your source code to remove comments and do other tricks like expanding macros in C.
Check the syntax of your code to see if you have obeyed the rules of the language. If you have not, it will complain!
Convert the source code into assembly language—this is very close to machine code, but still understandable by humans. Allegedly.
Convert the assembly language into machine code—yep, we are talking bits and bytes, ones and zeros here.
Check that you have used things like functions and global variables in a consistent way. For example, if you have called a non-existent function, it will complain.
If you are trying to produce an executable from several source code files, work out how to fit them all together.
Work out how to produce something that the system's run-time loader will be able to load into memory and run.
Finally, write the executable on the filesystem.
The word compiling is often used to refer to just steps 1 to 4—the others are referred to as linking. Sometimes step 1 is referred to as pre-processing and steps 3-4 as assembling.
Fortunately, almost all this detail is hidden from you, as
cc is a front end that manages calling all these
programs with the right arguments for you; simply typing
%cc foobar.c
will cause foobar.c to be compiled by all the
steps above. If you have more than one file to compile, just do
something like
%cc foo.c bar.c
Note that the syntax checking is just that—checking the syntax. It will not check for any logical mistakes you may have made, like putting the program into an infinite loop, or using a bubble sort when you meant to use a binary sort. [2]
There are lots and lots of options for cc, which
are all in the manual page. Here are a few of the most important
ones, with examples of how to use them.
-ofilenameThe output name of the file. If you do not use this option,
ccwill produce an executable calleda.out. [3]%cc foobar.cexecutable is a.out%cc -o foobar foobar.cexecutable is foobar-cJust compile the file, do not link it. Useful for toy programs where you just want to check the syntax, or if you are using a
Makefile.%cc -c foobar.cThis will produce an object file (not an executable) called
foobar.o. This can be linked together with other object files into an executable.-gCreate a debug version of the executable. This makes the compiler put information into the executable about which line of which source file corresponds to which function call. A debugger can use this information to show the source code as you step through the program, which is very useful; the disadvantage is that all this extra information makes the program much bigger. Normally, you compile with
-gwhile you are developing a program and then compile a “release version” without-gwhen you are satisfied it works properly.%cc -g foobar.cThis will produce a debug version of the program. [4]
-OCreate an optimized version of the executable. The compiler performs various clever tricks to try to produce an executable that runs faster than normal. You can add a number after the
-Oto specify a higher level of optimization, but this often exposes bugs in the compiler's optimizer.%cc -O -o foobar foobar.cThis will produce an optimized version of
foobar.
The following three flags will force cc
to check that your code complies to the relevant international
standard, often referred to as the ANSI
standard, though strictly speaking it is an
ISO standard.
-WallEnable all the warnings which the authors of
ccbelieve are worthwhile. Despite the name, it will not enable all the warningsccis capable of.-ansiTurn off most, but not all, of the non-ANSI C features provided by
cc. Despite the name, it does not guarantee strictly that your code will comply to the standard.-pedanticTurn off all
cc's non-ANSI C features.
Without these flags, cc will allow you to
use some of its non-standard extensions to the standard. Some
of these are very useful, but will not work with other
compilers—in fact, one of the main aims of the standard is
to allow people to write code that will work with any compiler
on any system. This is known as portable
code.
Generally, you should try to make your code as portable as possible, as otherwise you may have to completely rewrite the program later to get it to work somewhere else—and who knows what you may be using in a few years time?
%cc -Wall -ansi -pedantic -o foobar foobar.c
This will produce an executable foobar
after checking foobar.c for standard
compliance.
-llibrarySpecify a function library to be used at link time.
The most common example of this is when compiling a program that uses some of the mathematical functions in C. Unlike most other platforms, these are in a separate library from the standard C one and you have to tell the compiler to add it.
The rule is that if the library is called
lib, you givesomething.accthe argument-l. For example, the math library issomethinglibm.a, so you giveccthe argument-lm. A common “gotcha” with the math library is that it has to be the last library on the command line.%cc -o foobar foobar.c -lmThis will link the math library functions into
foobar.If you are compiling C++ code, use
c++.c++can also be invoked asclang++on FreeBSD.%c++ -o foobar foobar.ccThis will both produce an executable
foobarfrom the C++ source filefoobar.cc.
- 2.4.1.1. I am trying to write a program which uses the sin() function and I get an error like this. What does it mean?
- 2.4.1.2. All right, I wrote this simple program to practice using -lm. All it does is raise 2.1 to the power of 6.
- 2.4.1.3. So how do I fix this?
- 2.4.1.4. I compiled a file called foobar.c and I cannot find an executable called foobar. Where has it gone?
- 2.4.1.5. OK, I have an executable called foobar, I can see it when I run ls, but when I type in foobar at the command prompt it tells me there is no such file. Why can it not find it?
- 2.4.1.6. I called my executable test, but nothing happens when I run it. What is going on?
- 2.4.1.7. I compiled my program and it seemed to run all right at first, then there was an error and it said something about core dumped. What does that mean?
- 2.4.1.8. Fascinating stuff, but what I am supposed to do now?
- 2.4.1.9. When my program dumped core, it said something about a segmentation fault. What is that?
- 2.4.1.10. Sometimes when I get a core dump it says bus error. It says in my UNIX® book that this means a hardware problem, but the computer still seems to be working. Is this true?
- 2.4.1.11. This dumping core business sounds as though it could be quite useful, if I can make it happen when I want to. Can I do this, or do I have to wait until there is an error?
2.4.1.1. | I am trying to write a program which uses the
/var/tmp/cc0143941.o: Undefined symbol `_sin' referenced from text segment |
When using mathematical functions like
| |
2.4.1.2. | All right, I wrote this simple program to practice
using #include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float f;
f = pow(2.1, 6);
printf("2.1 ^ 6 = %f\n", f);
return 0;
}
and I compiled it as:
like you said I should, but I get this when I run it:
This is not the right answer! What is going on? |
When the compiler sees you call a function, it checks if it has already seen a prototype for it. If it has not, it assumes the function returns an int, which is definitely not what you want here. | |
2.4.1.3. | So how do I fix this? |
The prototypes for the mathematical functions are in
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
...
After recompiling it as you did before, run it:
If you are using any of the mathematical functions,
always include
| |
2.4.1.4. | I compiled a file called
|
Remember,
| |
2.4.1.5. | OK, I have an executable called
|
Unlike MS-DOS®, UNIX® does not
look in the current directory when it is trying to find
out which executable you want it to run, unless you tell
it to. Type | |
2.4.1.6. | I called my executable |
Most UNIX® systems have a program called
or choose a better name for your program! | |
2.4.1.7. | I compiled my program and it seemed to run all right at first, then there was an error and it said something about core dumped. What does that mean? |
The name core dump dates back
to the very early days of UNIX®, when the machines used
core memory for storing data. Basically, if the program
failed under certain conditions, the system would write
the contents of core memory to disk in a file called
| |
2.4.1.8. | Fascinating stuff, but what I am supposed to do now? |
Use | |
2.4.1.9. | When my program dumped core, it said something about a segmentation fault. What is that? |
This basically means that your program tried to perform some sort of illegal operation on memory; UNIX® is designed to protect the operating system and other programs from rogue programs. Common causes for this are:
Making one of these mistakes will not always lead to an error, but they are always bad practice. Some systems and compilers are more tolerant than others, which is why programs that ran well on one system can crash when you try them on an another. | |
2.4.1.10. | Sometimes when I get a core dump it says bus error. It says in my UNIX® book that this means a hardware problem, but the computer still seems to be working. Is this true? |
No, fortunately not (unless of course you really do have a hardware problem…). This is usually another way of saying that you accessed memory in a way you should not have. | |
2.4.1.11. | This dumping core business sounds as though it could be quite useful, if I can make it happen when I want to. Can I do this, or do I have to wait until there is an error? |
Yes, just go to another console or xterm, do
to find out the process ID of your program, and do
where
This is useful if your program has got stuck in an infinite loop, for instance. If your program happens to trap SIGABRT, there are several other signals which have a similar effect. Alternatively, you can create a core dump from
inside your program, by calling the
If you want to create a core dump from outside your
program, but do not want the process to terminate, you
can use the |
When you are working on a simple program with only one or two source files, typing in
%cc file1.c file2.c
is not too bad, but it quickly becomes very tedious when there are several files—and it can take a while to compile, too.
One way to get around this is to use object files and only recompile the source file if the source code has changed. So we could have something like:
%cc file1.o file2.o…file37.c…
if we had changed file37.c, but not any
of the others, since the last time we compiled. This may
speed up the compilation quite a bit, but does not solve the
typing problem.
Or we could write a shell script to solve the typing problem, but it would have to re-compile everything, making it very inefficient on a large project.
What happens if we have hundreds of source files lying about? What if we are working in a team with other people who forget to tell us when they have changed one of their source files that we use?
Perhaps we could put the two solutions together and write something like a shell script that would contain some kind of magic rule saying when a source file needs compiling. Now all we need now is a program that can understand these rules, as it is a bit too complicated for the shell.
This program is called make. It reads
in a file, called a makefile, that
tells it how different files depend on each other, and works
out which files need to be re-compiled and which ones do not.
For example, a rule could say something like “if
fromboz.o is older than
fromboz.c, that means someone must have
changed fromboz.c, so it needs to be
re-compiled.” The makefile also has rules telling
make how to re-compile the source file,
making it a much more powerful tool.
Makefiles are typically kept in the same directory as the
source they apply to, and can be called
makefile, Makefile
or MAKEFILE. Most programmers use the
name Makefile, as this puts it near the
top of a directory listing, where it can easily be
seen.
[5]
Here is a very simple make file:
foo: foo.c cc -o foo foo.c
It consists of two lines, a dependency line and a creation line.
The dependency line here consists of the name of the
program (known as the target), followed
by a colon, then whitespace, then the name of the source file.
When make reads this line, it looks to see
if foo exists; if it exists, it compares
the time foo was last modified to the
time foo.c was last modified. If
foo does not exist, or is older than
foo.c, it then looks at the creation line
to find out what to do. In other words, this is the rule for
working out when foo.c needs to be
re-compiled.
The creation line starts with a tab (press
the tab key) and then the command you would
type to create foo if you were doing it
at a command prompt. If foo is out of
date, or does not exist, make then executes
this command to create it. In other words, this is the rule
which tells make how to re-compile
foo.c.
So, when you type make, it will
make sure that foo is up to date with
respect to your latest changes to foo.c.
This principle can be extended to
Makefiles with hundreds of
targets—in fact, on FreeBSD, it is possible to compile
the entire operating system just by typing make
world in the appropriate directory!
Another useful property of makefiles is that the targets do not have to be programs. For instance, we could have a make file that looks like this:
foo: foo.c cc -o foo foo.c install: cp foo /home/me
We can tell make which target we want to make by typing:
%maketarget
make will then only look at that target
and ignore any others. For example, if we type
make foo with the makefile above, make
will ignore the install target.
If we just type make on its own,
make will always look at the first target and then stop
without looking at any others. So if we typed
make here, it will just go to the
foo target, re-compile
foo if necessary, and then stop without
going on to the install target.
Notice that the install target does not
actually depend on anything! This means that the command on
the following line is always executed when we try to make that
target by typing make install. In this
case, it will copy foo into the user's
home directory. This is often used by application makefiles,
so that the application can be installed in the correct
directory when it has been correctly compiled.
This is a slightly confusing subject to try to explain.
If you do not quite understand how make
works, the best thing to do is to write a simple program like
“hello world” and a make file like the one above
and experiment. Then progress to using more than one source
file, or having the source file include a header file. The
touch command is very useful here—it
changes the date on a file without you having to edit
it.
C code often starts with a list of files to include, for example stdio.h. Some of these files are system-include files, some of them are from the project you are now working on:
#include <stdio.h> #include "foo.h" int main(....
To make sure that this file is recompiled the moment
foo.h is changed, you have to add it in
your Makefile:
foo: foo.c foo.h
The moment your project is getting bigger and you have
more and more own include-files to maintain, it will be a
pain to keep track of all include files and the files which
are depending on it. If you change an include-file but
forget to recompile all the files which are depending on
it, the results will be devastating. gcc
has an option to analyze your files and to produce a list
of include-files and their dependencies: -MM.
If you add this to your Makefile:
depend: gcc -E -MM *.c > .depend
and run make depend, the file
.depend will appear with a list of
object-files, C-files and the include-files:
foo.o: foo.c foo.h
If you change foo.h, next time
you run make all files depending on
foo.h will be recompiled.
Do not forget to run make depend each
time you add an include-file to one of your files.
Makefiles can be rather complicated to write. Fortunately,
BSD-based systems like FreeBSD come with some very powerful
ones as part of the system. One very good example of this is
the FreeBSD ports system. Here is the essential part of a
typical ports Makefile:
MASTER_SITES= ftp://freefall.cdrom.com/pub/FreeBSD/LOCAL_PORTS/ DISTFILES= scheme-microcode+dist-7.3-freebsd.tgz .include <bsd.port.mk>
Now, if we go to the directory for this port and type
make, the following happens:
A check is made to see if the source code for this port is already on the system.
If it is not, an FTP connection to the URL in MASTER_SITES is set up to download the source.
The checksum for the source is calculated and compared it with one for a known, good, copy of the source. This is to make sure that the source was not corrupted while in transit.
Any changes required to make the source work on FreeBSD are applied—this is known as patching.
Any special configuration needed for the source is done. (Many UNIX® program distributions try to work out which version of UNIX® they are being compiled on and which optional UNIX® features are present—this is where they are given the information in the FreeBSD ports scenario).
The source code for the program is compiled. In effect, we change to the directory where the source was unpacked and do
make—the program's own make file has the necessary information to build the program.We now have a compiled version of the program. If we wish, we can test it now; when we feel confident about the program, we can type
make install. This will cause the program and any supporting files it needs to be copied into the correct location; an entry is also made into a package database, so that the port can easily be uninstalled later if we change our mind about it.
Now I think you will agree that is rather impressive for a four line script!
The secret lies in the last line, which tells
make to look in the system makefile called
bsd.port.mk. It is easy to overlook this
line, but this is where all the clever stuff comes
from—someone has written a makefile that tells
make to do all the things above (plus a
couple of other things I did not mention, including handling
any errors that may occur) and anyone can get access to that
just by putting a single line in their own make file!
If you want to have a look at these system makefiles,
they are in /usr/share/mk, but it is
probably best to wait until you have had a bit of practice with
makefiles, as they are very complicated (and if you do look at
them, make sure you have a flask of strong coffee
handy!)
Make is a very powerful tool, and can
do much more than the simple example above shows.
Unfortunately, there are several different versions of
make, and they all differ considerably.
The best way to learn what they can do is probably to read the
documentation—hopefully this introduction will have
given you a base from which you can do this.
The version of make that comes with FreeBSD is the
Berkeley make; there is a tutorial
for it in /usr/share/doc/psd/12.make. To
view it, do
%zmore paper.ascii.gz
in that directory.
Many applications in the ports use GNU
make, which has a very good set of
“info” pages. If you have installed any of these
ports, GNU make will automatically
have been installed as gmake. It is also
available as a port and package in its own right.
To view the info pages for GNU
make, you will have to edit the
dir file in the
/usr/local/info directory to add an entry
for it. This involves adding a line like
* Make: (make). The GNU Make utility.
to the file. Once you have done this, you can type
info and then select
from the menu (or in
Emacs, do C-h
i).
The debugger that comes with FreeBSD is called
gdb (GNU
debugger). You start it up by typing
%gdbprogname
although many people prefer to run it inside Emacs. You can do this by:
M-x gdb RET progname RETUsing a debugger allows you to run the program under more controlled circumstances. Typically, you can step through the program a line at a time, inspect the value of variables, change them, tell the debugger to run up to a certain point and then stop, and so on. You can even attach to a program that is already running, or load a core file to investigate why the program crashed. It is even possible to debug the kernel, though that is a little trickier than the user applications we will be discussing in this section.
gdb has quite good on-line help, as
well as a set of info pages, so this section will concentrate
on a few of the basic commands.
Finally, if you find its text-based command-prompt style off-putting, there is a graphical front-end for it (devel/xxgdb) in the Ports Collection.
This section is intended to be an introduction to using
gdb and does not cover specialized topics
such as debugging the kernel.
You will need to have compiled the program with the
-g option to get the most out of using
gdb. It will work without, but you will only
see the name of the function you are in, instead of the source
code. If you see a line like:
… (no debugging symbols found) …
when gdb starts up, you will know that
the program was not compiled with the -g
option.
At the gdb prompt, type
break main. This will tell the
debugger that you are not interested in watching the
preliminary set-up code in the program being run, and that it
should stop execution at the beginning of your code. Now type
run to start the program—it will
start at the beginning of the set-up code and then get stopped
by the debugger when it calls main().
(If you have ever wondered where main()
gets called from, now you know!).
You can now step through the program, a line at a time, by
pressing n. If you get to a function call,
you can step into it by pressing s. Once
you are in a function call, you can return from stepping into a
function call by pressing f. You can also
use up and down to take
a quick look at the caller.
Here is a simple example of how to spot a mistake in a
program with gdb. This is our program
(with a deliberate mistake):
#include <stdio.h>
int bazz(int anint);
main() {
int i;
printf("This is my program\n");
bazz(i);
return 0;
}
int bazz(int anint) {
printf("You gave me %d\n", anint);
return anint;
}This program sets i to be
5 and passes it to a function
bazz() which prints out the number we
gave it.
When we compile and run the program we get
%cc -g -o temp temp.c%./tempThis is my program anint = 4231
That was not what we expected! Time to see what is going on!
%gdb tempGDB is free software and you are welcome to distribute copies of it under certain conditions; type "show copying" to see the conditions. There is absolutely no warranty for GDB; type "show warranty" for details. GDB 4.13 (i386-unknown-freebsd), Copyright 1994 Free Software Foundation, Inc. (gdb)break mainSkip the set-up code Breakpoint 1 at 0x160f: file temp.c, line 9. gdb puts breakpoint at main() (gdb)runRun as far as main() Starting program: /home/james/tmp/temp Program starts running Breakpoint 1, main () at temp.c:9 gdb stops at main() (gdb)nGo to next line This is my program Program prints out (gdb)sstep into bazz() bazz (anint=4231) at temp.c:17 gdb displays stack frame (gdb)
Hang on a minute! How did anint get to be
4231? Did we not we set it to be
5 in main()? Let's
move up to main() and have a look.
(gdb)upMove up call stack #1 0x1625 in main () at temp.c:11 gdb displays stack frame (gdb)p iShow us the value of i $1 = 4231 gdb displays 4231
Oh dear! Looking at the code, we forgot to initialize i. We meant to put
… main() { int i; i = 5; printf("This is my program\n"); …
but we left the i=5; line out. As we
did not initialize i, it had whatever number
happened to be in that area of memory when the program ran,
which in this case happened to be
4231.
Note:
gdb displays the stack frame every
time we go into or out of a function, even if we are using
up and down to move
around the call stack. This shows the name of the function
and the values of its arguments, which helps us keep track
of where we are and what is going on. (The stack is a
storage area where the program stores information about the
arguments passed to functions and where to go when it
returns from a function call).
A core file is basically a file which contains the
complete state of the process when it crashed. In “the
good old days”, programmers had to print out hex
listings of core files and sweat over machine code manuals,
but now life is a bit easier. Incidentally, under FreeBSD and
other 4.4BSD systems, a core file is called
progname.corecore, to make it clearer which program a
core file belongs to.
To examine a core file, start up gdb in
the usual way. Instead of typing break or
run, type
(gdb) core progname.coreIf you are not in the same directory as the core file,
you will have to do dir
/path/to/core/file first.
You should see something like this:
%gdb a.outGDB is free software and you are welcome to distribute copies of it under certain conditions; type "show copying" to see the conditions. There is absolutely no warranty for GDB; type "show warranty" for details. GDB 4.13 (i386-unknown-freebsd), Copyright 1994 Free Software Foundation, Inc. (gdb)core a.out.coreCore was generated by `a.out'. Program terminated with signal 11, Segmentation fault. Cannot access memory at address 0x7020796d. #0 0x164a in bazz (anint=0x5) at temp.c:17 (gdb)
In this case, the program was called
a.out, so the core file is called
a.out.core. We can see that the program
crashed due to trying to access an area in memory that was not
available to it in a function called
bazz.
Sometimes it is useful to be able to see how a function was
called, as the problem could have occurred a long way up the
call stack in a complex program. The bt
command causes gdb to print out a
back-trace of the call stack:
(gdb) bt
#0 0x164a in bazz (anint=0x5) at temp.c:17
#1 0xefbfd888 in end ()
#2 0x162c in main () at temp.c:11
(gdb)The end() function is called when a
program crashes; in this case, the bazz()
function was called from main().
One of the neatest features about gdb
is that it can attach to a program that is already running. Of
course, that assumes you have sufficient permissions to do so.
A common problem is when you are stepping through a program
that forks, and you want to trace the child, but the debugger
will only let you trace the parent.
What you do is start up another gdb,
use ps to find the process ID for the
child, and do
(gdb) attach pidin gdb, and then debug as usual.
“That is all very well,” you are probably
thinking, “but by the time I have done that, the child
process will be over the hill and far away”. Fear
not, gentle reader, here is how to do it (courtesy of the
gdb info pages):
… if ((pid = fork()) < 0) /* _Always_ check this */ error(); else if (pid == 0) { /* child */ int PauseMode = 1; while (PauseMode) sleep(10); /* Wait until someone attaches to us */ … } else { /* parent */ …
Now all you have to do is attach to the child, set
PauseMode to 0, and wait
for the sleep() call to return!
Emacs is a highly customizable editor—indeed, it has been customized to the point where it is more like an operating system than an editor! Many developers and sysadmins do in fact spend practically all their time working inside Emacs, leaving it only to log out.
It is impossible even to summarize everything Emacs can do here, but here are some of the features of interest to developers:
Very powerful editor, allowing search-and-replace on both strings and regular expressions (patterns), jumping to start/end of block expression, etc, etc.
Pull-down menus and online help.
Language-dependent syntax highlighting and indentation.
Completely customizable.
You can compile and debug programs within Emacs.
On a compilation error, you can jump to the offending line of source code.
Friendly-ish front-end to the
infoprogram used for reading GNU hypertext documentation, including the documentation on Emacs itself.Friendly front-end to
gdb, allowing you to look at the source code as you step through your program.
And doubtless many more that have been overlooked.
Emacs can be installed on FreeBSD using the editors/emacs port.
Once it is installed, start it up and do C-h
t to read an Emacs tutorial—that means
hold down the control key, press
h, let go of the control
key, and then press t. (Alternatively, you
can use the mouse to select from the
menu.)
Although Emacs does have menus, it is well worth learning
the key bindings, as it is much quicker when you are editing
something to press a couple of keys than to try to find the
mouse and then click on the right place. And, when you are
talking to seasoned Emacs users, you will find they often
casually throw around expressions like “M-x
replace-s RET foo RET bar RET” so it is
useful to know what they mean. And in any case, Emacs has far
too many useful functions for them to all fit on the menu
bars.
Fortunately, it is quite easy to pick up the key-bindings, as they are displayed next to the menu item. My advice is to use the menu item for, say, opening a file until you understand how it works and feel confident with it, then try doing C-x C-f. When you are happy with that, move on to another menu command.
If you can not remember what a particular combination of keys does, select from the menu and type it in—Emacs will tell you what it does. You can also use the menu item to find out all the commands which contain a particular word in them, with the key binding next to it.
By the way, the expression above means hold down the
Meta key, press x, release
the Meta key, type
replace-s (short for
replace-string—another feature of
Emacs is that you can abbreviate commands), press the
return key, type foo
(the string you want replaced), press the
return key, type bar (the string you want to
replace foo with) and press
return again. Emacs will then do the
search-and-replace operation you have just requested.
If you are wondering what on earth the Meta key is, it is a special key that many UNIX® workstations have. Unfortunately, PC's do not have one, so it is usually the alt key (or if you are unlucky, the escape key).
Oh, and to get out of Emacs, do C-x C-c
(that means hold down the control key, press
x, press c and release the
control key). If you have any unsaved files
open, Emacs will ask you if you want to save them. (Ignore
the bit in the documentation where it says
C-z is the usual way to leave
Emacs—that leaves Emacs hanging around in the
background, and is only really useful if you are on a system
which does not have virtual terminals).
Emacs does many wonderful things; some of them are built in, some of them need to be configured.
Instead of using a proprietary macro language for configuration, Emacs uses a version of Lisp specially adapted for editors, known as Emacs Lisp. Working with Emacs Lisp can be quite helpful if you want to go on and learn something like Common Lisp. Emacs Lisp has many features of Common Lisp, although it is considerably smaller (and thus easier to master).
The best way to learn Emacs Lisp is to download the Emacs Tutorial
However, there is no need to actually know any Lisp to get
started with configuring Emacs, as I have included a sample
.emacs file, which should be enough to
get you started. Just copy it into your home directory and
restart Emacs if it is already running; it will read the
commands from the file and (hopefully) give you a useful basic
setup.
Unfortunately, there is far too much here to explain it in detail; however there are one or two points worth mentioning.
Everything beginning with a
;is a comment and is ignored by Emacs.In the first line, the
-*- Emacs-Lisp -*-is so that we can edit the.emacsfile itself within Emacs and get all the fancy features for editing Emacs Lisp. Emacs usually tries to guess this based on the filename, and may not get it right for.emacs.The tab key is bound to an indentation function in some modes, so when you press the tab key, it will indent the current line of code. If you want to put a tab character in whatever you are writing, hold the control key down while you are pressing the tab key.
This file supports syntax highlighting for C, C++, Perl, Lisp and Scheme, by guessing the language from the filename.
Emacs already has a pre-defined function called
next-error. In a compilation output window, this allows you to move from one compilation error to the next by doingM-n; we define a complementary function,previous-error, that allows you to go to a previous error by doingM-p. The nicest feature of all is thatC-c C-cwill open up the source file in which the error occurred and jump to the appropriate line.We enable Emacs's ability to act as a server, so that if you are doing something outside Emacs and you want to edit a file, you can just type in
%emacsclientfilenameand then you can edit the file in your Emacs! [6]
.emacs file;; -*-Emacs-Lisp-*-
;; This file is designed to be re-evaled; use the variable first-time
;; to avoid any problems with this.
(defvar first-time t
"Flag signifying this is the first time that .emacs has been evaled")
;; Meta
(global-set-key "\M- " 'set-mark-command)
(global-set-key "\M-\C-h" 'backward-kill-word)
(global-set-key "\M-\C-r" 'query-replace)
(global-set-key "\M-r" 'replace-string)
(global-set-key "\M-g" 'goto-line)
(global-set-key "\M-h" 'help-command)
;; Function keys
(global-set-key [f1] 'manual-entry)
(global-set-key [f2] 'info)
(global-set-key [f3] 'repeat-complex-command)
(global-set-key [f4] 'advertised-undo)
(global-set-key [f5] 'eval-current-buffer)
(global-set-key [f6] 'buffer-menu)
(global-set-key [f7] 'other-window)
(global-set-key [f8] 'find-file)
(global-set-key [f9] 'save-buffer)
(global-set-key [f10] 'next-error)
(global-set-key [f11] 'compile)
(global-set-key [f12] 'grep)
(global-set-key [C-f1] 'compile)
(global-set-key [C-f2] 'grep)
(global-set-key [C-f3] 'next-error)
(global-set-key [C-f4] 'previous-error)
(global-set-key [C-f5] 'display-faces)
(global-set-key [C-f8] 'dired)
(global-set-key [C-f10] 'kill-compilation)
;; Keypad bindings
(global-set-key [up] "\C-p")
(global-set-key [down] "\C-n")
(global-set-key [left] "\C-b")
(global-set-key [right] "\C-f")
(global-set-key [home] "\C-a")
(global-set-key [end] "\C-e")
(global-set-key [prior] "\M-v")
(global-set-key [next] "\C-v")
(global-set-key [C-up] "\M-\C-b")
(global-set-key [C-down] "\M-\C-f")
(global-set-key [C-left] "\M-b")
(global-set-key [C-right] "\M-f")
(global-set-key [C-home] "\M-<")
(global-set-key [C-end] "\M->")
(global-set-key [C-prior] "\M-<")
(global-set-key [C-next] "\M->")
;; Mouse
(global-set-key [mouse-3] 'imenu)
;; Misc
(global-set-key [C-tab] "\C-q\t") ; Control tab quotes a tab.
(setq backup-by-copying-when-mismatch t)
;; Treat 'y' or <CR> as yes, 'n' as no.
(fset 'yes-or-no-p 'y-or-n-p)
(define-key query-replace-map [return] 'act)
(define-key query-replace-map [?\C-m] 'act)
;; Load packages
(require 'desktop)
(require 'tar-mode)
;; Pretty diff mode
(autoload 'ediff-buffers "ediff" "Intelligent Emacs interface to diff" t)
(autoload 'ediff-files "ediff" "Intelligent Emacs interface to diff" t)
(autoload 'ediff-files-remote "ediff"
"Intelligent Emacs interface to diff")
(if first-time
(setq auto-mode-alist
(append '(("\\.cpp$" . c++-mode)
("\\.hpp$" . c++-mode)
("\\.lsp$" . lisp-mode)
("\\.scm$" . scheme-mode)
("\\.pl$" . perl-mode)
) auto-mode-alist)))
;; Auto font lock mode
(defvar font-lock-auto-mode-list
(list 'c-mode 'c++-mode 'c++-c-mode 'emacs-lisp-mode 'lisp-mode 'perl-mode 'scheme-mode)
"List of modes to always start in font-lock-mode")
(defvar font-lock-mode-keyword-alist
'((c++-c-mode . c-font-lock-keywords)
(perl-mode . perl-font-lock-keywords))
"Associations between modes and keywords")
(defun font-lock-auto-mode-select ()
"Automatically select font-lock-mode if the current major mode is in font-lock-auto-mode-list"
(if (memq major-mode font-lock-auto-mode-list)
(progn
(font-lock-mode t))
)
)
(global-set-key [M-f1] 'font-lock-fontify-buffer)
;; New dabbrev stuff
;(require 'new-dabbrev)
(setq dabbrev-always-check-other-buffers t)
(setq dabbrev-abbrev-char-regexp "\\sw\\|\\s_")
(add-hook 'emacs-lisp-mode-hook
'(lambda ()
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-fold-search) nil)
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-replace) nil)))
(add-hook 'c-mode-hook
'(lambda ()
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-fold-search) nil)
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-replace) nil)))
(add-hook 'text-mode-hook
'(lambda ()
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-fold-search) t)
(set (make-local-variable 'dabbrev-case-replace) t)))
;; C++ and C mode...
(defun my-c++-mode-hook ()
(setq tab-width 4)
(define-key c++-mode-map "\C-m" 'reindent-then-newline-and-indent)
(define-key c++-mode-map "\C-ce" 'c-comment-edit)
(setq c++-auto-hungry-initial-state 'none)
(setq c++-delete-function 'backward-delete-char)
(setq c++-tab-always-indent t)
(setq c-indent-level 4)
(setq c-continued-statement-offset 4)
(setq c++-empty-arglist-indent 4))
(defun my-c-mode-hook ()
(setq tab-width 4)
(define-key c-mode-map "\C-m" 'reindent-then-newline-and-indent)
(define-key c-mode-map "\C-ce" 'c-comment-edit)
(setq c-auto-hungry-initial-state 'none)
(setq c-delete-function 'backward-delete-char)
(setq c-tab-always-indent t)
;; BSD-ish indentation style
(setq c-indent-level 4)
(setq c-continued-statement-offset 4)
(setq c-brace-offset -4)
(setq c-argdecl-indent 0)
(setq c-label-offset -4))
;; Perl mode
(defun my-perl-mode-hook ()
(setq tab-width 4)
(define-key c++-mode-map "\C-m" 'reindent-then-newline-and-indent)
(setq perl-indent-level 4)
(setq perl-continued-statement-offset 4))
;; Scheme mode...
(defun my-scheme-mode-hook ()
(define-key scheme-mode-map "\C-m" 'reindent-then-newline-and-indent))
;; Emacs-Lisp mode...
(defun my-lisp-mode-hook ()
(define-key lisp-mode-map "\C-m" 'reindent-then-newline-and-indent)
(define-key lisp-mode-map "\C-i" 'lisp-indent-line)
(define-key lisp-mode-map "\C-j" 'eval-print-last-sexp))
;; Add all of the hooks...
(add-hook 'c++-mode-hook 'my-c++-mode-hook)
(add-hook 'c-mode-hook 'my-c-mode-hook)
(add-hook 'scheme-mode-hook 'my-scheme-mode-hook)
(add-hook 'emacs-lisp-mode-hook 'my-lisp-mode-hook)
(add-hook 'lisp-mode-hook 'my-lisp-mode-hook)
(add-hook 'perl-mode-hook 'my-perl-mode-hook)
;; Complement to next-error
(defun previous-error (n)
"Visit previous compilation error message and corresponding source code."
(interactive "p")
(next-error (- n)))
;; Misc...
(transient-mark-mode 1)
(setq mark-even-if-inactive t)
(setq visible-bell nil)
(setq next-line-add-newlines nil)
(setq compile-command "make")
(setq suggest-key-bindings nil)
(put 'eval-expression 'disabled nil)
(put 'narrow-to-region 'disabled nil)
(put 'set-goal-column 'disabled nil)
(if (>= emacs-major-version 21)
(setq show-trailing-whitespace t))
;; Elisp archive searching
(autoload 'format-lisp-code-directory "lispdir" nil t)
(autoload 'lisp-dir-apropos "lispdir" nil t)
(autoload 'lisp-dir-retrieve "lispdir" nil t)
(autoload 'lisp-dir-verify "lispdir" nil t)
;; Font lock mode
(defun my-make-face (face color &optional bold)
"Create a face from a color and optionally make it bold"
(make-face face)
(copy-face 'default face)
(set-face-foreground face color)
(if bold (make-face-bold face))
)
(if (eq window-system 'x)
(progn
(my-make-face 'blue "blue")
(my-make-face 'red "red")
(my-make-face 'green "dark green")
(setq font-lock-comment-face 'blue)
(setq font-lock-string-face 'bold)
(setq font-lock-type-face 'bold)
(setq font-lock-keyword-face 'bold)
(setq font-lock-function-name-face 'red)
(setq font-lock-doc-string-face 'green)
(add-hook 'find-file-hooks 'font-lock-auto-mode-select)
(setq baud-rate 1000000)
(global-set-key "\C-cmm" 'menu-bar-mode)
(global-set-key "\C-cms" 'scroll-bar-mode)
(global-set-key [backspace] 'backward-delete-char)
; (global-set-key [delete] 'delete-char)
(standard-display-european t)
(load-library "iso-transl")))
;; X11 or PC using direct screen writes
(if window-system
(progn
;; (global-set-key [M-f1] 'hilit-repaint-command)
;; (global-set-key [M-f2] [?\C-u M-f1])
(setq hilit-mode-enable-list
'(not text-mode c-mode c++-mode emacs-lisp-mode lisp-mode
scheme-mode)
hilit-auto-highlight nil
hilit-auto-rehighlight 'visible
hilit-inhibit-hooks nil
hilit-inhibit-rebinding t)
(require 'hilit19)
(require 'paren))
(setq baud-rate 2400) ; For slow serial connections
)
;; TTY type terminal
(if (and (not window-system)
(not (equal system-type 'ms-dos)))
(progn
(if first-time
(progn
(keyboard-translate ?\C-h ?\C-?)
(keyboard-translate ?\C-? ?\C-h)))))
;; Under UNIX
(if (not (equal system-type 'ms-dos))
(progn
(if first-time
(server-start))))
;; Add any face changes here
(add-hook 'term-setup-hook 'my-term-setup-hook)
(defun my-term-setup-hook ()
(if (eq window-system 'pc)
(progn
;; (set-face-background 'default "red")
)))
;; Restore the "desktop" - do this as late as possible
(if first-time
(progn
(desktop-load-default)
(desktop-read)))
;; Indicate that this file has been read at least once
(setq first-time nil)
;; No need to debug anything now
(setq debug-on-error nil)
;; All done
(message "All done, %s%s" (user-login-name) ".")
Now, this is all very well if you only want to program in
the languages already catered for in the
.emacs file (C, C++, Perl, Lisp and
Scheme), but what happens if a new language called
“whizbang” comes out, full of exciting
features?
The first thing to do is find out if whizbang comes with
any files that tell Emacs about the language. These usually
end in .el, short for “Emacs
Lisp”. For example, if whizbang is a FreeBSD port, we
can locate these files by doing
%find /usr/ports/lang/whizbang -name "*.el" -print
and install them by copying them into the Emacs site Lisp
directory. On FreeBSD, this is
/usr/local/share/emacs/site-lisp.
So for example, if the output from the find command was
/usr/ports/lang/whizbang/work/misc/whizbang.el
we would do
#cp /usr/ports/lang/whizbang/work/misc/whizbang.el /usr/local/share/emacs/site-lisp
Next, we need to decide what extension whizbang source
files have. Let's say for the sake of argument that they all
end in .wiz. We need to add an entry to
our .emacs file to make sure Emacs will
be able to use the information in
whizbang.el.
Find the auto-mode-alist entry in
.emacs and add a line for whizbang, such
as:
… ("\\.lsp$" . lisp-mode) ("\\.wiz$" . whizbang-mode) ("\\.scm$" . scheme-mode) …
This means that Emacs will automatically go into
whizbang-mode when you edit a file ending
in .wiz.
Just below this, you will find the
font-lock-auto-mode-list entry. Add
whizbang-mode to it like so:
;; Auto font lock mode (defvar font-lock-auto-mode-list (list 'c-mode 'c++-mode 'c++-c-mode 'emacs-lisp-mode 'whizbang-mode 'lisp-mode 'perl-mode 'scheme-mode) "List of modes to always start in font-lock-mode")
This means that Emacs will always enable
font-lock-mode (ie syntax highlighting)
when editing a .wiz file.
And that is all that is needed. If there is anything else
you want done automatically when you open up a
.wiz file, you can add a
whizbang-mode hook (see
my-scheme-mode-hook for a simple example
that adds auto-indent).
For information about setting up a development environment for contributing fixes to FreeBSD itself, please see development(7).
Brian Harvey and Matthew Wright Simply Scheme MIT 1994. ISBN 0-262-08226-8
Randall Schwartz Learning Perl O'Reilly 1993 ISBN 1-56592-042-2
Patrick Henry Winston and Berthold Klaus Paul Horn Lisp (3rd Edition) Addison-Wesley 1989 ISBN 0-201-08319-1
Brian W. Kernighan and Rob Pike The Unix Programming Environment Prentice-Hall 1984 ISBN 0-13-937681-X
Brian W. Kernighan and Dennis M. Ritchie The C Programming Language (2nd Edition) Prentice-Hall 1988 ISBN 0-13-110362-8
Bjarne Stroustrup The C++ Programming Language Addison-Wesley 1991 ISBN 0-201-53992-6
W. Richard Stevens Advanced Programming in the Unix Environment Addison-Wesley 1992 ISBN 0-201-56317-7
W. Richard Stevens Unix Network Programming Prentice-Hall 1990 ISBN 0-13-949876-1
[1] If you run it in the shell, you may get a core dump.
[2] In case you did not know, a binary sort is an efficient way of sorting things into order and a bubble sort is not.
[3] The reasons for this are buried in the mists of history.
[4] Note, we did not use the -o flag
to specify the executable name, so we will get an
executable called a.out.
Producing a debug version called
foobar is left as an exercise for
the reader!
[5] They do not use the MAKEFILE form
as block capitals are often used for documentation files
like README.
[6] Many Emacs users set their EDITOR
environment to
emacsclient so this happens every
time they need to edit a file.
This chapter describes some of the security issues that have plagued UNIX® programmers for decades and some of the new tools available to help programmers avoid writing exploitable code.
Writing secure applications takes a very scrutinous and pessimistic outlook on life. Applications should be run with the principle of “least privilege” so that no process is ever running with more than the bare minimum access that it needs to accomplish its function. Previously tested code should be reused whenever possible to avoid common mistakes that others may have already fixed.
One of the pitfalls of the UNIX® environment is how easy it is to make assumptions about the sanity of the environment. Applications should never trust user input (in all its forms), system resources, inter-process communication, or the timing of events. UNIX® processes do not execute synchronously so logical operations are rarely atomic.
Buffer Overflows have been around since the very beginnings of the Von-Neuman 1 architecture. They first gained widespread notoriety in 1988 with the Morris Internet worm. Unfortunately, the same basic attack remains effective today. By far the most common type of buffer overflow attack is based on corrupting the stack.
Most modern computer systems use a stack to pass arguments to procedures and to store local variables. A stack is a last in first out (LIFO) buffer in the high memory area of a process image. When a program invokes a function a new "stack frame" is created. This stack frame consists of the arguments passed to the function as well as a dynamic amount of local variable space. The "stack pointer" is a register that holds the current location of the top of the stack. Since this value is constantly changing as new values are pushed onto the top of the stack, many implementations also provide a "frame pointer" that is located near the beginning of a stack frame so that local variables can more easily be addressed relative to this value. 1 The return address for function calls is also stored on the stack, and this is the cause of stack-overflow exploits since overflowing a local variable in a function can overwrite the return address of that function, potentially allowing a malicious user to execute any code he or she wants.
Although stack-based attacks are by far the most common, it would also be possible to overrun the stack with a heap-based (malloc/free) attack.
The C programming language does not perform automatic bounds checking on arrays or pointers as many other languages do. In addition, the standard C library is filled with a handful of very dangerous functions.
strcpy(char *dest, const char
*src) | May overflow the dest buffer |
strcat(char *dest, const char
*src) | May overflow the dest buffer |
getwd(char *buf) | May overflow the buf buffer |
gets(char *s) | May overflow the s buffer |
[vf]scanf(const char *format,
...) | May overflow its arguments. |
realpath(char *path, char
resolved_path[]) | May overflow the path buffer |
[v]sprintf(char *str, const char
*format, ...) | May overflow the str buffer. |
The following example code contains a buffer overflow designed to overwrite the return address and skip the instruction immediately following the function call. (Inspired by 4)
#include <stdio.h>
void manipulate(char *buffer) {
char newbuffer[80];
strcpy(newbuffer,buffer);
}
int main() {
char ch,buffer[4096];
int i=0;
while ((buffer[i++] = getchar()) != '\n') {};
i=1;
manipulate(buffer);
i=2;
printf("The value of i is : %d\n",i);
return 0;
}Let us examine what the memory image of this process would look like if we were to input 160 spaces into our little program before hitting return.
[XXX figure here!]
Obviously more malicious input can be devised to execute actual compiled instructions (such as exec(/bin/sh)).
The most straightforward solution to the problem of
stack-overflows is to always use length restricted memory and
string copy functions. strncpy and
strncat are part of the standard C library.
These functions accept a length value as a parameter which
should be no larger than the size of the destination buffer.
These functions will then copy up to `length' bytes from the
source to the destination. However there are a number of
problems with these functions. Neither function guarantees NUL
termination if the size of the input buffer is as large as the
destination. The length parameter is also used inconsistently
between strncpy and strncat so it is easy for programmers to get
confused as to their proper usage. There is also a significant
performance loss compared to strcpy when
copying a short string into a large buffer since
strncpy NUL fills up the size
specified.
Another memory copy implementation exists
to get around these problems. The
strlcpy and strlcat
functions guarantee that they will always null terminate the
destination string when given a non-zero length argument.
Unfortunately there is still a very large assortment of code in public use which blindly copies memory around without using any of the bounded copy routines we just discussed. Fortunately, there is a way to help prevent such attacks — run-time bounds checking, which is implemented by several C/C++ compilers.
ProPolice is one such compiler feature, and is integrated into gcc(1) versions 4.1 and later. It replaces and extends the earlier StackGuard gcc(1) extension.
ProPolice helps to protect against stack-based buffer overflows and other attacks by laying pseudo-random numbers in key areas of the stack before calling any function. When a function returns, these “canaries” are checked and if they are found to have been changed the executable is immediately aborted. Thus any attempt to modify the return address or other variable stored on the stack in an attempt to get malicious code to run is unlikely to succeed, as the attacker would have to also manage to leave the pseudo-random canaries untouched.
Recompiling your application with ProPolice is an effective means of stopping most buffer-overflow attacks, but it can still be compromised.
Compiler-based mechanisms are completely useless for
binary-only software for which you cannot recompile. For
these situations there are a number of libraries which
re-implement the unsafe functions of the C-library
(strcpy, fscanf,
getwd, etc..) and ensure that these
functions can never write past the stack pointer.
- libsafe
- libverify
- libparanoia
Unfortunately these library-based defenses have a number of shortcomings. These libraries only protect against a very small set of security related issues and they neglect to fix the actual problem. These defenses may fail if the application was compiled with -fomit-frame-pointer. Also, the LD_PRELOAD and LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variables can be overwritten/unset by the user.
There are at least 6 different IDs associated with any given process. Because of this you have to be very careful with the access that your process has at any given time. In particular, all seteuid applications should give up their privileges as soon as it is no longer required.
The real user ID can only be changed by a superuser process. The login program sets this when a user initially logs in and it is seldom changed.
The effective user ID is set by the
exec() functions if a program has its
seteuid bit set. An application can call
seteuid() at any time to set the effective
user ID to either the real user ID or the saved set-user-ID.
When the effective user ID is set by exec()
functions, the previous value is saved in the saved set-user-ID.
The traditional method of restricting a process
is with the chroot() system call. This
system call changes the root directory from which all other
paths are referenced for a process and any child processes. For
this call to succeed the process must have execute (search)
permission on the directory being referenced. The new
environment does not actually take effect until you
chdir() into your new environment. It
should also be noted that a process can easily break out of a
chroot environment if it has root privilege. This could be
accomplished by creating device nodes to read kernel memory,
attaching a debugger to a process outside of the chroot(8)
environment, or in
many other creative ways.
The behavior of the chroot() system
call can be controlled somewhat with the
kern.chroot_allow_open_directories sysctl
variable. When this value is set to 0,
chroot() will fail with EPERM if there are
any directories open. If set to the default value of 1, then
chroot() will fail with EPERM if there are
any directories open and the process is already subject to a
chroot() call. For any other value, the
check for open directories will be bypassed completely.
The concept of a Jail extends upon the
chroot() by limiting the powers of the
superuser to create a true `virtual server'. Once a prison is
set up all network communication must take place through the
specified IP address, and the power of "root privilege" in this
jail is severely constrained.
While in a prison, any tests of superuser power within the
kernel using the suser() call will fail.
However, some calls to suser() have been
changed to a new interface suser_xxx().
This function is responsible for recognizing or denying access
to superuser power for imprisoned processes.
A superuser process within a jailed environment has the power to:
- Manipulate credential with
setuid,seteuid,setgid,setegid,setgroups,setreuid,setregid,setlogin - Set resource limits with
setrlimit - Modify some sysctl nodes (kern.hostname)
chroot()- Set flags on a vnode:
chflags,fchflags - Set attributes of a vnode such as file permission, owner, group, size, access time, and modification time.
- Bind to privileged ports in the Internet domain (ports < 1024)
Jail is a very useful tool for
running applications in a secure environment but it does have
some shortcomings. Currently, the IPC mechanisms have not been
converted to the suser_xxx so applications
such as MySQL cannot be run within a jail. Superuser access
may have a very limited meaning within a jail, but there is
no way to specify exactly what "very limited" means.
POSIX® has released a working draft that adds event auditing, access control lists, fine grained privileges, information labeling, and mandatory access control.
This is a work in progress and is the focus of the TrustedBSD project. Some of the initial work has been committed to FreeBSD-CURRENT (cap_set_proc(3)).
An application should never assume that anything about the users environment is sane. This includes (but is certainly not limited to): user input, signals, environment variables, resources, IPC, mmaps, the filesystem working directory, file descriptors, the # of open files, etc.
You should never assume that you can catch all forms of invalid input that a user might supply. Instead, your application should use positive filtering to only allow a specific subset of inputs that you deem safe. Improper data validation has been the cause of many exploits, especially with CGI scripts on the world wide web. For filenames you need to be extra careful about paths ("../", "/"), symbolic links, and shell escape characters.
Perl has a really cool feature called "Taint" mode which
can be used to prevent scripts from using data derived outside
the program in an unsafe way. This mode will check command line
arguments, environment variables, locale information, the
results of certain syscalls (readdir(),
readlink(),
getpwxxx()), and all file input.
A race condition is anomalous behavior caused by the unexpected dependence on the relative timing of events. In other words, a programmer incorrectly assumed that a particular event would always happen before another.
Some of the common causes of race conditions are signals,
access checks, and file opens. Signals are asynchronous events
by nature so special care must be taken in dealing with them.
Checking access with access(2) then
open(2) is clearly non-atomic. Users can
move files in between the two calls. Instead, privileged
applications should seteuid() and then call
open() directly. Along the same lines, an
application should always set a proper umask before
open() to obviate the need for spurious
chmod() calls.
To make your application more useful for speakers of other languages, we hope that you will program I18N compliant. The GNU gcc compiler and GUI libraries like QT and GTK support I18N through special handling of strings. Making a program I18N compliant is very easy. It allows contributors to port your application to other languages quickly. Refer to the library specific I18N documentation for more details.
In contrast with common perception, I18N compliant code is easy to write. Usually, it only involves wrapping your strings with library specific functions. In addition, please be sure to allow for wide or multibyte character support.
It has come to our attention that the individual I18N/L10N efforts for each country has been repeating each others' efforts. Many of us have been reinventing the wheel repeatedly and inefficiently. We hope that the various major groups in I18N could congregate into a group effort similar to the Core Team's responsibility.
Currently, we hope that, when you write or port I18N programs, you would send it out to each country's related FreeBSD mailing list for testing. In the future, we hope to create applications that work in all the languages out-of-the-box without dirty hacks.
The FreeBSD internationalization mailing list has been established. If you are an I18N/L10N developer, please send your comments, ideas, questions, and anything you deem related to it.
Beyond the basic I18N functions, like supporting various input encodings or supporting national conventions, such as the different decimal separators, at a higher level of I18N, it is possible to localize the messages written to the output by the various programs. A common way of doing this is using the POSIX.1 NLS functions, which are provided as a part of the FreeBSD base system.
POSIX.1 NLS is based on catalog files, which contain the
localized messages in the desired encoding. The messages are
organized into sets and each message is identified by an integer
number in the containing set. The catalog files are conventionally
named after the locale they contain localized messages for, followed
by the .msg extension. For instance, the
Hungarian messages for ISO8859-2 encoding should be stored in a file
called hu_HU.ISO8859-2.
These catalog files are common text files that contain the
numbered messages. It is possible to write comments by starting
the line with a $ sign. Set boundaries are also separated by
special comments, where the keyword set must
directly follow the $ sign. The set keyword
is then followed by the set number. For example:
$set 1
The actual message entries start with the message number and followed by the localized message. The well-known modifiers from printf(3) are accepted:
15 "File not found: %s\n"
The language catalog files have to be compiled into a binary form before they can be opened from the program. This conversion is done with the gencat(1) utility. Its first argument is the filename of the compiled catalog and its further arguments are the input catalogs. The localized messages can also be organized into more catalog files and then all of them can be processed with gencat(1).
Using the catalog files is simple. To use
the related functions, nl_types.h must be included. Before
using a catalog, it has to be opened with catopen(3).
The function takes two arguments. The first parameter is the name of the
installed and compiled catalog. Usually, the name of the
program is used, such as grep.
This name will be used when looking for the compiled
catalog file. The catopen(3) call looks for this file
in /usr/share/nls/
and in locale/catname/usr/local/share/nls/,
where locale/catnamelocale is the locale set and
catname is the catalog name being
discussed. The second parameter is a constant, which can have
two values:
NL_CAT_LOCALE, which means that the used catalog file will be based onLC_MESSAGES.0, which means thatLANGhas to be used to open the proper catalog.
The catopen(3) call returns a catalog identifier of
type nl_catd. Please refer to the manual page for a list of possible returned error
codes.
After opening a catalog catgets(3) can be used to retrieve a message. The first parameter is the catalog identifier returned by catopen(3), the second one is the number of the set, the third one is the number of the messages, and the fourth one is a fallback message, which will be returned if the requested message cannot be retrieved from the catalog file.
After using the catalog file, it must be closed by calling catclose(3), which has one argument, the catalog id.
The following example will demonstrate an easy solution on how to use NLS catalogs in a flexible way.
The below lines need to be put into a common header file of the program, which is included into all source files where localized messages are necessary:
#ifdef WITHOUT_NLS #define getstr(n) nlsstr[n] #else #include <nl_types.h> extern nl_catd catalog; #define getstr(n) catgets(catalog, 1, n, nlsstr[n]) #endif extern char *nlsstr[];
Next, put these lines into the global declaration part of the main source file:
#ifndef WITHOUT_NLS
#include <nl_types.h>
nl_catd catalog;
#endif
/*
* Default messages to use when NLS is disabled or no catalog
* is found.
*/
char *nlsstr[] = {
"",
/* 1*/ "some random message",
/* 2*/ "some other message"
};Next come the real code snippets, which open, read, and close the catalog:
#ifndef WITHOUT_NLS
catalog = catopen("myapp", NL_CAT_LOCALE);
#endif
...
printf(getstr(1));
...
#ifndef WITHOUT_NLS
catclose(catalog);
#endifThere is a good way of reducing the strings that need to be localized by using libc error messages. This is also useful to just avoid duplication and provide consistent error messages for the common errors that can be encountered by a great many of programs.
First, here is an example that does not use libc error messages:
#include <err.h> ... if (!S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) errx(1, "argument is not a directory");
This can be transformed to print an error message by
reading errno and printing an error message
accordingly:
#include <err.h>
#include <errno.h>
...
if (!S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) {
errno = ENOTDIR;
err(1, NULL);
}
In this example, the custom string is eliminated, thus
translators will have less work when localizing the program
and users will see the usual “Not a directory”
error message when they encounter this error. This message
will probably seem more familiar to them. Please note that
it was necessary to include errno.h in order to directly
access errno.
It is worth to note that there are cases when
errno is set automatically by a preceding
call, so it is not necessary to set it explicitly:
#include <err.h> ... if ((p = malloc(size)) == NULL) err(1, NULL);
Using the catalog files requires few repeatable steps,
such as compiling the catalogs and installing them to the
proper location. In order to simplify this process even
more, bsd.nls.mk introduces some macros.
It is not necessary to include bsd.nls.mk
explicitly, it is pulled in from the common Makefiles,
such as bsd.prog.mk or
bsd.lib.mk.
Usually it is enough to define NLSNAME,
which should have the catalog name mentioned as the first
argument of catopen(3) and list the catalog files in
NLS without their .msg
extension. Here is an example, which makes it possible to
to disable NLS when used with the code examples before.
The WITHOUT_NLS make(1) variable has
to be defined in order to build the program without NLS
support.
.if !defined(WITHOUT_NLS) NLS= es_ES.ISO8859-1 NLS+= hu_HU.ISO8859-2 NLS+= pt_BR.ISO8859-1 .else CFLAGS+= -DWITHOUT_NLS .endif
Conventionally, the catalog files are placed under the
nls subdirectory and
this is the default behaviour of bsd.nls.mk.
It is possible, though to override the location of the
catalogs with the NLSSRCDIR make(1)
variable. The default name of the precompiled catalog files
also follow the naming convention mentioned before. It can be
overridden by setting the NLSNAME variable.
There are other options to fine tune the processing of the catalog
files but usually it is not needed, thus they are not described
here. For further information on bsd.nls.mk,
please refer to the file itself, it is short and easy to
understand.
This chapter documents various guidelines and policies in force for the FreeBSD source tree.
Consistent coding style is extremely important, particularly with large projects like FreeBSD. Code should follow the FreeBSD coding styles described in style(9) and style.Makefile(5).
If a particular portion of the FreeBSD
src/ distribution is being maintained by a
person or group of persons, this is communicated through an
entry in the src/MAINTAINERS file.
Maintainers of ports within the Ports Collection express their
maintainership to the world by adding a
MAINTAINER line to the
Makefile of the port in question:
MAINTAINER=email-addresses
Tip:
For other parts of the repository, or for sections not listed as having a maintainer, or when you are unsure who the active maintainer is, try looking at the recent commit history of the relevant parts of the source tree. It is quite often the case that a maintainer is not explicitly named, but the people who are actively working in a part of the source tree for, say, the last couple of years are interested in reviewing changes. Even if this is not specifically mentioned in the documentation or the source itself, asking for a review as a form of courtesy is a very reasonable thing to do.
The role of the maintainer is as follows:
The maintainer owns and is responsible for that code. This means that he or she is responsible for fixing bugs and answering problem reports pertaining to that piece of the code, and in the case of contributed software, for tracking new versions, as appropriate.
Changes to directories which have a maintainer defined shall be sent to the maintainer for review before being committed. Only if the maintainer does not respond for an unacceptable period of time, to several emails, will it be acceptable to commit changes without review by the maintainer. However, it is suggested that you try to have the changes reviewed by someone else if at all possible.
It is of course not acceptable to add a person or group as maintainer unless they agree to assume this duty. On the other hand it does not have to be a committer and it can easily be a group of people.
Some parts of the FreeBSD distribution consist of software that is actively being maintained outside the FreeBSD project. For historical reasons, we call this contributed software. Some examples are sendmail, gcc and patch.
Over the last couple of years, various methods have been used in dealing with this type of software and all have some number of advantages and drawbacks. No clear winner has emerged.
Since this is the case, after some debate one of these methods has been selected as the “official” method and will be required for future imports of software of this kind. Furthermore, it is strongly suggested that existing contributed software converge on this model over time, as it has significant advantages over the old method, including the ability to easily obtain diffs relative to the “official” versions of the source by everyone (even without direct repository access). This will make it significantly easier to return changes to the primary developers of the contributed software.
Ultimately, however, it comes down to the people actually doing the work. If using this model is particularly unsuited to the package being dealt with, exceptions to these rules may be granted only with the approval of the core team and with the general consensus of the other developers. The ability to maintain the package in the future will be a key issue in the decisions.
Note:
Because it makes it harder to import future versions minor, trivial and/or cosmetic changes are strongly discouraged on files that are still tracking the vendor branch.
This section describes the vendor import procedure with Subversion in details.
Preparing the Tree
If this is your first import after the switch to SVN, you will have to flatten and clean up the vendor tree, and bootstrap merge history in the main tree. If not, you can safely omit this step.
During the conversion from CVS to SVN, vendor branches were imported with the same layout as the main tree. For example, the foo vendor sources ended up in
vendor/, but it is pointless and rather inconvenient. What we really want is to have the vendor source directly infoo/dist/contrib/foovendor/, like this:foo/dist%cd vendor/foo/dist/contrib/foo%svn move $(svn list) ../..%cd ../..%svn remove contrib%svn propdel -R svn:mergeinfo%svn commitNote that, the
propdelbit is necessary because starting with 1.5, Subversion will automatically addsvn:mergeinfoto any directory you copy or move. In this case, you will not need this information, since you are not going to merge anything from the tree you deleted.Note:
You may want to flatten the tags as well. The procedure is exactly the same. If you do this, put off the commit until the end.
Check the
disttree and perform any cleanup that is deemed to be necessary. You may want to disable keyword expansion, as it makes no sense on unmodified vendor code. In some cases, it can be even be harmful.%svn propdel svn:keywords -R .%svn commitBootstrapping of
svn:mergeinfoon the target directory (in the main tree) to the revision that corresponds to the last change was made to the vendor tree prior to importing new sources is also needed:%cd head/contrib/foo%svn merge --record-onlysvn_base/vendor/foo/dist@12345678.%svn commitwhere
svn_baseis the base directory of your SVN repository, e.g.svn+ssh://svn.FreeBSD.org/base.Importing New Sources
Prepare a full, clean tree of the vendor sources. With SVN, we can keep a full distribution in the vendor tree without bloating the main tree. Import everything but merge only what is needed.
Note that you will need to add any files that were added since the last vendor import, and remove any that were removed. To facilitate this, you should prepare sorted lists of the contents of the vendor tree and of the sources you are about to import:
%cd vendor/foo/dist%svn list -R | grep -v '/$' | sort > ../old%cd ../foo-9.9%find . -type f | cut -c 3- | sort > ../newWith these two files, the following command will list list removed files (files only in
old%comm -23 ../old../newWhile the command below will list added files (files only in
new%comm -13 ../old../newLet's put this together:
%cd vendor/foo/foo-9.9%tar cf - . | tar xf - -C ../dist%cd ../dist%comm -23 ../old../new| xargs svn remove%comm -13 ../old../new| xargs svn addWarning:
If there are new directories in the new distribution, the last command will fail. You will have to add the directories, and run it again. Conversely, if any directories were removed, you will have to remove them manually.
Check properties on any new files:
All text files should have
svn:eol-styleset tonative.All binary files should have
svn:mime-typeset toapplication/octet-stream, unless there is a more appropriate media type.Executable files should have
svn:executableset to*.There should be no other properties on any file in the tree.
Note:
You are ready to commit, but you should first check the output of
svn statandsvn diffto make sure everything is in order.Once you have committed the new vendor release, you should tag it for future reference. The best and quickest way is to do it directly in the repository:
%svn copysvn_base/vendor/foo/distsvn_base/vendor/foo/9.9To get the new tag, you can update your working copy of
vendor/.fooNote:
If you choose to do the copy in the checkout instead, do not forget to remove the generated
svn:mergeinfoas described above.Merging to -HEAD
After you have prepared your import, it is time to merge. Option
--accept=postponetells SVN not to handle merge conflicts yet, because they will be taken care of manually:%cd head/contrib/foo%svn update%svn merge --accept=postponesvn_base/vendor/foo/distResolve any conflicts, and make sure that any files that were added or removed in the vendor tree have been properly added or removed in the main tree. It is always a good idea to check differences against the vendor branch:
%svn diff --no-diff-deleted --old=svn_base/vendor/foo/dist --new=.The
--no-diff-deletedoption tells SVN not to check files that are in the vendor tree but not in the main tree.Note:
With SVN, there is no concept of on or off the vendor branch. If a file that previously had local modifications no longer does, just remove any left-over cruft, such as FreeBSD version tags, so it no longer shows up in diffs against the vendor tree.
If any changes are required for the world to build with the new sources, make them now — and test until you are satisfied that everything build and runs correctly.
Commit
Now, you are ready to commit. Make sure you get everything in one go. Ideally, you would have done all steps in a clean tree, in which case you can just commit from the top of that tree. That is the best way to avoid surprises. If you do it properly, the tree will move atomically from a consistent state with the old code to a consistent state with the new code.
It might occasionally be necessary to include an encumbered file in the FreeBSD source tree. For example, if a device requires a small piece of binary code to be loaded to it before the device will operate, and we do not have the source to that code, then the binary file is said to be encumbered. The following policies apply to including encumbered files in the FreeBSD source tree.
Any file which is interpreted or executed by the system CPU(s) and not in source format is encumbered.
Any file with a license more restrictive than BSD or GNU is encumbered.
A file which contains downloadable binary data for use by the hardware is not encumbered, unless (1) or (2) apply to it. It must be stored in an architecture neutral ASCII format (file2c or uuencoding is recommended).
Any encumbered file requires specific approval from the Core Team before it is added to the repository.
Encumbered files go in
src/contriborsrc/sys/contrib.The entire module should be kept together. There is no point in splitting it, unless there is code-sharing with non-encumbered code.
Object files are named
arch/filename.o.uu>Kernel files:
User-land files:
The Core team decides if the code should be part of
make world.The Release Engineering decides if it goes into the release.
If you are adding shared library support to a port or other piece of software that does not have one, the version numbers should follow these rules. Generally, the resulting numbers will have nothing to do with the release version of the software.
The three principles of shared library building are:
Start from
1.0If there is a change that is backwards compatible, bump minor number (note that ELF systems ignore the minor number)
If there is an incompatible change, bump major number
For instance, added functions and bugfixes result in the minor version number being bumped, while deleted functions, changed function call syntax, etc. will force the major version number to change.
Stick to version numbers of the form major.minor
(x.y).
Our a.out dynamic linker does not handle version numbers of the
form
x.y.z
well. Any version number after the y
(i.e. the third digit) is totally ignored when comparing shared
lib version numbers to decide which library to link with. Given
two shared libraries that differ only in the
“micro” revision, ld.so will
link with the higher one. That is, if you link with
libfoo.so.3.3.3, the linker only records
3.3 in the headers, and will link with
anything starting with
libfoo.so.3.(anything
>= 3).(highest
available).
Note:
ld.so will always use the highest
“minor” revision. For instance, it will use
libc.so.2.2 in preference to
libc.so.2.0, even if the program was
initially linked with libc.so.2.0.
In addition, our ELF dynamic linker does not handle minor
version numbers at all. However, one should still specify a
major and minor version number as our
Makefiles “do the right thing”
based on the type of system.
For non-port libraries, it is also our policy to change the
shared library version number only once between releases. In
addition, it is our policy to change the major shared library
version number only once between major OS releases (i.e. from
6.0 to 7.0). When you make a change to a system library that
requires the version number to be bumped, check the
Makefile's commit logs. It is the
responsibility of the committer to ensure that the first such
change since the release will result in the shared library
version number in the Makefile to be
updated, and any subsequent changes will not.
Regression tests are used to exercise a particular bit of the system to check that it works as expected, and to make sure that old bugs are not reintroduced.
The FreeBSD regression testing tools can be found in the FreeBSD
source tree in the directory src/tools/regression.
This section contains hints for doing proper micro-benchmarking on FreeBSD or of FreeBSD itself.
It is not possible to use all of the suggestions below every single time, but the more used, the better the benchmark's ability to test small differences will be.
Disable APM and any other kind of clock fiddling (ACPI ?).
Run in single user mode. E.g., cron(8), and other daemons only add noise. The sshd(8) daemon can also cause problems. If ssh access is required during testing either disable the SSHv1 key regeneration, or kill the parent
sshddaemon during the tests.Do not run ntpd(8).
If syslog(3) events are generated, run syslogd(8) with an empty
/etc/syslogd.conf, otherwise, do not run it.Minimize disk-I/O, avoid it entirely if possible.
Do not mount file systems that are not needed.
Mount
/,/usr, and any other file system as read-only if possible. This removes atime updates to disk (etc.) from the I/O picture.Reinitialize the read/write test file system with newfs(8) and populate it from a tar(1) or dump(8) file before every run. Unmount and mount it before starting the test. This results in a consistent file system layout. For a worldstone test this would apply to
/usr/obj(just reinitialize withnewfsand mount). To get 100% reproducibility, populate the file system from a dd(1) file (i.e.:dd if=myimage of=/dev/ad0s1h bs=1m)Use malloc backed or preloaded md(4) partitions.
Reboot between individual iterations of the test, this gives a more consistent state.
Remove all non-essential device drivers from the kernel. For instance if USB is not needed for the test, do not put USB in the kernel. Drivers which attach often have timeouts ticking away.
Unconfigure hardware that are not in use. Detach disks with atacontrol(8) and camcontrol(8) if the disks are not used for the test.
Do not configure the network unless it is being tested, or wait until after the test has been performed to ship the results off to another computer.
If the system must be connected to a public network, watch out for spikes of broadcast traffic. Even though it is hardly noticeable, it will take up CPU cycles. Multicast has similar caveats.
Put each file system on its own disk. This minimizes jitter from head-seek optimizations.
Minimize output to serial or VGA consoles. Running output into files gives less jitter. (Serial consoles easily become a bottleneck.) Do not touch keyboard while the test is running, even space or back-space shows up in the numbers.
Make sure the test is long enough, but not too long. If the test is too short, timestamping is a problem. If it is too long temperature changes and drift will affect the frequency of the quartz crystals in the computer. Rule of thumb: more than a minute, less than an hour.
Try to keep the temperature as stable as possible around the machine. This affects both quartz crystals and disk drive algorithms. To get real stable clock, consider stabilized clock injection. E.g., get a OCXO + PLL, inject output into clock circuits instead of motherboard xtal. Contact Poul-Henning Kamp
<[email protected]>for more information about this.Run the test at least 3 times but it is better to run more than 20 times both for “before” and “after” code. Try to interleave if possible (i.e.: do not run 20 times before then 20 times after), this makes it possible to spot environmental effects. Do not interleave 1:1, but 3:3, this makes it possible to spot interaction effects.
A good pattern is:
bababa{bbbaaa}*. This gives hint after the first 1+1 runs (so it is possible to stop the test if it goes entirely the wrong way), a standard deviation after the first 3+3 (gives a good indication if it is going to be worth a long run) and trending and interaction numbers later on.Use ministat(1) to see if the numbers are significant. Consider buying “Cartoon guide to statistics” ISBN: 0062731025, highly recommended, if you have forgotten or never learned about standard deviation and Student's T.
Do not use background fsck(8) unless the test is a benchmark of background
fsck. Also, disablebackground_fsckin/etc/rc.confunless the benchmark is not started at least 60+“fsckruntime” seconds after the boot, as rc(8) wakes up and checks iffsckneeds to run on any file systems when backgroundfsckis enabled. Likewise, make sure there are no snapshots lying around unless the benchmark is a test with snapshots.If the benchmark show unexpected bad performance, check for things like high interrupt volume from an unexpected source. Some versions of ACPI have been reported to “misbehave” and generate excess interrupts. To help diagnose odd test results, take a few snapshots of
vmstat -iand look for anything unusual.Make sure to be careful about optimization parameters for kernel and userspace, likewise debugging. It is easy to let something slip through and realize later the test was not comparing the same thing.
Do not ever benchmark with the
WITNESSandINVARIANTSkernel options enabled unless the test is interested to benchmarking those features.WITNESScan cause 400%+ drops in performance. Likewise, userspace malloc(3) parameters default differently in -CURRENT from the way they ship in production releases.
The source Tinderbox consists of:
A build script,
tinderbox, that automates checking out a specific version of the FreeBSD source tree and building it.A supervisor script,
tbmaster, that monitors individual Tinderbox instances, logs their output, and emails failure notices.A CGI script named
index.cgithat reads a set of tbmaster logs and presents an easy-to-read HTML summary of them.A set of build servers that continually test the tip of the most important FreeBSD code branches.
A webserver that keeps a complete set of Tinderbox logs and displays an up-to-date summary.
The scripts are maintained and were developed by Dag-Erling C. Smørgrav <[email protected]>,
and are now written in Perl, a move on from their original
incarnation as shell scripts. All scripts and configuration
files are kept in /projects/tinderbox/.
For more information about the tinderbox and tbmaster scripts at this stage, see their respective man pages: tinderbox(1) and tbmaster(1).
The index.cgi script generates the
HTML summary of tinderbox and tbmaster
logs. Although originally intended to be used as a
CGI script, as indicated by its name, this
script can also be run from the command line or from a
cron(8) job, in which case it will look for logs in the
directory where the script is located. It will automatically
detect context, generating HTTP headers
when it is run as a CGI script. It
conforms to XHTML standards and is styled
using CSS.
The script starts in the main() block
by attempting to verify that it is running on the official
Tinderbox website. If it is not, a page indicating it is not
an official website is produced, and a URL
to the official site is provided.
Next, it scans the log directory to get an inventory of configurations, branches and architectures for which log files exist, to avoid hard-coding a list into the script and potentially ending up with blank rows or columns. This information is derived from the names of the log files matching the following pattern:
tinderbox-$config-$branch-$arch-$machine.{brief,full}The configurations used on the official Tinderbox build
servers are named for the branches they build. For example,
the releng_8 configuration is used to build
RELENG_8 as well as all still-supported
release branches.
Once all of this startup procedure has been successfully
completed, do_config() is called for each
configuration.
The do_config() function generates
HTML for a single Tinderbox
configuration.
It works by first generating a header row, then iterating over each branch build with the specified configuration, producing a single row of results for each in the following manner:
For each item:
For each machine within that architecture:
If a brief log file exists, then:
Call
success()to determine the outcome of the build.Output the modification size.
Output the size of the brief log file with a link to the log file itself.
If a full log file also exists, then:
Output the size of the full log file with a link to the log file itself.
Otherwise:
No output.
The success() function mentioned
above scans a brief log file for the string “tinderbox
run completed” in order to determine whether the
build was successful.
Configurations and branches are sorted according to their branch rank. This is computed as follows:
HEADandCURRENThave rank 9999.RELENG_has rankxxx99.RELENG_has rankx_yxxyy.
This means that HEAD always ranks
highest, and RELENG branches are ranked in
numerical order, with each STABLE branch
ranking higher than the release branches forked off of it.
For instance, for FreeBSD 8, the order from highest to
lowest would be:
RELENG_8(branch rank 899).RELENG_8_3(branch rank 803).RELENG_8_2(branch rank 802).RELENG_8_1(branch rank 801).RELENG_8_0(branch rank 800).
The colors that Tinderbox uses for each cell in the table are defined by CSS. Successful builds are displayed with green text; unsuccessful builds are displayed with red text. The color fades as time passes since the corresponding build, with every half an hour bringing the color closer to grey.
The official Tinderbox build servers are hosted by Sentex Data Communications, who also host the FreeBSD Netperf Cluster.
Three build servers currently exist:
freebsd-current.sentex.ca builds:
HEADfor amd64, arm, i386, i386/pc98, ia64, mips, powerpc, powerpc64, and sparc64.RELENG_9and supported 9.Xbranches for amd64, arm, i386, i386/pc98, ia64, mips, powerpc, powerpc64, and sparc64.
freebsd-stable.sentex.ca builds:
RELENG_8and supported 8.Xbranches for amd64, i386, i386/pc98, ia64, mips, powerpc and sparc64.
freebsd-legacy.sentex.ca builds:
RELENG_7and supported 7.Xbranches for amd64, i386, i386/pc98, ia64, powerpc, and sparc64.
Summaries and logs from the official build servers are
available online at http://tinderbox.FreeBSD.org,
hosted by Dag-Erling C. Smørgrav <[email protected]> and set up as follows:
BSD sockets take interprocess communications to a new level. It is no longer necessary for the communicating processes to run on the same machine. They still can, but they do not have to.
Not only do these processes not have to run on the same machine, they do not have to run under the same operating system. Thanks to BSD sockets, your FreeBSD software can smoothly cooperate with a program running on a Macintosh®, another one running on a Sun™ workstation, yet another one running under Windows® 2000, all connected with an Ethernet-based local area network.
But your software can equally well cooperate with processes running in another building, or on another continent, inside a submarine, or a space shuttle.
It can also cooperate with processes that are not part of a computer (at least not in the strict sense of the word), but of such devices as printers, digital cameras, medical equipment. Just about anything capable of digital communications.
We have already hinted on the diversity of networking. Many different systems have to talk to each other. And they have to speak the same language. They also have to understand the same language the same way.
People often think that body language is universal. But it is not. Back in my early teens, my father took me to Bulgaria. We were sitting at a table in a park in Sofia, when a vendor approached us trying to sell us some roasted almonds.
I had not learned much Bulgarian by then, so, instead of saying no, I shook my head from side to side, the “universal” body language for no. The vendor quickly started serving us some almonds.
I then remembered I had been told that in Bulgaria shaking your head sideways meant yes. Quickly, I started nodding my head up and down. The vendor noticed, took his almonds, and walked away. To an uninformed observer, I did not change the body language: I continued using the language of shaking and nodding my head. What changed was the meaning of the body language. At first, the vendor and I interpreted the same language as having completely different meaning. I had to adjust my own interpretation of that language so the vendor would understand.
It is the same with computers: The same symbols may have different, even outright opposite meaning. Therefore, for two computers to understand each other, they must not only agree on the same language, but on the same interpretation of the language.
While various programming languages tend to have complex syntax and use a number of multi-letter reserved words (which makes them easy for the human programmer to understand), the languages of data communications tend to be very terse. Instead of multi-byte words, they often use individual bits. There is a very convincing reason for it: While data travels inside your computer at speeds approaching the speed of light, it often travels considerably slower between two computers.
Because the languages used in data communications are so terse, we usually refer to them as protocols rather than languages.
As data travels from one computer to another, it always uses more than one protocol. These protocols are layered. The data can be compared to the inside of an onion: You have to peel off several layers of “skin” to get to the data. This is best illustrated with a picture:
In this example, we are trying to get an image from a web page we are connected to via an Ethernet.
The image consists of raw data, which is simply a sequence of RGB values that our software can process, i.e., convert into an image and display on our monitor.
Alas, our software has no way of knowing how the raw data is organized: Is it a sequence of RGB values, or a sequence of grayscale intensities, or perhaps of CMYK encoded colors? Is the data represented by 8-bit quanta, or are they 16 bits in size, or perhaps 4 bits? How many rows and columns does the image consist of? Should certain pixels be transparent?
I think you get the picture...
To inform our software how to handle the raw data, it is encoded as a PNG file. It could be a GIF, or a JPEG, but it is a PNG.
And PNG is a protocol.
At this point, I can hear some of you yelling, “No, it is not! It is a file format!”
Well, of course it is a file format. But from the perspective of data communications, a file format is a protocol: The file structure is a language, a terse one at that, communicating to our process how the data is organized. Ergo, it is a protocol.
Alas, if all we received was the PNG file, our software would be facing a serious problem: How is it supposed to know the data is representing an image, as opposed to some text, or perhaps a sound, or what not? Secondly, how is it supposed to know the image is in the PNG format as opposed to GIF, or JPEG, or some other image format?
To obtain that information, we are using another protocol: HTTP. This protocol can tell us exactly that the data represents an image, and that it uses the PNG protocol. It can also tell us some other things, but let us stay focused on protocol layers here.
So, now we have some data wrapped in the PNG protocol, wrapped in the HTTP protocol. How did we get it from the server?
By using TCP/IP over Ethernet, that is how. Indeed, that is three more protocols. Instead of continuing inside out, I am now going to talk about Ethernet, simply because it is easier to explain the rest that way.
Ethernet is an interesting system of connecting computers in a local area network (LAN). Each computer has a network interface card (NIC), which has a unique 48-bit ID called its address. No two Ethernet NICs in the world have the same address.
These NICs are all connected with each other. Whenever one computer wants to communicate with another in the same Ethernet LAN, it sends a message over the network. Every NIC sees the message. But as part of the Ethernet protocol, the data contains the address of the destination NIC (among other things). So, only one of all the network interface cards will pay attention to it, the rest will ignore it.
But not all computers are connected to the same network. Just because we have received the data over our Ethernet does not mean it originated in our own local area network. It could have come to us from some other network (which may not even be Ethernet based) connected with our own network via the Internet.
All data is transferred over the Internet using IP, which stands for Internet Protocol. Its basic role is to let us know where in the world the data has arrived from, and where it is supposed to go to. It does not guarantee we will receive the data, only that we will know where it came from if we do receive it.
Even if we do receive the data, IP does not guarantee we will receive various chunks of data in the same order the other computer has sent it to us. So, we can receive the center of our image before we receive the upper left corner and after the lower right, for example.
It is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) that asks the sender to resend any lost data and that places it all into the proper order.
All in all, it took five different protocols for one computer to communicate to another what an image looks like. We received the data wrapped into the PNG protocol, which was wrapped into the HTTP protocol, which was wrapped into the TCP protocol, which was wrapped into the IP protocol, which was wrapped into the Ethernet protocol.
Oh, and by the way, there probably were several other protocols involved somewhere on the way. For example, if our LAN was connected to the Internet through a dial-up call, it used the PPP protocol over the modem which used one (or several) of the various modem protocols, et cetera, et cetera, et cetera...
As a developer you should be asking by now, “How am I supposed to handle it all?”
Luckily for you, you are not supposed to handle it all. You are supposed to handle some of it, but not all of it. Specifically, you need not worry about the physical connection (in our case Ethernet and possibly PPP, etc). Nor do you need to handle the Internet Protocol, or the Transmission Control Protocol.
In other words, you do not have to do anything to receive the data from the other computer. Well, you do have to ask for it, but that is almost as simple as opening a file.
Once you have received the data, it is up to you to figure out what to do with it. In our case, you would need to understand the HTTP protocol and the PNG file structure.
To use an analogy, all the internetworking protocols become a gray area: Not so much because we do not understand how it works, but because we are no longer concerned about it. The sockets interface takes care of this gray area for us:
We only need to understand any protocols that tell us how to interpret the data, not how to receive it from another process, nor how to send it to another process.
BSD sockets are built on the basic UNIX® model: Everything is a file. In our example, then, sockets would let us receive an HTTP file, so to speak. It would then be up to us to extract the PNG file from it.
Because of the complexity of internetworking, we cannot just
use the open system call, or
the open() C function. Instead, we need to
take several steps to “opening” a socket.
Once we do, however, we can start treating the
socket the same way we treat any
file descriptor: We can
read from it, write to
it, pipe it, and, eventually,
close it.
While FreeBSD offers different functions to work with sockets, we only need four to “open” a socket. And in some cases we only need two.
Typically, one of the ends of a socket-based data communication is a server, the other is a client.
The one function used by both, clients and servers, is socket(2). It is declared this way:
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
The return value is of the same type as that of
open, an integer. FreeBSD allocates
its value from the same pool as that of file handles.
That is what allows sockets to be treated the same way as
files.
The domain argument tells the
system what protocol family you want
it to use. Many of them exist, some are vendor specific,
others are very common. They are declared in
sys/socket.h.
Use PF_INET for
UDP, TCP and other
Internet protocols (IPv4).
Five values are defined for the
type argument, again, in
sys/socket.h. All of them start with
“SOCK_”. The most
common one is SOCK_STREAM, which
tells the system you are asking for a reliable
stream delivery service (which is
TCP when used with
PF_INET).
If you asked for SOCK_DGRAM, you
would be requesting a connectionless datagram
delivery service (in our case,
UDP).
If you wanted to be in charge of the low-level
protocols (such as IP), or even network
interfaces (e.g., the Ethernet), you would need to specify
SOCK_RAW.
Finally, the protocol argument
depends on the previous two arguments, and is not always
meaningful. In that case, use 0 for
its value.
The Unconnected Socket:
Nowhere, in the socket function
have we specified to what other system we should be
connected. Our newly created socket remains
unconnected.
This is on purpose: To use a telephone analogy, we have just attached a modem to the phone line. We have neither told the modem to make a call, nor to answer if the phone rings.
Various functions of the sockets family expect the
address of (or pointer to, to use C terminology) a small
area of the memory. The various C declarations in the
sys/socket.h refer to it as
struct sockaddr. This structure is
declared in the same file:
/*
* Structure used by kernel to store most
* addresses.
*/
struct sockaddr {
unsigned char sa_len; /* total length */
sa_family_t sa_family; /* address family */
char sa_data[14]; /* actually longer; address value */
};
#define SOCK_MAXADDRLEN 255 /* longest possible addresses */
Please note the vagueness with
which the sa_data field is declared,
just as an array of 14 bytes, with
the comment hinting there can be more than
14 of them.
This vagueness is quite deliberate. Sockets is a very powerful interface. While most people perhaps think of it as nothing more than the Internet interface—and most applications probably use it for that nowadays—sockets can be used for just about any kind of interprocess communications, of which the Internet (or, more precisely, IP) is only one.
The sys/socket.h refers to the
various types of protocols sockets will handle as
address families, and lists them
right before the definition of
sockaddr:
/* * Address families. */ #define AF_UNSPEC 0 /* unspecified */ #define AF_LOCAL 1 /* local to host (pipes, portals) */ #define AF_UNIX AF_LOCAL /* backward compatibility */ #define AF_INET 2 /* internetwork: UDP, TCP, etc. */ #define AF_IMPLINK 3 /* arpanet imp addresses */ #define AF_PUP 4 /* pup protocols: e.g. BSP */ #define AF_CHAOS 5 /* mit CHAOS protocols */ #define AF_NS 6 /* XEROX NS protocols */ #define AF_ISO 7 /* ISO protocols */ #define AF_OSI AF_ISO #define AF_ECMA 8 /* European computer manufacturers */ #define AF_DATAKIT 9 /* datakit protocols */ #define AF_CCITT 10 /* CCITT protocols, X.25 etc */ #define AF_SNA 11 /* IBM SNA */ #define AF_DECnet 12 /* DECnet */ #define AF_DLI 13 /* DEC Direct data link interface */ #define AF_LAT 14 /* LAT */ #define AF_HYLINK 15 /* NSC Hyperchannel */ #define AF_APPLETALK 16 /* Apple Talk */ #define AF_ROUTE 17 /* Internal Routing Protocol */ #define AF_LINK 18 /* Link layer interface */ #define pseudo_AF_XTP 19 /* eXpress Transfer Protocol (no AF) */ #define AF_COIP 20 /* connection-oriented IP, aka ST II */ #define AF_CNT 21 /* Computer Network Technology */ #define pseudo_AF_RTIP 22 /* Help Identify RTIP packets */ #define AF_IPX 23 /* Novell Internet Protocol */ #define AF_SIP 24 /* Simple Internet Protocol */ #define pseudo_AF_PIP 25 /* Help Identify PIP packets */ #define AF_ISDN 26 /* Integrated Services Digital Network*/ #define AF_E164 AF_ISDN /* CCITT E.164 recommendation */ #define pseudo_AF_KEY 27 /* Internal key-management function */ #define AF_INET6 28 /* IPv6 */ #define AF_NATM 29 /* native ATM access */ #define AF_ATM 30 /* ATM */ #define pseudo_AF_HDRCMPLT 31 /* Used by BPF to not rewrite headers * in interface output routine */ #define AF_NETGRAPH 32 /* Netgraph sockets */ #define AF_SLOW 33 /* 802.3ad slow protocol */ #define AF_SCLUSTER 34 /* Sitara cluster protocol */ #define AF_ARP 35 #define AF_BLUETOOTH 36 /* Bluetooth sockets */ #define AF_MAX 37
The one used for IP is
AF_INET. It is a symbol for the constant
2.
It is the address family listed
in the sa_family field of
sockaddr that decides how exactly the
vaguely named bytes of sa_data will be
used.
Specifically, whenever the address
family is AF_INET, we can use
struct sockaddr_in found in
netinet/in.h, wherever
sockaddr is expected:
/*
* Socket address, internet style.
*/
struct sockaddr_in {
uint8_t sin_len;
sa_family_t sin_family;
in_port_t sin_port;
struct in_addr sin_addr;
char sin_zero[8];
};
We can visualize its organization this way:
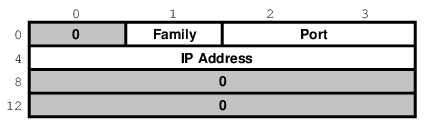
The three important fields are
sin_family, which is byte 1 of the
structure, sin_port, a 16-bit value
found in bytes 2 and 3, and sin_addr, a
32-bit integer representation of the IP
address, stored in bytes 4-7.
Now, let us try to fill it out. Let us assume we are
trying to write a client for the
daytime protocol, which simply states
that its server will write a text string representing the
current date and time to port 13. We want to use
TCP/IP, so we need to specify
AF_INET in the address family
field. AF_INET is defined as
2. Let us use the
IP address of 192.43.244.18, which is the time
server of US federal government (time.nist.gov).
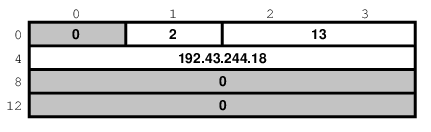
By the way the sin_addr field is
declared as being of the struct in_addr
type, which is defined in
netinet/in.h:
/*
* Internet address (a structure for historical reasons)
*/
struct in_addr {
in_addr_t s_addr;
};
In addition, in_addr_t is a 32-bit
integer.
The 192.43.244.18 is
just a convenient notation of expressing a 32-bit integer
by listing all of its 8-bit bytes, starting with the
most significant one.
So far, we have viewed sockaddr as
an abstraction. Our computer does not store
short integers as a single 16-bit
entity, but as a sequence of 2 bytes. Similarly, it stores
32-bit integers as a sequence of 4 bytes.
Suppose we coded something like this:
sa.sin_family = AF_INET; sa.sin_port = 13; sa.sin_addr.s_addr = (((((192 << 8) | 43) << 8) | 244) << 8) | 18;
What would the result look like?
Well, that depends, of course. On a Pentium®, or other x86, based computer, it would look like this:
On a different system, it might look like this:
And on a PDP it might look different yet. But the above two are the most common ways in use today.
Ordinarily, wanting to write portable code, programmers pretend that these differences do not exist. And they get away with it (except when they code in assembly language). Alas, you cannot get away with it that easily when coding for sockets.
Why?
Because when communicating with another computer, you usually do not know whether it stores data most significant byte (MSB) or least significant byte (LSB) first.
You might be wondering, “So, will sockets not handle it for me?”
It will not.
While that answer may surprise you at first, remember
that the general sockets interface only understands the
sa_len and sa_family
fields of the sockaddr structure. You
do not have to worry about the byte order there (of
course, on FreeBSD sa_family is only 1
byte anyway, but many other UNIX® systems do not have
sa_len and use 2 bytes for
sa_family, and expect the data in
whatever order is native to the computer).
But the rest of the data is just
sa_data[14] as far as sockets
goes. Depending on the address
family, sockets just forwards that data to its
destination.
Indeed, when we enter a port number, it is because we want the other computer to know what service we are asking for. And, when we are the server, we read the port number so we know what service the other computer is expecting from us. Either way, sockets only has to forward the port number as data. It does not interpret it in any way.
Similarly, we enter the IP address to tell everyone on the way where to send our data to. Sockets, again, only forwards it as data.
That is why, we (the programmers, not the sockets) have to distinguish between the byte order used by our computer and a conventional byte order to send the data in to the other computer.
We will call the byte order our computer uses the host byte order, or just the host order.
There is a convention of sending the multi-byte data over IP MSB first. This, we will refer to as the network byte order, or simply the network order.
Now, if we compiled the above code for an Intel based computer, our host byte order would produce:

But the network byte order requires that we store the data MSB first:

Unfortunately, our host order is the exact opposite of the network order.
We have several ways of dealing with it. One would be to reverse the values in our code:
sa.sin_family = AF_INET; sa.sin_port = 13 << 8; sa.sin_addr.s_addr = (((((18 << 8) | 244) << 8) | 43) << 8) | 192;
This will trick our compiler into storing the data in the network byte order. In some cases, this is exactly the way to do it (e.g., when programming in assembly language). In most cases, however, it can cause a problem.
Suppose, you wrote a sockets-based program in C. You know it is going to run on a Pentium®, so you enter all your constants in reverse and force them to the network byte order. It works well.
Then, some day, your trusted old Pentium® becomes a rusty old Pentium®. You replace it with a system whose host order is the same as the network order. You need to recompile all your software. All of your software continues to perform well, except the one program you wrote.
You have since forgotten that you had forced all of your constants to the opposite of the host order. You spend some quality time tearing out your hair, calling the names of all gods you ever heard of (and some you made up), hitting your monitor with a nerf bat, and performing all the other traditional ceremonies of trying to figure out why something that has worked so well is suddenly not working at all.
Eventually, you figure it out, say a couple of swear words, and start rewriting your code.
Luckily, you are not the first one to face the
problem. Someone else has created the htons(3) and
htonl(3) C functions to convert a
short and long
respectively from the host byte
order to the network byte
order, and the ntohs(3) and ntohl(3)
C functions to go the other way.
On MSB-first systems these functions do nothing. On LSB-first systems they convert values to the proper order.
So, regardless of what system your software is compiled on, your data will end up in the correct order if you use these functions.
Typically, the client initiates the connection to the server. The client knows which server it is about to call: It knows its IP address, and it knows the port the server resides at. It is akin to you picking up the phone and dialing the number (the address), then, after someone answers, asking for the person in charge of wingdings (the port).
Once a client has created a socket, it needs to connect it to a specific port on a remote system. It uses connect(2):
int connect(int s, const struct sockaddr *name, socklen_t namelen);
The s argument is the socket, i.e.,
the value returned by the socket
function. The name is a pointer to
sockaddr, the structure we have talked
about extensively. Finally, namelen
informs the system how many bytes are in our
sockaddr structure.
If connect is successful, it
returns 0. Otherwise it returns
-1 and stores the error code in
errno.
There are many reasons why
connect may fail. For example, with
an attempt to an Internet connection, the
IP address may not exist, or it may be
down, or just too busy, or it may not have a server
listening at the specified port. Or it may outright
refuse any request for specific
code.
We now know enough to write a very simple client, one
that will get current time from 192.43.244.18 and print it to
stdout.
/*
* daytime.c
*
* Programmed by G. Adam Stanislav
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
int main() {
register int s;
register int bytes;
struct sockaddr_in sa;
char buffer[BUFSIZ+1];
if ((s = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) {
perror("socket");
return 1;
}
bzero(&sa, sizeof sa);
sa.sin_family = AF_INET;
sa.sin_port = htons(13);
sa.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl((((((192 << 8) | 43) << 8) | 244) << 8) | 18);
if (connect(s, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, sizeof sa) < 0) {
perror("connect");
close(s);
return 2;
}
while ((bytes = read(s, buffer, BUFSIZ)) > 0)
write(1, buffer, bytes);
close(s);
return 0;
}
Go ahead, enter it in your editor, save it as
daytime.c, then compile and run
it:
%cc -O3 -o daytime daytime.c%./daytime52079 01-06-19 02:29:25 50 0 1 543.9 UTC(NIST) *%
In this case, the date was June 19, 2001, the time was 02:29:25 UTC. Naturally, your results will vary.
The typical server does not initiate the connection. Instead, it waits for a client to call it and request services. It does not know when the client will call, nor how many clients will call. It may be just sitting there, waiting patiently, one moment, The next moment, it can find itself swamped with requests from a number of clients, all calling in at the same time.
The sockets interface offers three basic functions to handle this.
Ports are like extensions to a phone line: After you dial a number, you dial the extension to get to a specific person or department.
There are 65535 IP ports, but a server usually processes requests that come in on only one of them. It is like telling the phone room operator that we are now at work and available to answer the phone at a specific extension. We use bind(2) to tell sockets which port we want to serve.
int bind(int s, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
Beside specifying the port in addr,
the server may include its IP
address. However, it can just use the symbolic constant
INADDR_ANY to indicate it will serve all
requests to the specified port regardless of what its
IP address is. This symbol, along with
several similar ones, is declared in
netinet/in.h
#define INADDR_ANY (u_int32_t)0x00000000
Suppose we were writing a server for the
daytime protocol over
TCP/IP. Recall that
it uses port 13. Our sockaddr_in
structure would look like this:
To continue our office phone analogy, after you have told the phone central operator what extension you will be at, you now walk into your office, and make sure your own phone is plugged in and the ringer is turned on. Plus, you make sure your call waiting is activated, so you can hear the phone ring even while you are talking to someone.
The server ensures all of that with the listen(2) function.
int listen(int s, int backlog);
In here, the backlog variable tells
sockets how many incoming requests to accept while you are
busy processing the last request. In other words, it
determines the maximum size of the queue of pending
connections.
After you hear the phone ringing, you accept the call by answering the call. You have now established a connection with your client. This connection remains active until either you or your client hang up.
The server accepts the connection by using the accept(2) function.
int accept(int s, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
Note that this time addrlen is a
pointer. This is necessary because in this case it is the
socket that fills out addr, the
sockaddr_in structure.
The return value is an integer. Indeed, the
accept returns a new
socket. You will use this new socket to
communicate with the client.
What happens to the old socket? It continues to listen
for more requests (remember the backlog
variable we passed to listen?) until
we close it.
Now, the new socket is meant only for
communications. It is fully connected. We cannot pass it
to listen again, trying to accept
additional connections.
Our first server will be somewhat more complex than our first client was: Not only do we have more sockets functions to use, but we need to write it as a daemon.
This is best achieved by creating a child process after binding the port. The main process then exits and returns control to the shell (or whatever program invoked it).
The child calls listen, then
starts an endless loop, which accepts a connection, serves
it, and eventually closes its socket.
/*
* daytimed - a port 13 server
*
* Programmed by G. Adam Stanislav
* June 19, 2001
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define BACKLOG 4
int main() {
register int s, c;
int b;
struct sockaddr_in sa;
time_t t;
struct tm *tm;
FILE *client;
if ((s = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) {
perror("socket");
return 1;
}
bzero(&sa, sizeof sa);
sa.sin_family = AF_INET;
sa.sin_port = htons(13);
if (INADDR_ANY)
sa.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
if (bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, sizeof sa) < 0) {
perror("bind");
return 2;
}
switch (fork()) {
case -1:
perror("fork");
return 3;
break;
default:
close(s);
return 0;
break;
case 0:
break;
}
listen(s, BACKLOG);
for (;;) {
b = sizeof sa;
if ((c = accept(s, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, &b)) < 0) {
perror("daytimed accept");
return 4;
}
if ((client = fdopen(c, "w")) == NULL) {
perror("daytimed fdopen");
return 5;
}
if ((t = time(NULL)) < 0) {
perror("daytimed time");
return 6;
}
tm = gmtime(&t);
fprintf(client, "%.4i-%.2i-%.2iT%.2i:%.2i:%.2iZ\n",
tm->tm_year + 1900,
tm->tm_mon + 1,
tm->tm_mday,
tm->tm_hour,
tm->tm_min,
tm->tm_sec);
fclose(client);
}
}
We start by creating a socket. Then we fill out the
sockaddr_in structure in
sa. Note the conditional use of
INADDR_ANY:
if (INADDR_ANY)
sa.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
Its value is 0. Since we have
just used bzero on the entire
structure, it would be redundant to set it to
0 again. But if we port our code to
some other system where INADDR_ANY is
perhaps not a zero, we need to assign it to
sa.sin_addr.s_addr. Most modern C
compilers are clever enough to notice that
INADDR_ANY is a constant. As long as it
is a zero, they will optimize the entire conditional
statement out of the code.
After we have called bind
successfully, we are ready to become a
daemon: We use
fork to create a child process. In
both, the parent and the child, the s
variable is our socket. The parent process will not need
it, so it calls close, then it
returns 0 to inform its own parent it
had terminated successfully.
Meanwhile, the child process continues working in the
background. It calls listen and sets
its backlog to 4. It does not need a
large value here because daytime is
not a protocol many clients request all the time, and
because it can process each request instantly anyway.
Finally, the daemon starts an endless loop, which performs the following steps:
Call
accept. It waits here until a client contacts it. At that point, it receives a new socket,c, which it can use to communicate with this particular client.It uses the C function
fdopento turn the socket from a low-level file descriptor to a C-styleFILEpointer. This will allow the use offprintflater on.It checks the time, and prints it in the ISO 8601 format to the
client“file”. It then usesfcloseto close the file. That will automatically close the socket as well.
We can generalize this, and use it as a model for many other servers:
This flowchart is good for sequential servers, i.e., servers that can serve one client at a time, just as we were able to with our daytime server. This is only possible whenever there is no real “conversation” going on between the client and the server: As soon as the server detects a connection to the client, it sends out some data and closes the connection. The entire operation may take nanoseconds, and it is finished.
The advantage of this flowchart is that, except for
the brief moment after the parent
forks and before it exits, there is
always only one process active: Our
server does not take up much memory and other system
resources.
Note that we have added initialize
daemon in our flowchart. We did not need to
initialize our own daemon, but this is a good place in the
flow of the program to set up any
signal handlers, open any files we
may need, etc.
Just about everything in the flow chart can be used literally on many different servers. The serve entry is the exception. We think of it as a “black box”, i.e., something you design specifically for your own server, and just “plug it into the rest.”
Not all protocols are that simple. Many receive a request from the client, reply to it, then receive another request from the same client. Because of that, they do not know in advance how long they will be serving the client. Such servers usually start a new process for each client. While the new process is serving its client, the daemon can continue listening for more connections.
Now, go ahead, save the above source code as
daytimed.c (it is customary to end
the names of daemons with the letter
d). After you have compiled it, try
running it:
%./daytimedbind: Permission denied%
What happened here? As you will recall, the daytime protocol uses port 13. But all ports below 1024 are reserved to the superuser (otherwise, anyone could start a daemon pretending to serve a commonly used port, while causing a security breach).
Try again, this time as the superuser:
#./daytimed#
What... Nothing? Let us try again:
#./daytimedbind: Address already in use#
Every port can only be bound by one program at a time. Our first attempt was indeed successful: It started the child daemon and returned quietly. It is still running and will continue to run until you either kill it, or any of its system calls fail, or you reboot the system.
Fine, we know it is running in the background. But is it working? How do we know it is a proper daytime server? Simple:
%telnet localhost 13Trying ::1... telnet: connect to address ::1: Connection refused Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. 2001-06-19T21:04:42Z Connection closed by foreign host.%
telnet tried the new IPv6, and failed. It retried with IPv4 and succeeded. The daemon works.
If you have access to another UNIX® system via telnet, you can use it to test accessing the server remotely. My computer does not have a static IP address, so this is what I did:
%whowhizkid ttyp0 Jun 19 16:59 (216.127.220.143) xxx ttyp1 Jun 19 16:06 (xx.xx.xx.xx)%telnet 216.127.220.143 13Trying 216.127.220.143... Connected to r47.bfm.org. Escape character is '^]'. 2001-06-19T21:31:11Z Connection closed by foreign host.%
Again, it worked. Will it work using the domain name?
%telnet r47.bfm.org 13Trying 216.127.220.143... Connected to r47.bfm.org. Escape character is '^]'. 2001-06-19T21:31:40Z Connection closed by foreign host.%
By the way, telnet prints
the Connection closed by foreign host
message after our daemon has closed the socket. This shows
us that, indeed, using
fclose(client); in our code works as
advertised.
FreeBSD C library contains many helper functions for sockets
programming. For example, in our sample client we hard coded
the time.nist.gov
IP address. But we do not always know the
IP address. Even if we do, our software is
more flexible if it allows the user to enter the
IP address, or even the domain name.
While there is no way to pass the domain name directly to
any of the sockets functions, the FreeBSD C library comes with
the gethostbyname(3) and gethostbyname2(3) functions,
declared in netdb.h.
struct hostent * gethostbyname(const char *name); struct hostent * gethostbyname2(const char *name, int af);
Both return a pointer to the hostent
structure, with much information about the domain. For our
purposes, the h_addr_list[0] field of the
structure points at h_length bytes of the
correct address, already stored in the network byte
order.
This allows us to create a much more flexible—and much more useful—version of our daytime program:
/*
* daytime.c
*
* Programmed by G. Adam Stanislav
* 19 June 2001
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
register int s;
register int bytes;
struct sockaddr_in sa;
struct hostent *he;
char buf[BUFSIZ+1];
char *host;
if ((s = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0) {
perror("socket");
return 1;
}
bzero(&sa, sizeof sa);
sa.sin_family = AF_INET;
sa.sin_port = htons(13);
host = (argc > 1) ? (char *)argv[1] : "time.nist.gov";
if ((he = gethostbyname(host)) == NULL) {
herror(host);
return 2;
}
bcopy(he->h_addr_list[0],&sa.sin_addr, he->h_length);
if (connect(s, (struct sockaddr *)&sa, sizeof sa) < 0) {
perror("connect");
return 3;
}
while ((bytes = read(s, buf, BUFSIZ)) > 0)
write(1, buf, bytes);
close(s);
return 0;
}
We now can type a domain name (or an IP
address, it works both ways) on the command line, and the
program will try to connect to its
daytime server. Otherwise, it will still
default to time.nist.gov. However, even in
this case we will use gethostbyname
rather than hard coding 192.43.244.18. That way, even if its
IP address changes in the future, we will
still find it.
Since it takes virtually no time to get the time from your
local server, you could run daytime
twice in a row: First to get the time from time.nist.gov, the second time from
your own system. You can then compare the results and see how
exact your system clock is:
%daytime ; daytime localhost52080 01-06-20 04:02:33 50 0 0 390.2 UTC(NIST) * 2001-06-20T04:02:35Z%
As you can see, my system was two seconds ahead of the NIST time.
Sometimes you may not be sure what port a certain service
uses. The getservbyname(3) function, also declared in
netdb.h comes in very handy in those
cases:
struct servent * getservbyname(const char *name, const char *proto);
The servent structure contains the
s_port, which contains the proper port,
already in network byte order.
Had we not known the correct port for the daytime service, we could have found it this way:
struct servent *se;
...
if ((se = getservbyname("daytime", "tcp")) == NULL {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot determine which port to use.\n");
return 7;
}
sa.sin_port = se->s_port;
You usually do know the port. But if you are developing a
new protocol, you may be testing it on an unofficial
port. Some day, you will register the protocol and its port
(if nowhere else, at least in your
/etc/services, which is where
getservbyname looks). Instead of
returning an error in the above code, you just use the
temporary port number. Once you have listed the protocol in
/etc/services, your software will find
its port without you having to rewrite the code.
Unlike a sequential server, a concurrent server has to be able to serve more than one client at a time. For example, a chat server may be serving a specific client for hours—it cannot wait till it stops serving a client before it serves the next one.
This requires a significant change in our flowchart:
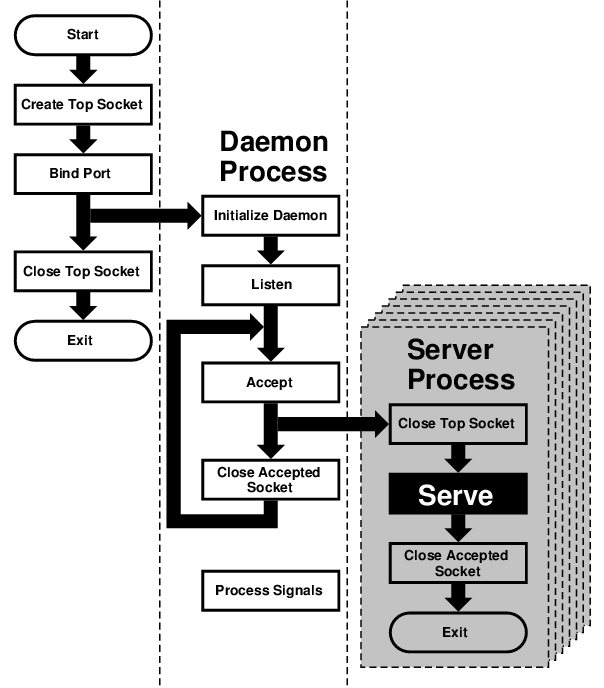
We moved the serve from the
daemon process to its own server
process. However, because each child process inherits
all open files (and a socket is treated just like a file), the
new process inherits not only the “accepted
handle,” i.e., the socket returned by the
accept call, but also the top
socket, i.e., the one opened by the top process right
at the beginning.
However, the server process does not
need this socket and should close it
immediately. Similarly, the daemon process
no longer needs the accepted socket, and
not only should, but must
close it—otherwise, it will run out
of available file descriptors sooner or
later.
After the server process is done
serving, it should close the accepted
socket. Instead of returning to
accept, it now exits.
Under UNIX®, a process does not really
exit. Instead, it
returns to its parent. Typically, a parent
process waits for its child process, and
obtains a return value. However, our daemon
process cannot simply stop and wait. That would
defeat the whole purpose of creating additional processes. But
if it never does wait, its children will
become zombies—no longer functional
but still roaming around.
For that reason, the daemon process needs to set signal handlers in its initialize daemon phase. At least a SIGCHLD signal has to be processed, so the daemon can remove the zombie return values from the system and release the system resources they are taking up.
That is why our flowchart now contains a process signals box, which is not connected to any other box. By the way, many servers also process SIGHUP, and typically interpret as the signal from the superuser that they should reread their configuration files. This allows us to change settings without having to kill and restart these servers.
This section should explain IPv6 and IPsec related implementation internals. These functionalities are derived from KAME project
The IPv6 related functions conforms, or tries to conform to the latest set of IPv6 specifications. For future reference we list some of the relevant documents below (NOTE: this is not a complete list - this is too hard to maintain...).
For details please refer to specific chapter in the document, RFCs, manual pages, or comments in the source code.
Conformance tests have been performed on the KAME STABLE kit
at TAHI project. Results can be viewed at
http://www.tahi.org/report/KAME/.
We also attended Univ. of New Hampshire IOL tests
(http://www.iol.unh.edu/) in the
past, with our past snapshots.
RFC1639: FTP Operation Over Big Address Records (FOOBAR)
RFC2428 is preferred over RFC1639. FTP clients will first try RFC2428, then RFC1639 if failed.
RFC1886: DNS Extensions to support IPv6
RFC1933: Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers
RFC1981: Path MTU Discovery for IPv6
RFC2080: RIPng for IPv6
usr.sbin/route6d support this.
RFC2292: Advanced Sockets API for IPv6
For supported library functions/kernel APIs, see
sys/netinet6/ADVAPI.
RFC2362: Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
RFC2362 defines packet formats for PIM-SM.
draft-ietf-pim-ipv6-01.txtis written based on this.
RFC2373: IPv6 Addressing Architecture
supports node required addresses, and conforms to the scope requirement.
RFC2374: An IPv6 Aggregatable Global Unicast Address Format
supports 64-bit length of Interface ID.
RFC2375: IPv6 Multicast Address Assignments
Userland applications use the well-known addresses assigned in the RFC.
RFC2428: FTP Extensions for IPv6 and NATs
RFC2428 is preferred over RFC1639. FTP clients will first try RFC2428, then RFC1639 if failed.
RFC2460: IPv6 specification
RFC2461: Neighbor discovery for IPv6
See 23.5.1.2 in this document for details.
RFC2462: IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
See 23.5.1.4 in this document for details.
RFC2463: ICMPv6 for IPv6 specification
See 23.5.1.9 in this document for details.
RFC2464: Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks
RFC2465: MIB for IPv6: Textual Conventions and General Group
Necessary statistics are gathered by the kernel. Actual IPv6 MIB support is provided as a patchkit for ucd-snmp.
RFC2466: MIB for IPv6: ICMPv6 group
Necessary statistics are gathered by the kernel. Actual IPv6 MIB support is provided as patchkit for ucd-snmp.
RFC2467: Transmission of IPv6 Packets over FDDI Networks
RFC2497: Transmission of IPv6 packet over ARCnet Networks
RFC2553: Basic Socket Interface Extensions for IPv6
IPv4 mapped address (3.7) and special behavior of IPv6 wildcard bind socket (3.8) are supported. See 23.5.1.12 in this document for details.
RFC2675: IPv6 Jumbograms
See 23.5.1.7 in this document for details.
RFC2710: Multicast Listener Discovery for IPv6
RFC2711: IPv6 router alert option
draft-ietf-ipngwg-router-renum-08: Router renumbering for IPv6draft-ietf-ipngwg-icmp-namelookups-02: IPv6 Name Lookups Through ICMPdraft-ietf-ipngwg-icmp-name-lookups-03: IPv6 Name Lookups Through ICMPdraft-ietf-pim-ipv6-01.txt: PIM for IPv6draft-itojun-ipv6-tcp-to-anycast-00: Disconnecting TCP connection toward IPv6 anycast addressdraft-yamamoto-wideipv6-comm-model-00See 23.5.1.6 in this document for details.
draft-ietf-ipngwg-scopedaddr-format-00.txt: An Extension of Format for IPv6 Scoped Addresses
Neighbor Discovery is fairly stable. Currently Address Resolution, Duplicated Address Detection, and Neighbor Unreachability Detection are supported. In the near future we will be adding Proxy Neighbor Advertisement support in the kernel and Unsolicited Neighbor Advertisement transmission command as admin tool.
If DAD fails, the address will be marked "duplicated" and message will be generated to syslog (and usually to console). The "duplicated" mark can be checked with ifconfig(8). It is administrators' responsibility to check for and recover from DAD failures. The behavior should be improved in the near future.
Some of the network driver loops multicast packets back to itself, even if instructed not to do so (especially in promiscuous mode). In such cases DAD may fail, because DAD engine sees inbound NS packet (actually from the node itself) and considers it as a sign of duplicate. You may want to look at #if condition marked "heuristics" in sys/netinet6/nd6_nbr.c:nd6_dad_timer() as workaround (note that the code fragment in "heuristics" section is not spec conformant).
Neighbor Discovery specification (RFC2461) does not talk about neighbor cache handling in the following cases:
when there was no neighbor cache entry, node received unsolicited RS/NS/NA/redirect packet without link-layer address
neighbor cache handling on medium without link-layer address (we need a neighbor cache entry for IsRouter bit)
For first case, we implemented workaround based on discussions on IETF ipngwg mailing list. For more details, see the comments in the source code and email thread started from (IPng 7155), dated Feb 6 1999.
IPv6 on-link determination rule (RFC2461) is quite different from assumptions in BSD network code. At this moment, no on-link determination rule is supported where default router list is empty (RFC2461, section 5.2, last sentence in 2nd paragraph - note that the spec misuse the word "host" and "node" in several places in the section).
To avoid possible DoS attacks and infinite loops, only 10
options on ND packet is accepted now. Therefore, if you have 20
prefix options attached to RA, only the first 10 prefixes will be
recognized. If this troubles you, please ask it on FREEBSD-CURRENT
mailing list and/or modify nd6_maxndopt in
sys/netinet6/nd6.c. If there are high demands
we may provide sysctl knob for the variable.
IPv6 uses scoped addresses. Therefore, it is very important to specify scope index (interface index for link-local address, or site index for site-local address) with an IPv6 address. Without scope index, scoped IPv6 address is ambiguous to the kernel, and kernel will not be able to determine the outbound interface for a packet.
Ordinary userland applications should use advanced API (RFC2292) to specify scope index, or interface index. For similar purpose, sin6_scope_id member in sockaddr_in6 structure is defined in RFC2553. However, the semantics for sin6_scope_id is rather vague. If you care about portability of your application, we suggest you to use advanced API rather than sin6_scope_id.
In the kernel, an interface index for link-local scoped address is embedded into 2nd 16bit-word (3rd and 4th byte) in IPv6 address. For example, you may see something like:
fe80:1::200:f8ff:fe01:6317
in the routing table and interface address structure (struct in6_ifaddr). The address above is a link-local unicast address which belongs to a network interface whose interface identifier is 1. The embedded index enables us to identify IPv6 link local addresses over multiple interfaces effectively and with only a little code change.
Routing daemons and configuration programs, like route6d(8) and ifconfig(8), will need to manipulate the "embedded" scope index. These programs use routing sockets and ioctls (like SIOCGIFADDR_IN6) and the kernel API will return IPv6 addresses with 2nd 16bit-word filled in. The APIs are for manipulating kernel internal structure. Programs that use these APIs have to be prepared about differences in kernels anyway.
When you specify scoped address to the command line, NEVER write
the embedded form (such as ff02:1::1 or fe80:2::fedc). This is not
supposed to work. Always use standard form, like ff02::1 or
fe80::fedc, with command line option for specifying interface (like
ping6 -I ne0 ff02::1). In general, if a command
does not have command line option to specify outgoing interface, that
command is not ready to accept scoped address. This may seem to be
opposite from IPv6's premise to support "dentist office" situation.
We believe that specifications need some improvements for this.
Some of the userland tools support extended numeric IPv6 syntax,
as documented in
draft-ietf-ipngwg-scopedaddr-format-00.txt. You
can specify outgoing link, by using name of the outgoing interface
like "fe80::1%ne0". This way you will be able to specify link-local
scoped address without much trouble.
To use this extension in your program, you will need to use getaddrinfo(3), and getnameinfo(3) with NI_WITHSCOPEID. The implementation currently assumes 1-to-1 relationship between a link and an interface, which is stronger than what specs say.
Most of the IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration is implemented in the kernel. Neighbor Discovery functions are implemented in the kernel as a whole. Router Advertisement (RA) input for hosts is implemented in the kernel. Router Solicitation (RS) output for endhosts, RS input for routers, and RA output for routers are implemented in the userland.
IPv6 link-local address is generated from IEEE802 address (Ethernet MAC address). Each of interface is assigned an IPv6 link-local address automatically, when the interface becomes up (IFF_UP). Also, direct route for the link-local address is added to routing table.
Here is an output of netstat command:
Internet6: Destination Gateway Flags Netif Expire fe80:1::%ed0/64 link#1 UC ed0 fe80:2::%ep0/64 link#2 UC ep0
Interfaces that has no IEEE802 address (pseudo interfaces like tunnel interfaces, or ppp interfaces) will borrow IEEE802 address from other interfaces, such as Ethernet interfaces, whenever possible. If there is no IEEE802 hardware attached, a last resort pseudo-random value, MD5(hostname), will be used as source of link-local address. If it is not suitable for your usage, you will need to configure the link-local address manually.
If an interface is not capable of handling IPv6 (such as lack of multicast support), link-local address will not be assigned to that interface. See section 2 for details.
Each interface joins the solicited multicast address and the link-local all-nodes multicast addresses (e.g. fe80::1:ff01:6317 and ff02::1, respectively, on the link the interface is attached). In addition to a link-local address, the loopback address (::1) will be assigned to the loopback interface. Also, ::1/128 and ff01::/32 are automatically added to routing table, and loopback interface joins node-local multicast group ff01::1.
In IPv6 specification, nodes are separated into two categories: routers and hosts. Routers forward packets addressed to others, hosts does not forward the packets. net.inet6.ip6.forwarding defines whether this node is router or host (router if it is 1, host if it is 0).
When a host hears Router Advertisement from the router, a host may autoconfigure itself by stateless address autoconfiguration. This behavior can be controlled by net.inet6.ip6.accept_rtadv (host autoconfigures itself if it is set to 1). By autoconfiguration, network address prefix for the receiving interface (usually global address prefix) is added. Default route is also configured. Routers periodically generate Router Advertisement packets. To request an adjacent router to generate RA packet, a host can transmit Router Solicitation. To generate a RS packet at any time, use the rtsol command. rtsold(8) daemon is also available. rtsold(8) generates Router Solicitation whenever necessary, and it works great for nomadic usage (notebooks/laptops). If one wishes to ignore Router Advertisements, use sysctl to set net.inet6.ip6.accept_rtadv to 0.
To generate Router Advertisement from a router, use the rtadvd(8) daemon.
Note that, IPv6 specification assumes the following items, and nonconforming cases are left unspecified:
Only hosts will listen to router advertisements
Hosts have single network interface (except loopback)
Therefore, this is unwise to enable net.inet6.ip6.accept_rtadv on routers, or multi-interface host. A misconfigured node can behave strange (nonconforming configuration allowed for those who would like to do some experiments).
To summarize the sysctl knob:
accept_rtadv forwarding role of the node --- --- --- 0 0 host (to be manually configured) 0 1 router 1 0 autoconfigured host (spec assumes that host has single interface only, autoconfigured host with multiple interface is out-of-scope) 1 1 invalid, or experimental (out-of-scope of spec)
RFC2462 has validation rule against incoming RA prefix information option, in 5.5.3 (e). This is to protect hosts from malicious (or misconfigured) routers that advertise very short prefix lifetime. There was an update from Jim Bound to ipngwg mailing list (look for "(ipng 6712)" in the archive) and it is implemented Jim's update.
See 23.5.1.2 in the document for relationship between DAD and autoconfiguration.
GIF (Generic InterFace) is a pseudo interface for configured tunnel. Details are described in gif(4). Currently
v6 in v6
v6 in v4
v4 in v6
v4 in v4
are available. Use gifconfig(8) to assign physical (outer) source and destination address to gif interfaces. Configuration that uses same address family for inner and outer IP header (v4 in v4, or v6 in v6) is dangerous. It is very easy to configure interfaces and routing tables to perform infinite level of tunneling. Please be warned.
gif can be configured to be ECN-friendly. See 23.5.4.5 for ECN-friendliness of tunnels, and gif(4) for how to configure.
If you would like to configure an IPv4-in-IPv6 tunnel with gif interface, read gif(4) carefully. You will need to remove IPv6 link-local address automatically assigned to the gif interface.
Current source selection rule is scope oriented (there are some exceptions - see below). For a given destination, a source IPv6 address is selected by the following rule:
If the source address is explicitly specified by the user (e.g. via the advanced API), the specified address is used.
If there is an address assigned to the outgoing interface (which is usually determined by looking up the routing table) that has the same scope as the destination address, the address is used.
This is the most typical case.
If there is no address that satisfies the above condition, choose a global address assigned to one of the interfaces on the sending node.
If there is no address that satisfies the above condition, and destination address is site local scope, choose a site local address assigned to one of the interfaces on the sending node.
If there is no address that satisfies the above condition, choose the address associated with the routing table entry for the destination. This is the last resort, which may cause scope violation.
For instance, ::1 is selected for ff01::1, fe80:1::200:f8ff:fe01:6317 for fe80:1::2a0:24ff:feab:839b (note that embedded interface index - described in 23.5.1.3 - helps us choose the right source address. Those embedded indices will not be on the wire). If the outgoing interface has multiple address for the scope, a source is selected longest match basis (rule 3). Suppose 2001:0DB8:808:1:200:f8ff:fe01:6317 and 2001:0DB8:9:124:200:f8ff:fe01:6317 are given to the outgoing interface. 2001:0DB8:808:1:200:f8ff:fe01:6317 is chosen as the source for the destination 2001:0DB8:800::1.
Note that the above rule is not documented in the IPv6 spec. It is considered "up to implementation" item. There are some cases where we do not use the above rule. One example is connected TCP session, and we use the address kept in tcb as the source. Another example is source address for Neighbor Advertisement. Under the spec (RFC2461 7.2.2) NA's source should be the target address of the corresponding NS's target. In this case we follow the spec rather than the above longest-match rule.
For new connections (when rule 1 does not apply), deprecated addresses (addresses with preferred lifetime = 0) will not be chosen as source address if other choices are available. If no other choices are available, deprecated address will be used as a last resort. If there are multiple choice of deprecated addresses, the above scope rule will be used to choose from those deprecated addresses. If you would like to prohibit the use of deprecated address for some reason, configure net.inet6.ip6.use_deprecated to 0. The issue related to deprecated address is described in RFC2462 5.5.4 (NOTE: there is some debate underway in IETF ipngwg on how to use "deprecated" address).
The Jumbo Payload hop-by-hop option is implemented and can be used to send IPv6 packets with payloads longer than 65,535 octets. But currently no physical interface whose MTU is more than 65,535 is supported, so such payloads can be seen only on the loopback interface (i.e. lo0).
If you want to try jumbo payloads, you first have to reconfigure the kernel so that the MTU of the loopback interface is more than 65,535 bytes; add the following to the kernel configuration file:
options "LARGE_LOMTU" #To test jumbo payload
and recompile the new kernel.
Then you can test jumbo payloads by the ping6(8) command with -b and -s options. The -b option must be specified to enlarge the size of the socket buffer and the -s option specifies the length of the packet, which should be more than 65,535. For example, type as follows:
%ping6 -b 70000 -s 68000 ::1
The IPv6 specification requires that the Jumbo Payload option must not be used in a packet that carries a fragment header. If this condition is broken, an ICMPv6 Parameter Problem message must be sent to the sender. specification is followed, but you cannot usually see an ICMPv6 error caused by this requirement.
When an IPv6 packet is received, the frame length is checked and compared to the length specified in the payload length field of the IPv6 header or in the value of the Jumbo Payload option, if any. If the former is shorter than the latter, the packet is discarded and statistics are incremented. You can see the statistics as output of netstat(8) command with `-s -p ip6' option:
%netstat -s -p ip6ip6: (snip) 1 with data size < data length
So, kernel does not send an ICMPv6 error unless the erroneous packet is an actual Jumbo Payload, that is, its packet size is more than 65,535 bytes. As described above, currently no physical interface with such a huge MTU is supported, so it rarely returns an ICMPv6 error.
TCP/UDP over jumbogram is not supported at this moment. This is because we have no medium (other than loopback) to test this. Contact us if you need this.
IPsec does not work on jumbograms. This is due to some specification twists in supporting AH with jumbograms (AH header size influences payload length, and this makes it real hard to authenticate inbound packet with jumbo payload option as well as AH).
There are fundamental issues in *BSD support for jumbograms. We would like to address those, but we need more time to finalize these. To name a few:
mbuf pkthdr.len field is typed as "int" in 4.4BSD, so it will not hold jumbogram with len > 2G on 32bit architecture CPUs. If we would like to support jumbogram properly, the field must be expanded to hold 4G + IPv6 header + link-layer header. Therefore, it must be expanded to at least int64_t (u_int32_t is NOT enough).
We mistakingly use "int" to hold packet length in many places. We need to convert them into larger integral type. It needs a great care, as we may experience overflow during packet length computation.
We mistakingly check for ip6_plen field of IPv6 header for packet payload length in various places. We should be checking mbuf pkthdr.len instead. ip6_input() will perform sanity check on jumbo payload option on input, and we can safely use mbuf pkthdr.len afterwards.
TCP code needs a careful update in bunch of places, of course.
IPv6 specification allows arbitrary number of extension headers
to be placed onto packets. If we implement IPv6 packet processing
code in the way BSD IPv4 code is implemented, kernel stack may
overflow due to long function call chain. sys/netinet6 code
is carefully designed to avoid kernel stack overflow. Because of
this, sys/netinet6 code defines its own protocol switch
structure, as "struct ip6protosw" (see
netinet6/ip6protosw.h). There is no such
update to IPv4 part (sys/netinet) for compatibility, but small
change is added to its pr_input() prototype. So "struct ipprotosw"
is also defined. Because of this, if you receive IPsec-over-IPv4
packet with massive number of IPsec headers, kernel stack may blow
up. IPsec-over-IPv6 is okay. (Off-course, for those all IPsec
headers to be processed, each such IPsec header must pass each
IPsec check. So an anonymous attacker will not be able to do such an
attack.)
After RFC2463 was published, IETF ipngwg has decided to disallow ICMPv6 error packet against ICMPv6 redirect, to prevent ICMPv6 storm on a network medium. This is already implemented into the kernel.
For userland programming, we support IPv6 socket API as specified in RFC2553, RFC2292 and upcoming Internet drafts.
TCP/UDP over IPv6 is available and quite stable. You can enjoy telnet(1), ftp(1), rlogin(1), rsh(1), ssh(1), etc. These applications are protocol independent. That is, they automatically chooses IPv4 or IPv6 according to DNS.
While ip_forward() calls ip_output(), ip6_forward() directly calls if_output() since routers must not divide IPv6 packets into fragments.
ICMPv6 should contain the original packet as long as possible up to 1280. UDP6/IP6 port unreach, for instance, should contain all extension headers and the *unchanged* UDP6 and IP6 headers. So, all IP6 functions except TCP never convert network byte order into host byte order, to save the original packet.
tcp_input(), udp6_input() and icmp6_input() can not assume that IP6 header is preceding the transport headers due to extension headers. So, in6_cksum() was implemented to handle packets whose IP6 header and transport header is not continuous. TCP/IP6 nor UDP6/IP6 header structures do not exist for checksum calculation.
To process IP6 header, extension headers and transport headers easily, network drivers are now required to store packets in one internal mbuf or one or more external mbufs. A typical old driver prepares two internal mbufs for 96 - 204 bytes data, however, now such packet data is stored in one external mbuf.
netstat -s -p ip6 tells you whether or not
your driver conforms such requirement. In the following example,
"cce0" violates the requirement. (For more information, refer to
Section 2.)
Mbuf statistics:
317 one mbuf
two or more mbuf::
lo0 = 8
cce0 = 10
3282 one ext mbuf
0 two or more ext mbuf
Each input function calls IP6_EXTHDR_CHECK in the beginning to check if the region between IP6 and its header is continuous. IP6_EXTHDR_CHECK calls m_pullup() only if the mbuf has M_LOOP flag, that is, the packet comes from the loopback interface. m_pullup() is never called for packets coming from physical network interfaces.
Both IP and IP6 reassemble functions never call m_pullup().
RFC2553 describes IPv4 mapped address (3.7) and special behavior of IPv6 wildcard bind socket (3.8). The spec allows you to:
Accept IPv4 connections by AF_INET6 wildcard bind socket.
Transmit IPv4 packet over AF_INET6 socket by using special form of the address like ::ffff:10.1.1.1.
but the spec itself is very complicated and does not specify how the socket layer should behave. Here we call the former one "listening side" and the latter one "initiating side", for reference purposes.
You can perform wildcard bind on both of the address families, on the same port.
The following table show the behavior of FreeBSD 4.x.
listening side initiating side
(AF_INET6 wildcard (connection to ::ffff:10.1.1.1)
socket gets IPv4 conn.)
--- ---
FreeBSD 4.x configurable supported
default: enabled
The following sections will give you more details, and how you can configure the behavior.
Comments on listening side:
It looks that RFC2553 talks too little on wildcard bind issue, especially on the port space issue, failure mode and relationship between AF_INET/INET6 wildcard bind. There can be several separate interpretation for this RFC which conform to it but behaves differently. So, to implement portable application you should assume nothing about the behavior in the kernel. Using getaddrinfo(3) is the safest way. Port number space and wildcard bind issues were discussed in detail on ipv6imp mailing list, in mid March 1999 and it looks that there is no concrete consensus (means, up to implementers). You may want to check the mailing list archives.
If a server application would like to accept IPv4 and IPv6 connections, there will be two alternatives.
One is using AF_INET and AF_INET6 socket (you will need two sockets). Use getaddrinfo(3) with AI_PASSIVE into ai_flags, and socket(2) and bind(2) to all the addresses returned. By opening multiple sockets, you can accept connections onto the socket with proper address family. IPv4 connections will be accepted by AF_INET socket, and IPv6 connections will be accepted by AF_INET6 socket.
Another way is using one AF_INET6 wildcard bind socket. Use getaddrinfo(3) with AI_PASSIVE into ai_flags and with AF_INET6 into ai_family, and set the 1st argument hostname to NULL. And socket(2) and bind(2) to the address returned. (should be IPv6 unspecified addr). You can accept either of IPv4 and IPv6 packet via this one socket.
To support only IPv6 traffic on AF_INET6 wildcard binded socket portably, always check the peer address when a connection is made toward AF_INET6 listening socket. If the address is IPv4 mapped address, you may want to reject the connection. You can check the condition by using IN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPED() macro.
To resolve this issue more easily, there is system dependent setsockopt(2) option, IPV6_BINDV6ONLY, used like below.
int on; setsockopt(s, IPPROTO_IPV6, IPV6_BINDV6ONLY, (char *)&on, sizeof (on)) < 0));
When this call succeed, then this socket only receive IPv6 packets.
Comments on initiating side:
Advise to application implementers: to implement a portable IPv6 application (which works on multiple IPv6 kernels), we believe that the following is the key to the success:
NEVER hardcode AF_INET nor AF_INET6.
Use getaddrinfo(3) and getnameinfo(3) throughout the system. Never use gethostby*(), getaddrby*(), inet_*() or getipnodeby*(). (To update existing applications to be IPv6 aware easily, sometime getipnodeby*() will be useful. But if possible, try to rewrite the code to use getaddrinfo(3) and getnameinfo(3).)
If you would like to connect to destination, use getaddrinfo(3) and try all the destination returned, like telnet(1) does.
Some of the IPv6 stack is shipped with buggy getaddrinfo(3). Ship a minimal working version with your application and use that as last resort.
If you would like to use AF_INET6 socket for both IPv4 and IPv6 outgoing connection, you will need to use getipnodebyname(3). When you would like to update your existing application to be IPv6 aware with minimal effort, this approach might be chosen. But please note that it is a temporal solution, because getipnodebyname(3) itself is not recommended as it does not handle scoped IPv6 addresses at all. For IPv6 name resolution, getaddrinfo(3) is the preferred API. So you should rewrite your application to use getaddrinfo(3), when you get the time to do it.
When writing applications that make outgoing connections, story goes much simpler if you treat AF_INET and AF_INET6 as totally separate address family. {set,get}sockopt issue goes simpler, DNS issue will be made simpler. We do not recommend you to rely upon IPv4 mapped address.
FreeBSD 4.x uses shared tcp code between IPv4 and IPv6 (from sys/netinet/tcp*) and separate udp4/6 code. It uses unified inpcb structure.
The platform can be configured to support IPv4 mapped address. Kernel configuration is summarized as follows:
By default, AF_INET6 socket will grab IPv4 connections in certain condition, and can initiate connection to IPv4 destination embedded in IPv4 mapped IPv6 address.
You can disable it on entire system with sysctl like below.
sysctl net.inet6.ip6.mapped_addr=0
Each socket can be configured to support special AF_INET6 wildcard bind (enabled by default). You can disable it on each socket basis with setsockopt(2) like below.
int on; setsockopt(s, IPPROTO_IPV6, IPV6_BINDV6ONLY, (char *)&on, sizeof (on)) < 0));
Wildcard AF_INET6 socket grabs IPv4 connection if and only if the following conditions are satisfied:
there is no AF_INET socket that matches the IPv4 connection
the AF_INET6 socket is configured to accept IPv4 traffic, i.e. getsockopt(IPV6_BINDV6ONLY) returns 0.
There is no problem with open/close ordering.
When RFC2553 was about to be finalized, there was discussion on how struct sockaddr_storage members are named. One proposal is to prepend "__" to the members (like "__ss_len") as they should not be touched. The other proposal was not to prepend it (like "ss_len") as we need to touch those members directly. There was no clear consensus on it.
As a result, RFC2553 defines struct sockaddr_storage as follows:
struct sockaddr_storage {
u_char __ss_len; /* address length */
u_char __ss_family; /* address family */
/* and bunch of padding */
};
On the contrary, XNET draft defines as follows:
struct sockaddr_storage {
u_char ss_len; /* address length */
u_char ss_family; /* address family */
/* and bunch of padding */
};
In December 1999, it was agreed that RFC2553bis should pick the latter (XNET) definition.
Current implementation conforms to XNET definition, based on RFC2553bis discussion.
If you look at multiple IPv6 implementations, you will be able to see both definitions. As an userland programmer, the most portable way of dealing with it is to:
ensure ss_family and/or ss_len are available on the platform, by using GNU autoconf,
have -Dss_family=__ss_family to unify all occurrences (including header file) into __ss_family, or
never touch __ss_family. cast to sockaddr * and use sa_family like:
struct sockaddr_storage ss; family = ((struct sockaddr *)&ss)->sa_family
Now following two items are required to be supported by standard drivers:
mbuf clustering requirement. In this stable release, we changed MINCLSIZE into MHLEN+1 for all the operating systems in order to make all the drivers behave as we expect.
multicast. If ifmcstat(8) yields no multicast group for a interface, that interface has to be patched.
If any of the drivers do not support the requirements, then the drivers can not be used for IPv6 and/or IPsec communication. If you find any problem with your card using IPv6/IPsec, then, please report it to the FreeBSD problem reports mailing list.
(NOTE: In the past we required all PCMCIA drivers to have a call to in6_ifattach(). We have no such requirement any more)
We categorize IPv4/IPv6 translator into 4 types:
Translator A --- It is used in the early stage of transition to make it possible to establish a connection from an IPv6 host in an IPv6 island to an IPv4 host in the IPv4 ocean.
Translator B --- It is used in the early stage of transition to make it possible to establish a connection from an IPv4 host in the IPv4 ocean to an IPv6 host in an IPv6 island.
Translator C --- It is used in the late stage of transition to make it possible to establish a connection from an IPv4 host in an IPv4 island to an IPv6 host in the IPv6 ocean.
Translator D --- It is used in the late stage of transition to make it possible to establish a connection from an IPv6 host in the IPv6 ocean to an IPv4 host in an IPv4 island.
TCP relay translator for category A is supported. This is called "FAITH". We also provide IP header translator for category A. (The latter is not yet put into FreeBSD 4.x yet.)
FAITH system uses TCP relay daemon called faithd(8) helped by the kernel. FAITH will reserve an IPv6 address prefix, and relay TCP connection toward that prefix to IPv4 destination.
For example, if the reserved IPv6 prefix is 2001:0DB8:0200:ffff::, and the IPv6 destination for TCP connection is 2001:0DB8:0200:ffff::163.221.202.12, the connection will be relayed toward IPv4 destination 163.221.202.12.
destination IPv4 node (163.221.202.12) ^ | IPv4 tcp toward 163.221.202.12 FAITH-relay dual stack node ^ | IPv6 TCP toward 2001:0DB8:0200:ffff::163.221.202.12 source IPv6 node
faithd(8) must be invoked on FAITH-relay dual stack node.
For more details, consult
src/usr.sbin/faithd/README
IPsec is mainly organized by three components.
Policy Management
Key Management
AH and ESP handling
The kernel implements experimental policy management code. There are two way to manage security policy. One is to configure per-socket policy using setsockopt(2). In this cases, policy configuration is described in ipsec_set_policy(3). The other is to configure kernel packet filter-based policy using PF_KEY interface, via setkey(8).
The policy entry is not re-ordered with its indexes, so the order of entry when you add is very significant.
The key management code implemented in this kit (sys/netkey) is a home-brew PFKEY v2 implementation. This conforms to RFC2367.
The home-brew IKE daemon, "racoon" is included in the
kit (kame/kame/racoon). Basically you will need to run racoon as
daemon, then set up a policy to require keys (like
ping -P 'out ipsec esp/transport//use').
The kernel will contact racoon daemon as necessary to exchange
keys.
IPsec module is implemented as "hooks" to the standard IPv4/IPv6 processing. When sending a packet, ip{,6}_output() checks if ESP/AH processing is required by checking if a matching SPD (Security Policy Database) is found. If ESP/AH is needed, {esp,ah}{4,6}_output() will be called and mbuf will be updated accordingly. When a packet is received, {esp,ah}4_input() will be called based on protocol number, i.e. (*inetsw[proto])(). {esp,ah}4_input() will decrypt/check authenticity of the packet, and strips off daisy-chained header and padding for ESP/AH. It is safe to strip off the ESP/AH header on packet reception, since we will never use the received packet in "as is" form.
By using ESP/AH, TCP4/6 effective data segment size will be affected by extra daisy-chained headers inserted by ESP/AH. Our code takes care of the case.
Basic crypto functions can be found in directory "sys/crypto". ESP/AH transform are listed in {esp,ah}_core.c with wrapper functions. If you wish to add some algorithm, add wrapper function in {esp,ah}_core.c, and add your crypto algorithm code into sys/crypto.
Tunnel mode is partially supported in this release, with the following restrictions:
IPsec tunnel is not combined with GIF generic tunneling interface. It needs a great care because we may create an infinite loop between ip_output() and tunnelifp->if_output(). Opinion varies if it is better to unify them, or not.
MTU and Don't Fragment bit (IPv4) considerations need more checking, but basically works fine.
Authentication model for AH tunnel must be revisited. We will need to improve the policy management engine, eventually.
The IPsec code in the kernel conforms (or, tries to conform) to the following standards:
"old IPsec" specification documented in
rfc182[5-9].txt
"new IPsec" specification documented in
rfc240[1-6].txt,
rfc241[01].txt, rfc2451.txt
and draft-mcdonald-simple-ipsec-api-01.txt
(draft expired, but you can take from
ftp://ftp.kame.net/pub/internet-drafts/).
(NOTE: IKE specifications, rfc241[7-9].txt are
implemented in userland, as "racoon" IKE daemon)
Currently supported algorithms are:
old IPsec AH
null crypto checksum (no document, just for debugging)
keyed MD5 with 128bit crypto checksum (
rfc1828.txt)keyed SHA1 with 128bit crypto checksum (no document)
HMAC MD5 with 128bit crypto checksum (
rfc2085.txt)HMAC SHA1 with 128bit crypto checksum (no document)
old IPsec ESP
null encryption (no document, similar to
rfc2410.txt)DES-CBC mode (
rfc1829.txt)
new IPsec AH
null crypto checksum (no document, just for debugging)
keyed MD5 with 96bit crypto checksum (no document)
keyed SHA1 with 96bit crypto checksum (no document)
HMAC MD5 with 96bit crypto checksum (
rfc2403.txt)HMAC SHA1 with 96bit crypto checksum (
rfc2404.txt)
new IPsec ESP
null encryption (
rfc2410.txt)DES-CBC with derived IV (
draft-ietf-ipsec-ciph-des-derived-01.txt, draft expired)DES-CBC with explicit IV (
rfc2405.txt)3DES-CBC with explicit IV (
rfc2451.txt)BLOWFISH CBC (
rfc2451.txt)CAST128 CBC (
rfc2451.txt)RC5 CBC (
rfc2451.txt)each of the above can be combined with:
ESP authentication with HMAC-MD5(96bit)
ESP authentication with HMAC-SHA1(96bit)
The following algorithms are NOT supported:
old IPsec AH
HMAC MD5 with 128bit crypto checksum + 64bit replay prevention (
rfc2085.txt)keyed SHA1 with 160bit crypto checksum + 32bit padding (
rfc1852.txt)
IPsec (in kernel) and IKE (in userland as "racoon") has been tested at several interoperability test events, and it is known to interoperate with many other implementations well. Also, current IPsec implementation as quite wide coverage for IPsec crypto algorithms documented in RFC (we cover algorithms without intellectual property issues only).
ECN-friendly IPsec tunnel is supported as described in
draft-ipsec-ecn-00.txt.
Normal IPsec tunnel is described in RFC2401. On encapsulation, IPv4 TOS field (or, IPv6 traffic class field) will be copied from inner IP header to outer IP header. On decapsulation outer IP header will be simply dropped. The decapsulation rule is not compatible with ECN, since ECN bit on the outer IP TOS/traffic class field will be lost.
To make IPsec tunnel ECN-friendly, we should modify encapsulation and decapsulation procedure. This is described in http://www.aciri.org/floyd/papers/draft-ipsec-ecn-00.txt, chapter 3.
IPsec tunnel implementation can give you three behaviors, by setting net.inet.ipsec.ecn (or net.inet6.ipsec6.ecn) to some value:
RFC2401: no consideration for ECN (sysctl value -1)
ECN forbidden (sysctl value 0)
ECN allowed (sysctl value 1)
Note that the behavior is configurable in per-node manner, not per-SA manner (draft-ipsec-ecn-00 wants per-SA configuration, but it looks too much for me).
The behavior is summarized as follows (see source code for more detail):
encapsulate decapsulate
--- ---
RFC2401 copy all TOS bits drop TOS bits on outer
from inner to outer. (use inner TOS bits as is)
ECN forbidden copy TOS bits except for ECN drop TOS bits on outer
(masked with 0xfc) from inner (use inner TOS bits as is)
to outer. set ECN bits to 0.
ECN allowed copy TOS bits except for ECN use inner TOS bits with some
CE (masked with 0xfe) from change. if outer ECN CE bit
inner to outer. is 1, enable ECN CE bit on
set ECN CE bit to 0. the inner.
General strategy for configuration is as follows:
if both IPsec tunnel endpoint are capable of ECN-friendly behavior, you should better configure both end to “ECN allowed” (sysctl value 1).
if the other end is very strict about TOS bit, use "RFC2401" (sysctl value -1).
in other cases, use "ECN forbidden" (sysctl value 0).
The default behavior is "ECN forbidden" (sysctl value 0).
For more information, please refer to:
http://www.aciri.org/floyd/papers/draft-ipsec-ecn-00.txt, RFC2481 (Explicit Congestion Notification), src/sys/netinet6/{ah,esp}_input.c
(Thanks goes to Kenjiro Cho <[email protected]>
for detailed analysis)
Here are (some of) platforms that KAME code have tested IPsec/IKE interoperability in the past. Note that both ends may have modified their implementation, so use the following list just for reference purposes.
Altiga, Ashley-laurent (vpcom.com), Data Fellows (F-Secure), Ericsson ACC, FreeS/WAN, HITACHI, IBM AIX®, IIJ, Intel, Microsoft® Windows NT®, NIST (linux IPsec + plutoplus), Netscreen, OpenBSD, RedCreek, Routerware, SSH, Secure Computing, Soliton, Toshiba, VPNet, Yamaha RT100i
- 9. Building and Installing a FreeBSD Kernel
- 10. Kernel Debugging
- 10.1. Obtaining a Kernel Crash Dump
- 10.2. Debugging a Kernel Crash Dump with
kgdb - 10.3. Debugging a Crash Dump with DDD
- 10.4. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using DDB
- 10.5. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using Remote GDB
- 10.6. Debugging a Console Driver
- 10.7. Debugging Deadlocks
- 10.8. Kernel debugging with Dcons
- 10.9. Glossary of Kernel Options for Debugging
Being a kernel developer requires understanding of the kernel build process. To debug the FreeBSD kernel it is required to be able to build one. There are two known ways to do so:
The “Traditional” Way
The “New” Way
Note:
It is supposed that the reader of this chapter is familiar with the information described in the Building and Installing a Custom Kernel chapter of the FreeBSD Handbook. If this is not the case, please read through the above mentioned chapter to understand how the build process works.
Up to version 4.X of FreeBSD this was the recommended way to
build a new kernel. It can still be used on newer versions
(instead of the “buildkernel” target of the toplevel
/usr/src/ makefiles).
Building the kernel this way may be useful when working on the
kernel code and it may actually be faster than the
“New” procedure when only a single option or two were
tweaked in the kernel configuration file. On the other hand, it
might lead to unexpected kernel build breakage when used by
beginners on newer versions of FreeBSD.
This procedure is well supported and recommended under the latest FreeBSD releases and is documented in the Building and Installing a Custom Kernel chapter of the FreeBSD Handbook.
- 10.1. Obtaining a Kernel Crash Dump
- 10.2. Debugging a Kernel Crash Dump with
kgdb - 10.3. Debugging a Crash Dump with DDD
- 10.4. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using DDB
- 10.5. On-Line Kernel Debugging Using Remote GDB
- 10.6. Debugging a Console Driver
- 10.7. Debugging Deadlocks
- 10.8. Kernel debugging with Dcons
- 10.9. Glossary of Kernel Options for Debugging
When running a development kernel (e.g., FreeBSD-CURRENT), such as a kernel under extreme conditions (e.g., very high load averages, tens of thousands of connections, exceedingly high number of concurrent users, hundreds of jail(8)s, etc.), or using a new feature or device driver on FreeBSD-STABLE (e.g., PAE), sometimes a kernel will panic. In the event that it does, this chapter will demonstrate how to extract useful information out of a crash.
A system reboot is inevitable once a kernel panics. Once a system is rebooted, the contents of a system's physical memory (RAM) is lost, as well as any bits that are on the swap device before the panic. To preserve the bits in physical memory, the kernel makes use of the swap device as a temporary place to store the bits that are in RAM across a reboot after a crash. In doing this, when FreeBSD boots after a crash, a kernel image can now be extracted and debugging can take place.
Note:
A swap device that has been configured as a dump device still acts as a swap device. Dumps to non-swap devices (such as tapes or CDRWs, for example) are not supported at this time. A “swap device” is synonymous with a “swap partition.”
Several types of kernel crash dumps are available: full memory dumps, which hold the complete contents of physical memory, minidumps, which hold only memory pages in use by the kernel (FreeBSD 6.2 and higher), and textdumps, which hold captured scripted or interactive debugger output (FreeBSD 7.1 and higher). Minidumps are the default dump type as of FreeBSD 7.0, and in most cases will capture all necessary information present in a full memory dump, as most problems can be isolated only using kernel state.
Before the kernel will dump the contents of its physical
memory to a dump device, a dump device must be configured. A
dump device is specified by using the dumpon(8) command
to tell the kernel where to save kernel crash dumps. The
dumpon(8) program must be called after the swap partition
has been configured with swapon(8). This is normally
handled by setting the dumpdev variable in
rc.conf(5) to the path of the swap device (the
recommended way to extract a kernel dump) or
AUTO to use the first configured swap
device. The default for dumpdev is
AUTO in HEAD, and changed to
NO on RELENG_* branches (except for RELENG_7,
which was left set to AUTO).
On FreeBSD 9.0-RELEASE and later versions,
bsdinstall will ask whether crash dumps
should be enabled on the target system during the install process.
Tip:
Check /etc/fstab or
swapinfo(8) for a list of swap devices.
Important:
Make sure the dumpdir
specified in rc.conf(5) exists before a kernel
crash!
#mkdir /var/crash#chmod 700 /var/crash
Also, remember that the contents of
/var/crash is sensitive and very likely
contains confidential information such as passwords.
Once a dump has been written to a dump device, the dump
must be extracted before the swap device is mounted.
To extract a dump
from a dump device, use the savecore(8) program. If
dumpdev has been set in rc.conf(5),
savecore(8) will be called automatically on the first
multi-user boot after the crash and before the swap device
is mounted. The location of the extracted core is placed in
the rc.conf(5) value dumpdir, by
default /var/crash and will be named
vmcore.0.
In the event that there is already a file called
vmcore.0 in
/var/crash (or whatever
dumpdir is set to), the kernel will
increment the trailing number for every crash to avoid
overwriting an existing vmcore (e.g.,
vmcore.1). While debugging, it is
highly likely that you will want to use the highest version
vmcore in
/var/crash when searching for the right
vmcore.
Tip:
If you are testing a new kernel but need to boot a different one in
order to get your system up and running again, boot it only into single
user mode using the -s flag at the boot prompt, and
then perform the following steps:
#fsck -p#mount -a -t ufs# make sure /var/crash is writable#savecore /var/crash /dev/ad0s1b#exit# exit to multi-user
This instructs savecore(8) to extract a kernel dump
from /dev/ad0s1b and place the contents in
/var/crash. Do not forget to make sure the
destination directory /var/crash has enough
space for the dump. Also, do not forget to specify the correct path to your swap
device as it is likely different than
/dev/ad0s1b!
Note:
This section covers kgdb(1) as found in FreeBSD 5.3
and later. In previous versions, one must use
gdb -k to read a core dump file.
Once a dump has been obtained, getting useful information
out of the dump is relatively easy for simple problems. Before
launching into the internals of kgdb(1) to debug
the crash dump, locate the debug version of your kernel
(normally called kernel.debug) and the path
to the source files used to build your kernel (normally
/usr/obj/usr/src/sys/,
where KERNCONFKERNCONFident specified in a kernel
config(5)). With those two pieces of info, let the
debugging commence!
To enter into the debugger and begin getting information from the dump, the following steps are required at a minimum:
#cd /usr/obj/usr/src/sys/KERNCONF#kgdb kernel.debug /var/crash/vmcore.0
You can debug the crash dump using the kernel sources just like you can for any other program.
This first dump is from a 5.2-BETA kernel and the crash
comes from deep within the kernel. The output below has been
modified to include line numbers on the left. This first trace
inspects the instruction pointer and obtains a back trace. The
address that is used on line 41 for the list
command is the instruction pointer and can be found on line
17. Most developers will request having at least this
information sent to them if you are unable to debug the problem
yourself. If, however, you do solve the problem, make sure that
your patch winds its way into the source tree via a problem
report, mailing lists, or by being able to commit it!
1:#cd /usr/obj/usr/src/sys/2:KERNCONF#kgdb kernel.debug /var/crash/vmcore.03:GNU gdb 5.2.1 (FreeBSD) 4:Copyright 2002 Free Software Foundation, Inc. 5:GDB is free software, covered by the GNU General Public License, and you are 6:welcome to change it and/or distribute copies of it under certain conditions. 7:Type "show copying" to see the conditions. 8:There is absolutely no warranty for GDB. Type "show warranty" for details. 9:This GDB was configured as "i386-undermydesk-freebsd"... 10:panic: page fault 11:panic messages: 12:--- 13:Fatal trap 12: page fault while in kernel mode 14:cpuid = 0; apic id = 00 15:fault virtual address = 0x300 16:fault code: = supervisor read, page not present 17:instruction pointer = 0x8:0xc0713860 18:stack pointer = 0x10:0xdc1d0b70 19:frame pointer = 0x10:0xdc1d0b7c 20:code segment = base 0x0, limit 0xfffff, type 0x1b 21: = DPL 0, pres 1, def32 1, gran 1 22:processor eflags = resume, IOPL = 0 23:current process = 14394 (uname) 24:trap number = 12 25:panic: page fault 26 cpuid = 0; 27:Stack backtrace: 28 29:syncing disks, buffers remaining... 2199 2199 panic: mi_switch: switch in a critical section 30:cpuid = 0; 31:Uptime: 2h43m19s 32:Dumping 255 MB 33: 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 34:--- 35:Reading symbols from /boot/kernel/snd_maestro3.ko...done. 36:Loaded symbols for /boot/kernel/snd_maestro3.ko 37:Reading symbols from /boot/kernel/snd_pcm.ko...done. 38:Loaded symbols for /boot/kernel/snd_pcm.ko 39:#0 doadump () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:240 40:240 dumping++; 41:(kgdb)list *0xc071386042:0xc0713860 is in lapic_ipi_wait (/usr/src/sys/i386/i386/local_apic.c:663). 43:658 incr = 0; 44:659 delay = 1; 45:660 } else 46:661 incr = 1; 47:662 for (x = 0; x < delay; x += incr) { 48:663 if ((lapic->icr_lo & APIC_DELSTAT_MASK) == APIC_DELSTAT_IDLE) 49:664 return (1); 50:665 ia32_pause(); 51:666 } 52:667 return (0); 53:(kgdb)backtrace54:#0 doadump () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:240 55:#1 0xc055fd9b in boot (howto=260) at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:372 56:#2 0xc056019d in panic () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:550 57:#3 0xc0567ef5 in mi_switch () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_synch.c:470 58:#4 0xc055fa87 in boot (howto=256) at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:312 59:#5 0xc056019d in panic () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_shutdown.c:550 60:#6 0xc0720c66 in trap_fatal (frame=0xdc1d0b30, eva=0) 61: at /usr/src/sys/i386/i386/trap.c:821 62:#7 0xc07202b3 in trap (frame= 63: {tf_fs = -1065484264, tf_es = -1065484272, tf_ds = -1065484272, tf_edi = 1, tf_esi = 0, tf_ebp = -602076292, tf_isp = -602076324, tf_ebx = 0, tf_edx = 0, tf_ecx = 1000000, tf_eax = 243, tf_trapno = 12, tf_err = 0, tf_eip = -1066321824, tf_cs = 8, tf_eflags = 65671, tf_esp = 243, tf_ss = 0}) 64: at /usr/src/sys/i386/i386/trap.c:250 65:#8 0xc070c9f8 in calltrap () at {standard input}:94 66:#9 0xc07139f3 in lapic_ipi_vectored (vector=0, dest=0) 67: at /usr/src/sys/i386/i386/local_apic.c:733 68:#10 0xc0718b23 in ipi_selected (cpus=1, ipi=1) 69: at /usr/src/sys/i386/i386/mp_machdep.c:1115 70:#11 0xc057473e in kseq_notify (ke=0xcc05e360, cpu=0) 71: at /usr/src/sys/kern/sched_ule.c:520 72:#12 0xc0575cad in sched_add (td=0xcbcf5c80) 73: at /usr/src/sys/kern/sched_ule.c:1366 74:#13 0xc05666c6 in setrunqueue (td=0xcc05e360) 75: at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_switch.c:422 76:#14 0xc05752f4 in sched_wakeup (td=0xcbcf5c80) 77: at /usr/src/sys/kern/sched_ule.c:999 78:#15 0xc056816c in setrunnable (td=0xcbcf5c80) 79: at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_synch.c:570 80:#16 0xc0567d53 in wakeup (ident=0xcbcf5c80) 81: at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_synch.c:411 82:#17 0xc05490a8 in exit1 (td=0xcbcf5b40, rv=0) 83: at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_exit.c:509 84:#18 0xc0548011 in sys_exit () at /usr/src/sys/kern/kern_exit.c:102 85:#19 0xc0720fd0 in syscall (frame= 86: {tf_fs = 47, tf_es = 47, tf_ds = 47, tf_edi = 0, tf_esi = -1, tf_ebp = -1077940712, tf_isp = -602075788, tf_ebx = 672411944, tf_edx = 10, tf_ecx = 672411600, tf_eax = 1, tf_trapno = 12, tf_err = 2, tf_eip = 671899563, tf_cs = 31, tf_eflags = 642, tf_esp = -1077940740, tf_ss = 47}) 87: at /usr/src/sys/i386/i386/trap.c:1010 88:#20 0xc070ca4d in Xint0x80_syscall () at {standard input}:136 89:---Can't read userspace from dump, or kernel process--- 90:(kgdb)quit
This next trace is an older dump from the FreeBSD 2 time
frame, but is more involved and demonstrates more of the
features of gdb. Long lines have been folded
to improve readability, and the lines are numbered for
reference. Despite this, it is a real-world error trace taken
during the development of the pcvt console driver.
1:Script started on Fri Dec 30 23:15:22 1994 2:#cd /sys/compile/URIAH3:#gdb -k kernel /var/crash/vmcore.14:Reading symbol data from /usr/src/sys/compile/URIAH/kernel ...done. 5:IdlePTD 1f3000 6:panic: because you said to! 7:current pcb at 1e3f70 8:Reading in symbols for ../../i386/i386/machdep.c...done. 9:(kgdb)backtrace10:#0 boot (arghowto=256) (../../i386/i386/machdep.c line 767) 11:#1 0xf0115159 in panic () 12:#2 0xf01955bd in diediedie () (../../i386/i386/machdep.c line 698) 13:#3 0xf010185e in db_fncall () 14:#4 0xf0101586 in db_command (-266509132, -266509516, -267381073) 15:#5 0xf0101711 in db_command_loop () 16:#6 0xf01040a0 in db_trap () 17:#7 0xf0192976 in kdb_trap (12, 0, -272630436, -266743723) 18:#8 0xf019d2eb in trap_fatal (...) 19:#9 0xf019ce60 in trap_pfault (...) 20:#10 0xf019cb2f in trap (...) 21:#11 0xf01932a1 in exception:calltrap () 22:#12 0xf0191503 in cnopen (...) 23:#13 0xf0132c34 in spec_open () 24:#14 0xf012d014 in vn_open () 25:#15 0xf012a183 in open () 26:#16 0xf019d4eb in syscall (...) 27:(kgdb)up 1028:Reading in symbols for ../../i386/i386/trap.c...done. 29:#10 0xf019cb2f in trap (frame={tf_es = -260440048, tf_ds = 16, tf_\ 30:edi = 3072, tf_esi = -266445372, tf_ebp = -272630356, tf_isp = -27\ 31:2630396, tf_ebx = -266427884, tf_edx = 12, tf_ecx = -266427884, tf\ 32:_eax = 64772224, tf_trapno = 12, tf_err = -272695296, tf_eip = -26\ 33:6672343, tf_cs = -266469368, tf_eflags = 66066, tf_esp = 3072, tf_\ 34:ss = -266427884}) (../../i386/i386/trap.c line 283) 35:283 (void) trap_pfault(&frame, FALSE); 36:(kgdb)frame frame->tf_ebp frame->tf_eip37:Reading in symbols for ../../i386/isa/pcvt/pcvt_drv.c...done. 38:#0 0xf01ae729 in pcopen (dev=3072, flag=3, mode=8192, p=(struct p\ 39:roc *) 0xf07c0c00) (../../i386/isa/pcvt/pcvt_drv.c line 403) 40:403 return ((*linesw[tp->t_line].l_open)(dev, tp)); 41:(kgdb)list42:398 43:399 tp->t_state |= TS_CARR_ON; 44:400 tp->t_cflag |= CLOCAL; /* cannot be a modem (:-) */ 45:401 46:402 #if PCVT_NETBSD || (PCVT_FREEBSD >= 200) 47:403 return ((*linesw[tp->t_line].l_open)(dev, tp)); 48:404 #else 49:405 return ((*linesw[tp->t_line].l_open)(dev, tp, flag)); 50:406 #endif /* PCVT_NETBSD || (PCVT_FREEBSD >= 200) */ 51:407 } 52:(kgdb)print tp53:Reading in symbols for ../../i386/i386/cons.c...done. 54:$1 = (struct tty *) 0x1bae 55:(kgdb)print tp->t_line56:$2 = 1767990816 57:(kgdb)up58:#1 0xf0191503 in cnopen (dev=0x00000000, flag=3, mode=8192, p=(st\ 59:ruct proc *) 0xf07c0c00) (../../i386/i386/cons.c line 126) 60: return ((*cdevsw[major(dev)].d_open)(dev, flag, mode, p)); 61:(kgdb)up62:#2 0xf0132c34 in spec_open () 63:(kgdb)up64:#3 0xf012d014 in vn_open () 65:(kgdb)up66:#4 0xf012a183 in open () 67:(kgdb)up68:#5 0xf019d4eb in syscall (frame={tf_es = 39, tf_ds = 39, tf_edi =\ 69: 2158592, tf_esi = 0, tf_ebp = -272638436, tf_isp = -272629788, tf\ 70:_ebx = 7086, tf_edx = 1, tf_ecx = 0, tf_eax = 5, tf_trapno = 582, \ 71:tf_err = 582, tf_eip = 75749, tf_cs = 31, tf_eflags = 582, tf_esp \ 72:= -272638456, tf_ss = 39}) (../../i386/i386/trap.c line 673) 73:673 error = (*callp->sy_call)(p, args, rval); 74:(kgdb)up75:Initial frame selected; you cannot go up. 76:(kgdb)quit
Comments to the above script:
- line 6:
This is a dump taken from within DDB (see below), hence the panic comment “because you said to!”, and a rather long stack trace; the initial reason for going into DDB has been a page fault trap though.
- line 20:
This is the location of function
trap()in the stack trace.- line 36:
Force usage of a new stack frame; this is no longer necessary. The stack frames are supposed to point to the right locations now, even in case of a trap. From looking at the code in source line 403, there is a high probability that either the pointer access for “tp” was messed up, or the array access was out of bounds.
- line 52:
The pointer looks suspicious, but happens to be a valid address.
- line 56:
However, it obviously points to garbage, so we have found our error! (For those unfamiliar with that particular piece of code:
tp->t_linerefers to the line discipline of the console device here, which must be a rather small integer number.)
Tip:
If your system is crashing regularly and you are running
out of disk space, deleting old vmcore
files in /var/crash could save a
considerable amount of disk space!
Examining a kernel crash dump with a graphical debugger like
ddd is also possible (you will need to install
the devel/ddd port in order to use the
ddd debugger). Add the -k
option to the ddd command line you would use
normally. For example;
#ddd --debugger kgdb kernel.debug /var/crash/vmcore.0
You should then be able to go about looking at the crash dump using
ddd's graphical interface.
While kgdb as an off-line debugger provides a very
high level of user interface, there are some things it cannot do. The
most important ones being breakpointing and single-stepping kernel
code.
If you need to do low-level debugging on your kernel, there is an
on-line debugger available called DDB. It allows setting of
breakpoints, single-stepping kernel functions, examining and changing
kernel variables, etc. However, it cannot access kernel source files,
and only has access to the global and static symbols, not to the full
debug information like gdb does.
To configure your kernel to include DDB, add the options
options KDB
options DDB
to your config file, and rebuild. (See The FreeBSD Handbook for details on configuring the FreeBSD kernel).
Note:
If you have an older version of the boot blocks, your debugger symbols might not be loaded at all. Update the boot blocks; the recent ones load the DDB symbols automatically.
Once your DDB kernel is running, there are several ways to enter
DDB. The first, and earliest way is to type the boot flag
-d right at the boot prompt. The kernel will start up
in debug mode and enter DDB prior to any device probing. Hence you can
even debug the device probe/attach functions. Users of FreeBSD-CURRENT
will need to use the boot menu option, six, to escape to a command
prompt.
The second scenario is to drop to the debugger once the system has booted. There are two simple ways to accomplish this. If you would like to break to the debugger from the command prompt, simply type the command:
#sysctl debug.kdb.enter=1
Note:
To force a panic on the fly, issue the following command:
#sysctl debug.kdb.panic=1
Alternatively, if you are at the system console, you may use
a hot-key on the keyboard. The default break-to-debugger
sequence is Ctrl+Alt+ESC. For
syscons, this sequence can be remapped and some of the
distributed maps out there do this, so check to make sure you
know the right sequence to use. There is an option available
for serial consoles that allows the use of a serial line BREAK on the
console line to enter DDB (options BREAK_TO_DEBUGGER
in the kernel config file). It is not the default since there are a lot
of serial adapters around that gratuitously generate a BREAK
condition, for example when pulling the cable.
The third way is that any panic condition will branch to DDB if the kernel is configured to use it. For this reason, it is not wise to configure a kernel with DDB for a machine running unattended.
To obtain the unattended functionality, add:
options KDB_UNATTENDED
to the kernel configuration file and rebuild/reinstall.
The DDB commands roughly resemble some gdb
commands. The first thing you probably need to do is to set a
breakpoint:
break function-name addressNumbers are taken hexadecimal by default, but to make them distinct
from symbol names; hexadecimal numbers starting with the letters
a-f need to be preceded with 0x
(this is optional for other numbers). Simple expressions are allowed,
for example: function-name + 0x103.
To exit the debugger and continue execution, type:
continueTo get a stack trace, use:
traceNote:
Note that when entering DDB via a hot-key, the kernel is currently servicing an interrupt, so the stack trace might be not of much use to you.
If you want to remove a breakpoint, use
deldel address-expression
The first form will be accepted immediately after a breakpoint hit, and deletes the current breakpoint. The second form can remove any breakpoint, but you need to specify the exact address; this can be obtained from:
show bor:
show breakTo single-step the kernel, try:
sThis will step into functions, but you can make DDB trace them until the matching return statement is reached by:
nNote:
This is different from gdb's
next statement; it is like gdb's
finish. Pressing n more than once
will cause a continue.
To examine data from memory, use (for example):
x/wx 0xf0133fe0,40x/hd db_symtab_spacex/bc termbuf,10x/s stringbuf
for word/halfword/byte access, and hexadecimal/decimal/character/ string display. The number after the comma is the object count. To display the next 0x10 items, simply use:
x ,10Similarly, use
x/ia foofunc,10
to disassemble the first 0x10 instructions of
foofunc, and display them along with their offset
from the beginning of foofunc.
To modify memory, use the write command:
w/b termbuf 0xa 0xb 0w/w 0xf0010030 0 0
The command modifier
(b/h/w)
specifies the size of the data to be written, the first following
expression is the address to write to and the remainder is interpreted
as data to write to successive memory locations.
If you need to know the current registers, use:
show regAlternatively, you can display a single register value by e.g.
p $eaxand modify it by:
set $eax new-valueShould you need to call some kernel functions from DDB, simply say:
call func(arg1, arg2, ...)The return value will be printed.
For a ps(1) style summary of all running processes, use:
psNow you have examined why your kernel failed, and you wish to reboot. Remember that, depending on the severity of previous malfunctioning, not all parts of the kernel might still be working as expected. Perform one of the following actions to shut down and reboot your system:
panicThis will cause your kernel to dump core and reboot, so you can
later analyze the core on a higher level with gdb.
This command
usually must be followed by another continue
statement.
call boot(0)Might be a good way to cleanly shut down the running system,
sync() all disks, and finally, in some cases,
reboot. As long as
the disk and filesystem interfaces of the kernel are not damaged, this
could be a good way for an almost clean shutdown.
call cpu_reset()This is the final way out of disaster and almost the same as hitting the Big Red Button.
If you need a short command summary, simply type:
helpIt is highly recommended to have a printed copy of the ddb(4) manual page ready for a debugging session. Remember that it is hard to read the on-line manual while single-stepping the kernel.
This feature has been supported since FreeBSD 2.2, and it is actually a very neat one.
GDB has already supported remote debugging for a long time. This is done using a very simple protocol along a serial line. Unlike the other methods described above, you will need two machines for doing this. One is the host providing the debugging environment, including all the sources, and a copy of the kernel binary with all the symbols in it, and the other one is the target machine that simply runs a similar copy of the very same kernel (but stripped of the debugging information).
You should configure the kernel in question with config
-g if building the “traditional” way. If
building the “new” way, make sure that
makeoptions DEBUG=-g is in the configuration.
In both cases, include DDB in the configuration, and
compile it as usual. This gives a large binary, due to the
debugging information. Copy this kernel to the target machine, strip
the debugging symbols off with strip -x, and boot it
using the -d boot option. Connect the serial line
of the target machine that has "flags 080" set on its uart device
to any serial line of the debugging host. See uart(4) for
information on how to set the flags on an uart device.
Now, on the debugging machine, go to the compile directory of the target
kernel, and start gdb:
%kgdb kernelGDB is free software and you are welcome to distribute copies of it under certain conditions; type "show copying" to see the conditions. There is absolutely no warranty for GDB; type "show warranty" for details. GDB 4.16 (i386-unknown-freebsd), Copyright 1996 Free Software Foundation, Inc...(kgdb)
Initialize the remote debugging session (assuming the first serial port is being used) by:
(kgdb)target remote /dev/cuau0
Now, on the target host (the one that entered DDB right before even starting the device probe), type:
Debugger("Boot flags requested debugger")
Stopped at Debugger+0x35: movb $0, edata+0x51bc
db> gdbDDB will respond with:
Next trap will enter GDB remote protocol mode
Every time you type gdb, the mode will be toggled
between remote GDB and local DDB. In order to force a next trap
immediately, simply type s (step). Your hosting GDB
will now gain control over the target kernel:
Remote debugging using /dev/cuau0
Debugger (msg=0xf01b0383 "Boot flags requested debugger")
at ../../i386/i386/db_interface.c:257
(kgdb)You can use this session almost as any other GDB session, including full access to the source, running it in gud-mode inside an Emacs window (which gives you an automatic source code display in another Emacs window), etc.
Since you need a console driver to run DDB on, things are more
complicated if the console driver itself is failing. You might remember
the use of a serial console (either with modified boot blocks, or by
specifying -h at the Boot: prompt),
and hook up a standard terminal onto your first serial port. DDB works
on any configured console driver, including a serial
console.
You may experience so called deadlocks, a situation where
a system stops doing useful work. To provide a helpful bug
report in this situation, use ddb(4) as described in the
previous section. Include the output of ps
and trace for suspected processes in the
report.
If possible, consider doing further investigation. The recipe below is especially useful if you suspect that a deadlock occurs in the VFS layer. Add these options to the kernel configuration file.
makeoptions DEBUG=-g options INVARIANTS options INVARIANT_SUPPORT options WITNESS options WITNESS_SKIPSPIN options DEBUG_LOCKS options DEBUG_VFS_LOCKS options DIAGNOSTIC
When a deadlock occurs, in addition to the output of the
ps command, provide information from the
show pcpu, show allpcpu,
show locks, show alllocks,
show lockedvnods and
alltrace.
To obtain meaningful backtraces for threaded processes, use
thread thread-id to switch to the thread
stack, and do a backtrace with where.
dcons(4) is a very simple console driver that is not directly connected with any physical devices. It just reads and writes characters from and to a buffer in a kernel or loader. Due to its simple nature, it is very useful for kernel debugging, especially with a FireWire® device. Currently, FreeBSD provides two ways to interact with the buffer from outside of the kernel using dconschat(8).
Most FireWire® (IEEE1394) host controllers are based on the OHCI specification that supports physical access to the host memory. This means that once the host controller is initialized, we can access the host memory without the help of software (kernel). We can exploit this facility for interaction with dcons(4). dcons(4) provides similar functionality as a serial console. It emulates two serial ports, one for the console and DDB, the other for GDB. Because remote memory access is fully handled by the hardware, the dcons(4) buffer is accessible even when the system crashes.
FireWire® devices are not limited to those integrated into motherboards. PCI cards exist for desktops, and a cardbus interface can be purchased for laptops.
To enable FireWire® and Dcons support in the kernel of the target machine:
Make sure your kernel supports
dcons,dcons_cromandfirewire.Dconsshould be statically linked with the kernel. Fordcons_cromandfirewire, modules should be OK.Make sure physical DMA is enabled. You may need to add
hw.firewire.phydma_enable=1to/boot/loader.conf.Add options for debugging.
Add
dcons_gdb=1in/boot/loader.confif you use GDB over FireWire®.Enable
dconsin/etc/ttys.Optionally, to force
dconsto be the high-level console, addhw.firewire.dcons_crom.force_console=1toloader.conf.
To enable FireWire® and Dcons support in loader(8) on i386 or amd64:
Add
LOADER_FIREWIRE_SUPPORT=YES in
/etc/make.conf and rebuild
loader(8):
#cd /sys/boot/i386 && make clean && make && make install
To enable dcons(4) as an active low-level
console, add boot_multicons="YES" to
/boot/loader.conf.
Here are a few configuration examples. A sample kernel configuration file would contain:
device dcons device dcons_crom options KDB options DDB options GDB options ALT_BREAK_TO_DEBUGGER
And a sample /boot/loader.conf
would contain:
dcons_crom_load="YES" dcons_gdb=1 boot_multicons="YES" hw.firewire.phydma_enable=1 hw.firewire.dcons_crom.force_console=1
To enable FireWire® support in the kernel on the host machine:
#kldload firewire
Find out the EUI64 (the unique 64
bit identifier) of the FireWire® host controller, and
use fwcontrol(8) or dmesg to
find the EUI64 of the target machine.
Run dconschat(8), with:
#dconschat -e \# -br -G 12345 -t00-11-22-33-44-55-66-77
The following key combinations can be used once dconschat(8) is running:
| ~ . | Disconnect |
| ~ Ctrl+B | ALT BREAK |
| ~ Ctrl+R | RESET target |
| ~ Ctrl+Z | Suspend dconschat |
Attach remote GDB by starting kgdb(1) with a remote debugging session:
kgdb -r :12345 kernelHere are some general tips:
To take full advantage of the speed of FireWire®, disable other slow console drivers:
#conscontrol delete ttyd0 # serial console#conscontrol delete consolectl # video/keyboard
There exists a GDB mode for
emacs(1); this is what you will need to add to your
.emacs:
(setq gud-gdba-command-name "kgdb -a -a -a -r :12345")
(setq gdb-many-windows t)
(xterm-mouse-mode 1)
M-x gdbaAnd for DDD (devel/ddd):
# remote serial protocol LANG=C ddd --debugger kgdb -r :12345 kernel # live core debug LANG=C ddd --debugger kgdb kernel /dev/fwmem0.2
This section provides a brief glossary of compile-time kernel options used for debugging:
options KDB: compiles in the kernel debugger framework. Required foroptions DDBandoptions GDB. Little or no performance overhead. By default, the debugger will be entered on panic instead of an automatic reboot.options KDB_UNATTENDED: change the default value of thedebug.debugger_on_panicsysctl to 0, which controls whether the debugger is entered on panic. Whenoptions KDBis not compiled into the kernel, the behavior is to automatically reboot on panic; when it is compiled into the kernel, the default behavior is to drop into the debugger unlessoptions KDB_UNATTENDEDis compiled in. If you want to leave the kernel debugger compiled into the kernel but want the system to come back up unless you're on-hand to use the debugger for diagnostics, use this option.options KDB_TRACE: change the default value of thedebug.trace_on_panicsysctl to 1, which controls whether the debugger automatically prints a stack trace on panic. Especially if running withoptions KDB_UNATTENDED, this can be helpful to gather basic debugging information on the serial or firewire console while still rebooting to recover.options DDB: compile in support for the console debugger, DDB. This interactive debugger runs on whatever the active low-level console of the system is, which includes the video console, serial console, or firewire console. It provides basic integrated debugging facilities, such as stack tracing, process and thread listing, dumping of lock state, VM state, file system state, and kernel memory management. DDB does not require software running on a second machine or being able to generate a core dump or full debugging kernel symbols, and provides detailed diagnostics of the kernel at run-time. Many bugs can be fully diagnosed using only DDB output. This option depends onoptions KDB.options GDB: compile in support for the remote debugger, GDB, which can operate over serial cable or firewire. When the debugger is entered, GDB may be attached to inspect structure contents, generate stack traces, etc. Some kernel state is more awkward to access than in DDB, which is able to generate useful summaries of kernel state automatically, such as automatically walking lock debugging or kernel memory management structures, and a second machine running the debugger is required. On the other hand, GDB combines information from the kernel source and full debugging symbols, and is aware of full data structure definitions, local variables, and is scriptable. This option is not required to run GDB on a kernel core dump. This option depends onoptions KDB.options BREAK_TO_DEBUGGER,options ALT_BREAK_TO_DEBUGGER: allow a break signal or alternative signal on the console to enter the debugger. If the system hangs without a panic, this is a useful way to reach the debugger. Due to the current kernel locking, a break signal generated on a serial console is significantly more reliable at getting into the debugger, and is generally recommended. This option has little or no performance impact.options INVARIANTS: compile into the kernel a large number of run-time assertion checks and tests, which constantly test the integrity of kernel data structures and the invariants of kernel algorithms. These tests can be expensive, so are not compiled in by default, but help provide useful "fail stop" behavior, in which certain classes of undesired behavior enter the debugger before kernel data corruption occurs, making them easier to debug. Tests include memory scrubbing and use-after-free testing, which is one of the more significant sources of overhead. This option depends onoptions INVARIANT_SUPPORT.options INVARIANT_SUPPORT: many of the tests present inoptions INVARIANTSrequire modified data structures or additional kernel symbols to be defined.options WITNESS: this option enables run-time lock order tracking and verification, and is an invaluable tool for deadlock diagnosis. WITNESS maintains a graph of acquired lock orders by lock type, and checks the graph at each acquire for cycles (implicit or explicit). If a cycle is detected, a warning and stack trace are generated to the console, indicating that a potential deadlock might have occurred. WITNESS is required in order to use theshow locks,show witnessandshow alllocksDDB commands. This debug option has significant performance overhead, which may be somewhat mitigated through the use ofoptions WITNESS_SKIPSPIN. Detailed documentation may be found in witness(4).options WITNESS_SKIPSPIN: disable run-time checking of spinlock lock order with WITNESS. As spin locks are acquired most frequently in the scheduler, and scheduler events occur often, this option can significantly speed up systems running with WITNESS. This option depends onoptions WITNESS.options WITNESS_KDB: change the default value of thedebug.witness.kdbsysctl to 1, which causes WITNESS to enter the debugger when a lock order violation is detected, rather than simply printing a warning. This option depends onoptions WITNESS.options SOCKBUF_DEBUG: perform extensive run-time consistency checking on socket buffers, which can be useful for debugging both socket bugs and race conditions in protocols and device drivers that interact with sockets. This option significantly impacts network performance, and may change the timing in device driver races.options DEBUG_VFS_LOCKS: track lock acquisition points for lockmgr/vnode locks, expanding the amount of information displayed byshow lockedvnodsin DDB. This option has a measurable performance impact.options DEBUG_MEMGUARD: a replacement for the malloc(9) kernel memory allocator that uses the VM system to detect reads or writes from allocated memory after free. Details may be found in memguard(9). This option has a significant performance impact, but can be very helpful in debugging kernel memory corruption bugs.options DIAGNOSTIC: enable additional, more expensive diagnostic tests along the lines ofoptions INVARIANTS.
- 11. x86 Assembly Language Programming
- 11.1. Synopsis
- 11.2. The Tools
- 11.3. System Calls
- 11.4. Return Values
- 11.5. Creating Portable Code
- 11.6. Our First Program
- 11.7. Writing UNIX® Filters
- 11.8. Buffered Input and Output
- 11.9. Command Line Arguments
- 11.10. UNIX® Environment
- 11.11. Working with Files
- 11.12. One-Pointed Mind
- 11.13. Using the FPU
- 11.14. Caveats
- 11.15. Acknowledgements
- 11.1. Synopsis
- 11.2. The Tools
- 11.3. System Calls
- 11.4. Return Values
- 11.5. Creating Portable Code
- 11.6. Our First Program
- 11.7. Writing UNIX® Filters
- 11.8. Buffered Input and Output
- 11.9. Command Line Arguments
- 11.10. UNIX® Environment
- 11.11. Working with Files
- 11.12. One-Pointed Mind
- 11.13. Using the FPU
- 11.14. Caveats
- 11.15. Acknowledgements
This chapter was written by G. Adam Stanislav <[email protected]>.
Assembly language programming under UNIX® is highly undocumented. It is generally assumed that no one would ever want to use it because various UNIX® systems run on different microprocessors, so everything should be written in C for portability.
In reality, C portability is quite a myth. Even C programs need to be modified when ported from one UNIX® to another, regardless of what processor each runs on. Typically, such a program is full of conditional statements depending on the system it is compiled for.
Even if we believe that all of UNIX® software should be written in C, or some other high-level language, we still need assembly language programmers: Who else would write the section of C library that accesses the kernel?
In this chapter I will attempt to show you how you can use assembly language writing UNIX® programs, specifically under FreeBSD.
This chapter does not explain the basics of assembly language. There are enough resources about that (for a complete online course in assembly language, see Randall Hyde's Art of Assembly Language; or if you prefer a printed book, take a look at Jeff Duntemann's Assembly Language Step-by-Step). However, once the chapter is finished, any assembly language programmer will be able to write programs for FreeBSD quickly and efficiently.
Copyright © 2000-2001 G. Adam Stanislav. All rights reserved.
The most important tool for assembly language programming is the assembler, the software that converts assembly language code into machine language.
Two very different assemblers are available for FreeBSD. One is as(1), which uses the traditional UNIX® assembly language syntax. It comes with the system.
The other is /usr/ports/devel/nasm. It uses the Intel syntax. Its main advantage is that it can assemble code for many operating systems. It needs to be installed separately, but is completely free.
This chapter uses nasm syntax because most assembly language programmers coming to FreeBSD from other operating systems will find it easier to understand. And, because, quite frankly, that is what I am used to.
The output of the assembler, like that of any compiler, needs to be linked to form an executable file.
The standard ld(1) linker comes with FreeBSD. It works with the code assembled with either assembler.
By default, the FreeBSD kernel uses the C calling
convention. Further, although the kernel is accessed
using int 80h,
it is assumed the program will call a function that
issues int 80h, rather than
issuing int 80h directly.
This convention is very convenient, and quite superior to the Microsoft® convention used by MS-DOS®. Why? Because the UNIX® convention allows any program written in any language to access the kernel.
An assembly language program can do that as well. For example, we could open a file:
kernel: int 80h ; Call kernel ret open: push dword mode push dword flags push dword path mov eax, 5 call kernel add esp, byte 12 ret
This is a very clean and portable way of coding. If you need to port the code to a UNIX® system which uses a different interrupt, or a different way of passing parameters, all you need to change is the kernel procedure.
But assembly language programmers like to shave off cycles. The above example
requires a call/ret combination.
We can eliminate it by
pushing an extra dword:
open: push dword mode push dword flags push dword path mov eax, 5 push eax ; Or any other dword int 80h add esp, byte 16
The 5 that we have placed in
EAX identifies
the kernel function, in this case open.
FreeBSD is an extremely flexible system. It offers other ways of calling the kernel. For it to work, however, the system must have Linux emulation installed.
Linux is a UNIX® like system. However, its kernel uses the same
system-call convention of passing parameters in registers
MS-DOS® does. As with the UNIX® convention,
the function number is placed in EAX.
The parameters, however, are not passed on the stack but in
EBX, ECX, EDX, ESI, EDI, EBP:
open: mov eax, 5 mov ebx, path mov ecx, flags mov edx, mode int 80h
This convention has a great disadvantage over
the UNIX® way, at least as far as assembly language programming
is concerned: Every time you make a kernel call
you must push the registers, then
pop them later. This makes your code
bulkier and slower. Nevertheless, FreeBSD gives
you a choice.
If you do choose the Linux convention, you must let the system know about it. After your program is assembled and linked, you need to brand the executable:
%brandelf -t Linuxfilename
If you are coding specifically for FreeBSD, you should always use the UNIX® convention: It is faster, you can store global variables in registers, you do not have to brand the executable, and you do not impose the installation of the Linux emulation package on the target system.
If you want to create portable code that can also run on Linux, you will probably still want to give the FreeBSD users as efficient a code as possible. I will show you how you can accomplish that after I have explained the basics.
To tell the kernel which system service you are calling,
place its number in EAX. Of course, you need
to know what the number is.
The numbers are listed in syscalls.
locate syscalls finds this file
in several different formats, all produced automatically
from syscalls.master.
You can find the master file for the default UNIX® calling
convention in
/usr/src/sys/kern/syscalls.master.
If you need to use the other convention implemented
in the Linux emulation mode, read
/usr/src/sys/i386/linux/syscalls.master.
Note:
Not only do FreeBSD and Linux use different calling conventions, they sometimes use different numbers for the same functions.
syscalls.master describes how
the call is to be made:
0 STD NOHIDE { int nosys(void); } syscall nosys_args int
1 STD NOHIDE { void exit(int rval); } exit rexit_args void
2 STD POSIX { int fork(void); }
3 STD POSIX { ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t nbyte); }
4 STD POSIX { ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t nbyte); }
5 STD POSIX { int open(char *path, int flags, int mode); }
6 STD POSIX { int close(int fd); }
etc...
It is the leftmost column that tells us the number to place in
EAX.
The rightmost column tells us what parameters to
push. They are pushed
from right to left.
For example, to open a file, we need
to push the mode first,
then flags, then the address at which
the path is stored.
A system call would not be useful most of the time if it did not return some kind of a value: The file descriptor of an open file, the number of bytes read to a buffer, the system time, etc.
Additionally, the system needs to inform us if an error occurs: A file does not exist, system resources are exhausted, we passed an invalid parameter, etc.
The traditional place to look for information about various system calls under UNIX® systems are the manual pages. FreeBSD describes its system calls in section 2, sometimes in section 3.
For example, open(2) says:
If successful,
open()returns a non-negative integer, termed a file descriptor. It returns-1on failure, and setserrnoto indicate the error.
The assembly language programmer new to UNIX® and FreeBSD will
immediately ask the puzzling question: Where is
errno and how do I get to it?
Note:
The information presented in the manual pages applies to C programs. The assembly language programmer needs additional information.
Unfortunately, it depends... For most system calls it is
in EAX, but not for all.
A good rule of thumb,
when working with a system call for
the first time, is to look for
the return value in EAX.
If it is not there, you
need further research.
Note:
I am aware of one system call that returns the value in
EDX: SYS_fork. All others
I have worked with use EAX.
But I have not worked with them all yet.
Tip:
If you cannot find the answer here or anywhere else, study libc source code and see how it interfaces with the kernel.
Actually, nowhere...
errno is part of the C language, not the
UNIX® kernel. When accessing kernel services directly, the
error code is returned in EAX,
the same register the proper
return value generally ends up in.
This makes perfect sense. If there is no error, there is no error code. If there is an error, there is no return value. One register can contain either.
When using the standard FreeBSD calling convention,
the carry flag is cleared upon success,
set upon failure.
When using the Linux emulation mode, the signed
value in EAX is non-negative upon success,
and contains the return value. In case of an error, the value
is negative, i.e., -errno.
Portability is generally not one of the strengths of assembly language. Yet, writing assembly language programs for different platforms is possible, especially with nasm. I have written assembly language libraries that can be assembled for such different operating systems as Windows® and FreeBSD.
It is all the more possible when you want your code to run on two platforms which, while different, are based on similar architectures.
For example, FreeBSD is UNIX®, Linux is UNIX® like. I only mentioned three differences between them (from an assembly language programmer's perspective): The calling convention, the function numbers, and the way of returning values.
In many cases the function numbers are the same. However, even when they are not, the problem is easy to deal with: Instead of using numbers in your code, use constants which you have declared differently depending on the target architecture:
%ifdef LINUX %define SYS_execve 11 %else %define SYS_execve 59 %endif
Both, the calling convention, and the return value (the
errno problem) can be resolved with macros:
%ifdef LINUX %macro system 0 call kernel %endmacro align 4 kernel: push ebx push ecx push edx push esi push edi push ebp mov ebx, [esp+32] mov ecx, [esp+36] mov edx, [esp+40] mov esi, [esp+44] mov ebp, [esp+48] int 80h pop ebp pop edi pop esi pop edx pop ecx pop ebx or eax, eax js .errno clc ret .errno: neg eax stc ret %else %macro system 0 int 80h %endmacro %endif
The above solutions can handle most cases of writing code portable between FreeBSD and Linux. Nevertheless, with some kernel services the differences are deeper.
In that case, you need to write two different handlers for those particular system calls, and use conditional assembly. Luckily, most of your code does something other than calling the kernel, so usually you will only need a few such conditional sections in your code.
You can avoid portability issues in your main code altogether by writing a library of system calls. Create a separate library for FreeBSD, a different one for Linux, and yet other libraries for more operating systems.
In your library, write a separate function (or procedure, if
you prefer the traditional assembly language terminology) for each system
call. Use the C calling convention of passing parameters.
But still use EAX to pass the call number in.
In that case, your FreeBSD library can be very simple, as
many seemingly different functions can be just labels to
the same code:
sys.open: sys.close: [etc...] int 80h ret
Your Linux library will require more different functions. But even here you can group system calls using the same number of parameters:
sys.exit: sys.close: [etc... one-parameter functions] push ebx mov ebx, [esp+12] int 80h pop ebx jmp sys.return ... sys.return: or eax, eax js sys.err clc ret sys.err: neg eax stc ret
The library approach may seem inconvenient at first because it requires you to produce a separate file your code depends on. But it has many advantages: For one, you only need to write it once and can use it for all your programs. You can even let other assembly language programmers use it, or perhaps use one written by someone else. But perhaps the greatest advantage of the library is that your code can be ported to other systems, even by other programmers, by simply writing a new library without any changes to your code.
If you do not like the idea of having a library, you can at least place all your system calls in a separate assembly language file and link it with your main program. Here, again, all porters have to do is create a new object file to link with your main program.
If you are releasing your software as (or with) source code, you can use macros and place them in a separate file, which you include in your code.
Porters of your software will simply write a new include file. No library or external object file is necessary, yet your code is portable without any need to edit the code.
Note:
This is the approach we will use throughout this chapter.
We will name our include file system.inc, and
add to it whenever we deal with a new system call.
We can start our system.inc by declaring the
standard file descriptors:
%define stdin 0 %define stdout 1 %define stderr 2
Next, we create a symbolic name for each system call:
%define SYS_nosys 0 %define SYS_exit 1 %define SYS_fork 2 %define SYS_read 3 %define SYS_write 4 ; [etc...]
We add a short, non-global procedure with a long name, so we do not accidentally reuse the name in our code:
section .text align 4 access.the.bsd.kernel: int 80h ret
We create a macro which takes one argument, the syscall number:
%macro system 1 mov eax, %1 call access.the.bsd.kernel %endmacro
Finally, we create macros for each syscall. These macros take no arguments.
%macro sys.exit 0 system SYS_exit %endmacro %macro sys.fork 0 system SYS_fork %endmacro %macro sys.read 0 system SYS_read %endmacro %macro sys.write 0 system SYS_write %endmacro ; [etc...]
Go ahead, enter it into your editor and save it as
system.inc. We will add more to it as we
discuss more syscalls.
We are now ready for our first program, the mandatory Hello, World!
1: %include 'system.inc' 2: 3: section .data 4: hello db 'Hello, World!', 0Ah 5: hbytes equ $-hello 6: 7: section .text 8: global _start 9: _start: 10: push dword hbytes 11: push dword hello 12: push dword stdout 13: sys.write 14: 15: push dword 0 16: sys.exit
Here is what it does: Line 1 includes the defines, the macros,
and the code from system.inc.
Lines 3-5 are the data: Line 3 starts the data section/segment.
Line 4 contains the string "Hello, World!" followed by a new
line (0Ah). Line 5 creates a constant that contains
the length of the string from line 4 in bytes.
Lines 7-16 contain the code. Note that FreeBSD uses the elf
file format for its executables, which requires every
program to start at the point labeled _start (or, more
precisely, the linker expects that). This label has to be
global.
Lines 10-13 ask the system to write hbytes bytes
of the hello string to stdout.
Lines 15-16 ask the system to end the program with the return
value of 0. The SYS_exit syscall never
returns, so the code ends there.
Note:
If you have come to UNIX® from MS-DOS®
assembly language background, you may be used to writing directly
to the video hardware. You will never have to worry about
this in FreeBSD, or any other flavor of UNIX®. As far as
you are concerned, you are writing to a file known as
stdout. This can be the video screen, or
a telnet terminal, or an actual file,
or even the input of another program. Which one it is,
is for the system to figure out.
Type the code (except the line numbers) in an editor, and save
it in a file named hello.asm. You need
nasm to assemble it.
If you do not have nasm, type:
%suPassword:your root password#cd /usr/ports/devel/nasm#make install#exit%
You may type make install clean instead of just
make install if you do not want to keep
nasm source code.
Either way, FreeBSD will automatically download nasm from the Internet, compile it, and install it on your system.
Note:
If your system is not FreeBSD, you need to get nasm from its home page. You can still use it to assemble FreeBSD code.
Now you can assemble, link, and run the code:
%nasm -f elf hello.asm%ld -s -o hello hello.o%./helloHello, World!%
A common type of UNIX® application is a filter—a program
that reads data from the stdin, processes it
somehow, then writes the result to stdout.
In this chapter, we shall develop a simple filter, and
learn how to read from stdin and write to
stdout. This filter will convert each byte
of its input into a hexadecimal number followed by a
blank space.
%include 'system.inc' section .data hex db '0123456789ABCDEF' buffer db 0, 0, ' ' section .text global _start _start: ; read a byte from stdin push dword 1 push dword buffer push dword stdin sys.read add esp, byte 12 or eax, eax je .done ; convert it to hex movzx eax, byte [buffer] mov edx, eax shr dl, 4 mov dl, [hex+edx] mov [buffer], dl and al, 0Fh mov al, [hex+eax] mov [buffer+1], al ; print it push dword 3 push dword buffer push dword stdout sys.write add esp, byte 12 jmp short _start .done: push dword 0 sys.exit
In the data section we create an array called hex.
It contains the 16 hexadecimal digits in ascending order.
The array is followed by a buffer which we will use for
both input and output. The first two bytes of the buffer
are initially set to 0. This is where we will write
the two hexadecimal digits (the first byte also is
where we will read the input). The third byte is a
space.
The code section consists of four parts: Reading the byte, converting it to a hexadecimal number, writing the result, and eventually exiting the program.
To read the byte, we ask the system to read one byte
from stdin, and store it in the first byte
of the buffer. The system returns the number
of bytes read in EAX. This will be 1
while data is coming, or 0, when no more input
data is available. Therefore, we check the value of
EAX. If it is 0,
we jump to .done, otherwise we continue.
Note:
For simplicity sake, we are ignoring the possibility of an error condition at this time.
The hexadecimal conversion reads the byte from the
buffer into EAX, or actually just
AL, while clearing the remaining bits of
EAX to zeros. We also copy the byte to
EDX because we need to convert the upper
four bits (nibble) separately from the lower
four bits. We store the result in the first two
bytes of the buffer.
Next, we ask the system to write the three bytes
of the buffer, i.e., the two hexadecimal digits and
the blank space, to stdout. We then
jump back to the beginning of the program and
process the next byte.
Once there is no more input left, we ask the system to exit our program, returning a zero, which is the traditional value meaning the program was successful.
Go ahead, and save the code in a file named hex.asm,
then type the following (the ^D means press the
control key and type D while holding the
control key down):
%nasm -f elf hex.asm%ld -s -o hex hex.o%./hexHello, World!48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21 0AHere I come!48 65 72 65 20 49 20 63 6F 6D 65 21 0A^D%
Note:
If you are migrating to UNIX® from MS-DOS®,
you may be wondering why each line ends with 0A
instead of 0D 0A.
This is because UNIX® does not use the cr/lf convention, but
a "new line" convention, which is 0A in hexadecimal.
Can we improve this? Well, for one, it is a bit confusing because
once we have converted a line of text, our input no longer
starts at the beginning of the line. We can modify it to print
a new line instead of a space after each 0A:
%include 'system.inc' section .data hex db '0123456789ABCDEF' buffer db 0, 0, ' ' section .text global _start _start: mov cl, ' ' .loop: ; read a byte from stdin push dword 1 push dword buffer push dword stdin sys.read add esp, byte 12 or eax, eax je .done ; convert it to hex movzx eax, byte [buffer] mov [buffer+2], cl cmp al, 0Ah jne .hex mov [buffer+2], al .hex: mov edx, eax shr dl, 4 mov dl, [hex+edx] mov [buffer], dl and al, 0Fh mov al, [hex+eax] mov [buffer+1], al ; print it push dword 3 push dword buffer push dword stdout sys.write add esp, byte 12 jmp short .loop .done: push dword 0 sys.exit
We have stored the space in the CL register. We can
do this safely because, unlike Microsoft® Windows®, UNIX® system
calls do not modify the value of any register they do not use
to return a value in.
That means we only need to set CL once. We have, therefore,
added a new label .loop and jump to it for the next byte
instead of jumping at _start. We have also added the
.hex label so we can either have a blank space or a
new line as the third byte of the buffer.
Once you have changed hex.asm to reflect
these changes, type:
%nasm -f elf hex.asm%ld -s -o hex hex.o%./hexHello, World!48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21 0AHere I come!48 65 72 65 20 49 20 63 6F 6D 65 21 0A^D%
That looks better. But this code is quite inefficient! We are making a system call for every single byte twice (once to read it, another time to write the output).
We can improve the efficiency of our code by buffering our input and output. We create an input buffer and read a whole sequence of bytes at one time. Then we fetch them one by one from the buffer.
We also create an output buffer. We store our output in it until
it is full. At that time we ask the kernel to write the contents
of the buffer to stdout.
The program ends when there is no more input. But we still need
to ask the kernel to write the contents of our output buffer
to stdout one last time, otherwise some of our output
would make it to the output buffer, but never be sent out.
Do not forget that, or you will be wondering why some of your
output is missing.
%include 'system.inc' %define BUFSIZE 2048 section .data hex db '0123456789ABCDEF' section .bss ibuffer resb BUFSIZE obuffer resb BUFSIZE section .text global _start _start: sub eax, eax sub ebx, ebx sub ecx, ecx mov edi, obuffer .loop: ; read a byte from stdin call getchar ; convert it to hex mov dl, al shr al, 4 mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, dl and al, 0Fh mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, ' ' cmp dl, 0Ah jne .put mov al, dl .put: call putchar jmp short .loop align 4 getchar: or ebx, ebx jne .fetch call read .fetch: lodsb dec ebx ret read: push dword BUFSIZE mov esi, ibuffer push esi push dword stdin sys.read add esp, byte 12 mov ebx, eax or eax, eax je .done sub eax, eax ret align 4 .done: call write ; flush output buffer push dword 0 sys.exit align 4 putchar: stosb inc ecx cmp ecx, BUFSIZE je write ret align 4 write: sub edi, ecx ; start of buffer push ecx push edi push dword stdout sys.write add esp, byte 12 sub eax, eax sub ecx, ecx ; buffer is empty now ret
We now have a third section in the source code, named
.bss. This section is not included in our
executable file, and, therefore, cannot be initialized. We use
resb instead of db.
It simply reserves the requested size of uninitialized memory
for our use.
We take advantage of the fact that the system does not modify the
registers: We use registers for what, otherwise, would have to be
global variables stored in the .data section. This is
also why the UNIX® convention of passing parameters to system calls
on the stack is superior to the Microsoft convention of passing
them in the registers: We can keep the registers for our own use.
We use EDI and ESI as pointers to the next byte
to be read from or written to. We use EBX and
ECX to keep count of the number of bytes in the
two buffers, so we know when to dump the output to, or read more
input from, the system.
Let us see how it works now:
%nasm -f elf hex.asm%ld -s -o hex hex.o%./hexHello, World!Here I come!48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21 0A 48 65 72 65 20 49 20 63 6F 6D 65 21 0A^D%
Not what you expected? The program did not print the output
until we pressed ^D. That is easy to fix by
inserting three lines of code to write the output every time
we have converted a new line to 0A. I have marked
the three lines with > (do not copy the > in your
hex.asm).
%include 'system.inc' %define BUFSIZE 2048 section .data hex db '0123456789ABCDEF' section .bss ibuffer resb BUFSIZE obuffer resb BUFSIZE section .text global _start _start: sub eax, eax sub ebx, ebx sub ecx, ecx mov edi, obuffer .loop: ; read a byte from stdin call getchar ; convert it to hex mov dl, al shr al, 4 mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, dl and al, 0Fh mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, ' ' cmp dl, 0Ah jne .put mov al, dl .put: call putchar > cmp al, 0Ah > jne .loop > call write jmp short .loop align 4 getchar: or ebx, ebx jne .fetch call read .fetch: lodsb dec ebx ret read: push dword BUFSIZE mov esi, ibuffer push esi push dword stdin sys.read add esp, byte 12 mov ebx, eax or eax, eax je .done sub eax, eax ret align 4 .done: call write ; flush output buffer push dword 0 sys.exit align 4 putchar: stosb inc ecx cmp ecx, BUFSIZE je write ret align 4 write: sub edi, ecx ; start of buffer push ecx push edi push dword stdout sys.write add esp, byte 12 sub eax, eax sub ecx, ecx ; buffer is empty now ret
Now, let us see how it works:
%nasm -f elf hex.asm%ld -s -o hex hex.o%./hexHello, World!48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21 0AHere I come!48 65 72 65 20 49 20 63 6F 6D 65 21 0A^D%
Not bad for a 644-byte executable, is it!
Note:
This approach to buffered input/output still contains a hidden danger. I will discuss—and fix—it later, when I talk about the dark side of buffering.
Warning:
This may be a somewhat advanced topic, mostly of interest to programmers familiar with the theory of compilers. If you wish, you may skip to the next section, and perhaps read this later.
While our sample program does not require it, more sophisticated filters often need to look ahead. In other words, they may need to see what the next character is (or even several characters). If the next character is of a certain value, it is part of the token currently being processed. Otherwise, it is not.
For example, you may be parsing the input stream for a textual string (e.g., when implementing a language compiler): If a character is followed by another character, or perhaps a digit, it is part of the token you are processing. If it is followed by white space, or some other value, then it is not part of the current token.
This presents an interesting problem: How to return the next character back to the input stream, so it can be read again later?
One possible solution is to store it in a character variable,
then set a flag. We can modify getchar to check the flag,
and if it is set, fetch the byte from that variable instead of the
input buffer, and reset the flag. But, of course, that slows us
down.
The C language has an ungetc() function, just for that
purpose. Is there a quick way to implement it in our code?
I would like you to scroll back up and take a look at the
getchar procedure and see if you can find a nice and
fast solution before reading the next paragraph. Then come back
here and see my own solution.
The key to returning a character back to the stream is in how we are getting the characters to start with:
First we check if the buffer is empty by testing the value
of EBX. If it is zero, we call the
read procedure.
If we do have a character available, we use lodsb, then
decrease the value of EBX. The lodsb
instruction is effectively identical to:
mov al, [esi] inc esi
The byte we have fetched remains in the buffer until the next
time read is called. We do not know when that happens,
but we do know it will not happen until the next call to
getchar. Hence, to "return" the last-read byte back
to the stream, all we have to do is decrease the value of
ESI and increase the value of EBX:
ungetc: dec esi inc ebx ret
But, be careful! We are perfectly safe doing this if our look-ahead
is at most one character at a time. If we are examining more than
one upcoming character and call ungetc several times
in a row, it will work most of the time, but not all the time
(and will be tough to debug). Why?
Because as long as getchar does not have to call
read, all of the pre-read bytes are still in the buffer,
and our ungetc works without a glitch. But the moment
getchar calls read,
the contents of the buffer change.
We can always rely on ungetc working properly on the last
character we have read with getchar, but not on anything
we have read before that.
If your program reads more than one byte ahead, you have at least two choices:
If possible, modify the program so it only reads one byte ahead. This is the simplest solution.
If that option is not available, first of all determine the maximum
number of characters your program needs to return to the input
stream at one time. Increase that number slightly, just to be
sure, preferably to a multiple of 16—so it aligns nicely.
Then modify the .bss section of your code, and create
a small "spare" buffer right before your input buffer,
something like this:
section .bss resb 16 ; or whatever the value you came up with ibuffer resb BUFSIZE obuffer resb BUFSIZE
You also need to modify your ungetc to pass the value
of the byte to unget in AL:
ungetc: dec esi inc ebx mov [esi], al ret
With this modification, you can call ungetc
up to 17 times in a row safely (the first call will still
be within the buffer, the remaining 16 may be either within
the buffer or within the "spare").
Our hex program will be more useful if it can read the names of an input and output file from its command line, i.e., if it can process the command line arguments. But... Where are they?
Before a UNIX® system starts a program, it pushes some
data on the stack, then jumps at the _start
label of the program. Yes, I said jumps, not calls. That means the
data can be accessed by reading [esp+offset],
or by simply popping it.
The value at the top of the stack contains the number of
command line arguments. It is traditionally called
argc, for "argument count."
Command line arguments follow next, all argc of them.
These are typically referred to as argv, for
"argument value(s)." That is, we get argv[0],
argv[1], ...,
argv[argc-1]. These are not the actual
arguments, but pointers to arguments, i.e., memory addresses of
the actual arguments. The arguments themselves are
NUL-terminated character strings.
The argv list is followed by a NULL pointer,
which is simply a 0. There is more, but this is
enough for our purposes right now.
Note:
If you have come from the MS-DOS® programming environment, the main difference is that each argument is in a separate string. The second difference is that there is no practical limit on how many arguments there can be.
Armed with this knowledge, we are almost ready for the next
version of hex.asm. First, however, we need to
add a few lines to system.inc:
First, we need to add two new entries to our list of system call numbers:
%define SYS_open 5 %define SYS_close 6
Then we add two new macros at the end of the file:
%macro sys.open 0 system SYS_open %endmacro %macro sys.close 0 system SYS_close %endmacro
Here, then, is our modified source code:
%include 'system.inc' %define BUFSIZE 2048 section .data fd.in dd stdin fd.out dd stdout hex db '0123456789ABCDEF' section .bss ibuffer resb BUFSIZE obuffer resb BUFSIZE section .text align 4 err: push dword 1 ; return failure sys.exit align 4 global _start _start: add esp, byte 8 ; discard argc and argv[0] pop ecx jecxz .init ; no more arguments ; ECX contains the path to input file push dword 0 ; O_RDONLY push ecx sys.open jc err ; open failed add esp, byte 8 mov [fd.in], eax pop ecx jecxz .init ; no more arguments ; ECX contains the path to output file push dword 420 ; file mode (644 octal) push dword 0200h | 0400h | 01h ; O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY push ecx sys.open jc err add esp, byte 12 mov [fd.out], eax .init: sub eax, eax sub ebx, ebx sub ecx, ecx mov edi, obuffer .loop: ; read a byte from input file or stdin call getchar ; convert it to hex mov dl, al shr al, 4 mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, dl and al, 0Fh mov al, [hex+eax] call putchar mov al, ' ' cmp dl, 0Ah jne .put mov al, dl .put: call putchar cmp al, dl jne .loop call write jmp short .loop align 4 getchar: or ebx, ebx jne .fetch call read .fetch: lodsb dec ebx ret read: push dword BUFSIZE mov esi, ibuffer push esi push dword [fd.in] sys.read add esp, byte 12 mov ebx, eax or eax, eax je .done sub eax, eax ret align 4 .done: call write ; flush output buffer ; close files push dword [fd.in] sys.close push dword [fd.out] sys.close ; return success push dword 0 sys.exit align 4 putchar: stosb inc ecx cmp ecx, BUFSIZE je write ret align 4 write: sub edi, ecx ; start of buffer push ecx push edi push dword [fd.out] sys.write add esp, byte 12 sub eax, eax sub ecx, ecx ; buffer is empty now ret
In our .data section we now have two new variables,
fd.in and fd.out. We store the input and
output file descriptors here.
In the .text section we have replaced the references
to stdin and stdout with
[fd.in] and [fd.out].
The .text section now starts with a simple error
handler, which does nothing but exit the program with a return
value of 1.
The error handler is before _start so we are
within a short distance from where the errors occur.
Naturally, the program execution still begins at _start.
First, we remove argc and argv[0] from the
stack: They are of no interest to us (in this program, that is).
We pop argv[1] to ECX. This
register is particularly suited for pointers, as we can handle
NULL pointers with jecxz. If argv[1]
is not NULL, we try to open the file named in the first
argument. Otherwise, we continue the program as before: Reading
from stdin, writing to stdout.
If we fail to open the input file (e.g., it does not exist),
we jump to the error handler and quit.
If all went well, we now check for the second argument. If
it is there, we open the output file. Otherwise, we send
the output to stdout. If we fail to open the output
file (e.g., it exists and we do not have the write permission),
we, again, jump to the error handler.
The rest of the code is the same as before, except we close
the input and output files before exiting, and, as mentioned,
we use [fd.in] and [fd.out].
Our executable is now a whopping 768 bytes long.
Can we still improve it? Of course! Every program can be improved. Here are a few ideas of what we could do:
Have our error handler print a message to
stderr.Add error handlers to the
readandwritefunctions.Close
stdinwhen we open an input file,stdoutwhen we open an output file.Add command line switches, such as
-iand-o, so we can list the input and output files in any order, or perhaps read fromstdinand write to a file.Print a usage message if command line arguments are incorrect.
I shall leave these enhancements as an exercise to the reader: You already know everything you need to know to implement them.
An important UNIX® concept is the environment, which is defined by environment variables. Some are set by the system, others by you, yet others by the shell, or any program that loads another program.
I said earlier that when a program starts executing, the stack
contains argc followed by the NULL-terminated
argv array, followed by something else. The
"something else" is the environment, or,
to be more precise, a NULL-terminated array of pointers to
environment variables. This is often referred
to as env.
The structure of env is the same as that of
argv, a list of memory addresses followed by a
NULL (0). In this case, there is no
"envc"—we figure out where the array ends
by searching for the final NULL.
The variables usually come in the name=value
format, but sometimes the =value part
may be missing. We need to account for that possibility.
I could just show you some code that prints the environment the same way the UNIX® env command does. But I thought it would be more interesting to write a simple assembly language CGI utility.
I have a detailed CGI tutorial on my web site, but here is a very quick overview of CGI:
The web server communicates with the CGI program by setting environment variables.
The CGI program sends its output to
stdout. The web server reads it from there.It must start with an HTTP header followed by two blank lines.
It then prints the HTML code, or whatever other type of data it is producing.
Note:
While certain environment variables use standard names, others vary, depending on the web server. That makes webvars quite a useful diagnostic tool.
Our webvars program, then, must send out the HTTP header followed by some HTML mark-up. It then must read the environment variables one by one and send them out as part of the HTML page.
The code follows. I placed comments and explanations right inside the code:
;;;;;;; webvars.asm ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; ; Copyright (c) 2000 G. Adam Stanislav ; All rights reserved. ; ; Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without ; modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions ; are met: ; 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright ; notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. ; 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright ; notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the ; documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. ; ; THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND ; ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE ; IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ; ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE ; FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL ; DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS ; OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) ; HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT ; LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY ; OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF ; SUCH DAMAGE. ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; ; Version 1.0 ; ; Started: 8-Dec-2000 ; Updated: 8-Dec-2000 ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; %include 'system.inc' section .data http db 'Content-type: text/html', 0Ah, 0Ah db '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>', 0Ah db '<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C/DTD XHTML Strict//EN" ' db '"DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">', 0Ah db '<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" ' db 'xml.lang="en" lang="en">', 0Ah db '<head>', 0Ah db '<title>Web Environment</title>', 0Ah db '<meta name="author" content="G. Adam Stanislav" />', 0Ah db '</head>', 0Ah, 0Ah db '<body bgcolor="#ffffff" text="#000000" link="#0000ff" ' db 'vlink="#840084" alink="#0000ff">', 0Ah db '<div class="webvars">', 0Ah db '<h1>Web Environment</h1>', 0Ah db '<p>The following <b>environment variables</b> are defined ' db 'on this web server:</p>', 0Ah, 0Ah db '<table align="center" width="80" border="0" cellpadding="10" ' db 'cellspacing="0" class="webvars">', 0Ah httplen equ $-http left db '<tr>', 0Ah db '<td class="name"><tt>' leftlen equ $-left middle db '</tt></td>', 0Ah db '<td class="value"><tt><b>' midlen equ $-middle undef db '<i>(undefined)</i>' undeflen equ $-undef right db '</b></tt></td>', 0Ah db '</tr>', 0Ah rightlen equ $-right wrap db '</table>', 0Ah db '</div>', 0Ah db '</body>', 0Ah db '</html>', 0Ah, 0Ah wraplen equ $-wrap section .text global _start _start: ; First, send out all the http and xhtml stuff that is ; needed before we start showing the environment push dword httplen push dword http push dword stdout sys.write ; Now find how far on the stack the environment pointers ; are. We have 12 bytes we have pushed before "argc" mov eax, [esp+12] ; We need to remove the following from the stack: ; ; The 12 bytes we pushed for sys.write ; The 4 bytes of argc ; The EAX*4 bytes of argv ; The 4 bytes of the NULL after argv ; ; Total: ; 20 + eax * 4 ; ; Because stack grows down, we need to ADD that many bytes ; to ESP. lea esp, [esp+20+eax*4] cld ; This should already be the case, but let's be sure. ; Loop through the environment, printing it out .loop: pop edi or edi, edi ; Done yet? je near .wrap ; Print the left part of HTML push dword leftlen push dword left push dword stdout sys.write ; It may be tempting to search for the '=' in the env string next. ; But it is possible there is no '=', so we search for the ; terminating NUL first. mov esi, edi ; Save start of string sub ecx, ecx not ecx ; ECX = FFFFFFFF sub eax, eax repne scasb not ecx ; ECX = string length + 1 mov ebx, ecx ; Save it in EBX ; Now is the time to find '=' mov edi, esi ; Start of string mov al, '=' repne scasb not ecx add ecx, ebx ; Length of name push ecx push esi push dword stdout sys.write ; Print the middle part of HTML table code push dword midlen push dword middle push dword stdout sys.write ; Find the length of the value not ecx lea ebx, [ebx+ecx-1] ; Print "undefined" if 0 or ebx, ebx jne .value mov ebx, undeflen mov edi, undef .value: push ebx push edi push dword stdout sys.write ; Print the right part of the table row push dword rightlen push dword right push dword stdout sys.write ; Get rid of the 60 bytes we have pushed add esp, byte 60 ; Get the next variable jmp .loop .wrap: ; Print the rest of HTML push dword wraplen push dword wrap push dword stdout sys.write ; Return success push dword 0 sys.exit
This code produces a 1,396-byte executable. Most of it is data, i.e., the HTML mark-up we need to send out.
Assemble and link it as usual:
%nasm -f elf webvars.asm%ld -s -o webvars webvars.o
To use it, you need to upload webvars to your
web server. Depending on how your web server is set up, you
may have to store it in a special cgi-bin directory,
or perhaps rename it with a .cgi extension.
Then you need to use your browser to view its output.
To see its output on my web server, please go to
http://www.int80h.org/webvars/.
If curious about the additional environment variables
present in a password protected web directory, go to
http://www.int80h.org/private/,
using the name asm and password
programmer.
We have already done some basic file work: We know how to open and close them, how to read and write them using buffers. But UNIX® offers much more functionality when it comes to files. We will examine some of it in this section, and end up with a nice file conversion utility.
Indeed, let us start at the end, that is, with the file conversion utility. It always makes programming easier when we know from the start what the end product is supposed to do.
One of the first programs I wrote for UNIX® was tuc, a text-to-UNIX® file converter. It converts a text file from other operating systems to a UNIX® text file. In other words, it changes from different kind of line endings to the newline convention of UNIX®. It saves the output in a different file. Optionally, it converts a UNIX® text file to a DOS text file.
I have used tuc extensively, but always only to convert from some other OS to UNIX®, never the other way. I have always wished it would just overwrite the file instead of me having to send the output to a different file. Most of the time, I end up using it like this:
%tucmyfile tempfile%mvtempfile myfile
It would be nice to have a ftuc, i.e., fast tuc, and use it like this:
%ftucmyfile
In this chapter, then, we will write ftuc in assembly language (the original tuc is in C), and study various file-oriented kernel services in the process.
At first sight, such a file conversion is very simple: All you have to do is strip the carriage returns, right?
If you answered yes, think again: That approach will work most of the time (at least with MS DOS text files), but will fail occasionally.
The problem is that not all non UNIX® text files end their line with the carriage return / line feed sequence. Some use carriage returns without line feeds. Others combine several blank lines into a single carriage return followed by several line feeds. And so on.
A text file converter, then, must be able to handle any possible line endings:
carriage return / line feed
carriage return
line feed / carriage return
line feed
It should also handle files that use some kind of a combination of the above (e.g., carriage return followed by several line feeds).
The problem is easily solved by the use of a technique called finite state machine, originally developed by the designers of digital electronic circuits. A finite state machine is a digital circuit whose output is dependent not only on its input but on its previous input, i.e., on its state. The microprocessor is an example of a finite state machine: Our assembly language code is assembled to machine language in which some assembly language code produces a single byte of machine language, while others produce several bytes. As the microprocessor fetches the bytes from the memory one by one, some of them simply change its state rather than produce some output. When all the bytes of the op code are fetched, the microprocessor produces some output, or changes the value of a register, etc.
Because of that, all software is essentially a sequence of state instructions for the microprocessor. Nevertheless, the concept of finite state machine is useful in software design as well.
Our text file converter can be designed as a finite state machine with three possible states. We could call them states 0-2, but it will make our life easier if we give them symbolic names:
ordinary
cr
lf
Our program will start in the ordinary state. During this state, the program action depends on its input as follows:
If the input is anything other than a carriage return or line feed, the input is simply passed on to the output. The state remains unchanged.
If the input is a carriage return, the state is changed to cr. The input is then discarded, i.e., no output is made.
If the input is a line feed, the state is changed to lf. The input is then discarded.
Whenever we are in the cr state, it is because the last input was a carriage return, which was unprocessed. What our software does in this state again depends on the current input:
If the input is anything other than a carriage return or line feed, output a line feed, then output the input, then change the state to ordinary.
If the input is a carriage return, we have received two (or more) carriage returns in a row. We discard the input, we output a line feed, and leave the state unchanged.
If the input is a line feed, we output the line feed and change the state to ordinary. Note that this is not the same as the first case above – if we tried to combine them, we would be outputting two line feeds instead of one.
Finally, we are in the lf state after we have received a line feed that was not preceded by a carriage return. This will happen when our file already is in UNIX® format, or whenever several lines in a row are expressed by a single carriage return followed by several line feeds, or when line ends with a line feed / carriage return sequence. Here is how we need to handle our input in this state:
If the input is anything other than a carriage return or line feed, we output a line feed, then output the input, then change the state to ordinary. This is exactly the same action as in the cr state upon receiving the same kind of input.
If the input is a carriage return, we discard the input, we output a line feed, then change the state to ordinary.
If the input is a line feed, we output the line feed, and leave the state unchanged.
The above finite state machine works for the entire file, but leaves the possibility that the final line end will be ignored. That will happen whenever the file ends with a single carriage return or a single line feed. I did not think of it when I wrote tuc, just to discover that occasionally it strips the last line ending.
This problem is easily fixed by checking the state after the entire file was processed. If the state is not ordinary, we simply need to output one last line feed.
Note:
Now that we have expressed our algorithm as a finite state machine, we could easily design a dedicated digital electronic circuit (a "chip") to do the conversion for us. Of course, doing so would be considerably more expensive than writing an assembly language program.
Because our file conversion program may be combining two
characters into one, we need to use an output counter. We
initialize it to 0, and increase it
every time we send a character to the output. At the end of
the program, the counter will tell us what size we need
to set the file to.
The hardest part of working with a finite state machine is analyzing the problem and expressing it as a finite state machine. That accomplished, the software almost writes itself.
In a high-level language, such as C, there are several main
approaches. One is to use a switch statement
which chooses what function should be run. For example,
switch (state) {
default:
case REGULAR:
regular(inputchar);
break;
case CR:
cr(inputchar);
break;
case LF:
lf(inputchar);
break;
}
Another approach is by using an array of function pointers, something like this:
(output[state])(inputchar);
Yet another is to have state be a
function pointer, set to point at the appropriate function:
(*state)(inputchar);
This is the approach we will use in our program because it is very easy to do in assembly language, and very fast, too. We will simply keep the address of the right procedure in EBX, and then just issue:
call ebx
This is possibly faster than hardcoding the address in the code because the microprocessor does not have to fetch the address from the memory—it is already stored in one of its registers. I said possibly because with the caching modern microprocessors do, either way may be equally fast.
Because our program works on a single file, we cannot use the approach that worked for us before, i.e., to read from an input file and to write to an output file.
UNIX® allows us to map a file, or a section of a file,
into memory. To do that, we first need to open the file with the
appropriate read/write flags. Then we use the mmap
system call to map it into the memory. One nice thing about
mmap is that it automatically works with
virtual memory: We can map more of the file into the memory than
we have physical memory available, yet still access it through
regular memory op codes, such as mov,
lods, and stos.
Whatever changes we make to the memory image of the file will be
written to the file by the system. We do not even have to keep
the file open: As long as it stays mapped, we can
read from it and write to it.
The 32-bit Intel microprocessors can access up to four gigabytes of memory – physical or virtual. The FreeBSD system allows us to use up to a half of it for file mapping.
For simplicity sake, in this tutorial we will only convert files that can be mapped into the memory in their entirety. There are probably not too many text files that exceed two gigabytes in size. If our program encounters one, it will simply display a message suggesting we use the original tuc instead.
If you examine your copy of syscalls.master,
you will find two separate syscalls named mmap.
This is because of evolution of UNIX®: There was the traditional
BSD mmap,
syscall 71. That one was superseded by the POSIX® mmap,
syscall 197. The FreeBSD system supports both because
older programs were written by using the original BSD
version. But new software uses the POSIX® version,
which is what we will use.
The syscalls.master file lists
the POSIX® version like this:
197 STD BSD { caddr_t mmap(caddr_t addr, size_t len, int prot, \
int flags, int fd, long pad, off_t pos); }
This differs slightly from what mmap(2) says. That is because mmap(2) describes the C version.
The difference is in the long pad argument, which is not present in the C version. However, the FreeBSD syscalls add a 32-bit pad after pushing a 64-bit argument. In this case, off_t is a 64-bit value.
When we are finished working with a memory-mapped file,
we unmap it with the munmap syscall:
Tip:
For an in-depth treatment of mmap, see
W. Richard Stevens'
Unix
Network Programming, Volume 2, Chapter 12.
Because we need to tell mmap how many bytes
of the file to map into the memory, and because we want to map
the entire file, we need to determine the size of the file.
We can use the fstat syscall to get all
the information about an open file that the system can give us.
That includes the file size.
Again, syscalls.master lists two versions
of fstat, a traditional one
(syscall 62), and a POSIX® one
(syscall 189). Naturally, we will use the
POSIX® version:
189 STD POSIX { int fstat(int fd, struct stat *sb); }
This is a very straightforward call: We pass to it the address
of a stat structure and the descriptor
of an open file. It will fill out the contents of the
stat structure.
I do, however, have to say that I tried to declare the
stat structure in the
.bss section, and
fstat did not like it: It set the carry
flag indicating an error. After I changed the code to allocate
the structure on the stack, everything was working fine.
Because our program may combine carriage return / line feed sequences into straight line feeds, our output may be smaller than our input. However, since we are placing our output into the same file we read the input from, we may have to change the size of the file.
The ftruncate system call allows us to do
just that. Despite its somewhat misleading name, the
ftruncate system call can be used to both
truncate the file (make it smaller) and to grow it.
And yes, we will find two versions of ftruncate
in syscalls.master, an older one
(130), and a newer one (201). We will use
the newer one:
201 STD BSD { int ftruncate(int fd, int pad, off_t length); }
Please note that this one contains a int pad again.
We now know everything we need to write ftuc.
We start by adding some new lines in system.inc.
First, we define some constants and structures, somewhere at
or near the beginning of the file:
;;;;;;; open flags %define O_RDONLY 0 %define O_WRONLY 1 %define O_RDWR 2 ;;;;;;; mmap flags %define PROT_NONE 0 %define PROT_READ 1 %define PROT_WRITE 2 %define PROT_EXEC 4 ;; %define MAP_SHARED 0001h %define MAP_PRIVATE 0002h ;;;;;;; stat structure struc stat st_dev resd 1 ; = 0 st_ino resd 1 ; = 4 st_mode resw 1 ; = 8, size is 16 bits st_nlink resw 1 ; = 10, ditto st_uid resd 1 ; = 12 st_gid resd 1 ; = 16 st_rdev resd 1 ; = 20 st_atime resd 1 ; = 24 st_atimensec resd 1 ; = 28 st_mtime resd 1 ; = 32 st_mtimensec resd 1 ; = 36 st_ctime resd 1 ; = 40 st_ctimensec resd 1 ; = 44 st_size resd 2 ; = 48, size is 64 bits st_blocks resd 2 ; = 56, ditto st_blksize resd 1 ; = 64 st_flags resd 1 ; = 68 st_gen resd 1 ; = 72 st_lspare resd 1 ; = 76 st_qspare resd 4 ; = 80 endstruc
We define the new syscalls:
%define SYS_mmap 197 %define SYS_munmap 73 %define SYS_fstat 189 %define SYS_ftruncate 201
We add the macros for their use:
%macro sys.mmap 0 system SYS_mmap %endmacro %macro sys.munmap 0 system SYS_munmap %endmacro %macro sys.ftruncate 0 system SYS_ftruncate %endmacro %macro sys.fstat 0 system SYS_fstat %endmacro
And here is our code:
;;;;;;; Fast Text-to-Unix Conversion (ftuc.asm) ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ;; ;; Started: 21-Dec-2000 ;; Updated: 22-Dec-2000 ;; ;; Copyright 2000 G. Adam Stanislav. ;; All rights reserved. ;; ;;;;;;; v.1 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; %include 'system.inc' section .data db 'Copyright 2000 G. Adam Stanislav.', 0Ah db 'All rights reserved.', 0Ah usg db 'Usage: ftuc filename', 0Ah usglen equ $-usg co db "ftuc: Can't open file.", 0Ah colen equ $-co fae db 'ftuc: File access error.', 0Ah faelen equ $-fae ftl db 'ftuc: File too long, use regular tuc instead.', 0Ah ftllen equ $-ftl mae db 'ftuc: Memory allocation error.', 0Ah maelen equ $-mae section .text align 4 memerr: push dword maelen push dword mae jmp short error align 4 toolong: push dword ftllen push dword ftl jmp short error align 4 facerr: push dword faelen push dword fae jmp short error align 4 cantopen: push dword colen push dword co jmp short error align 4 usage: push dword usglen push dword usg error: push dword stderr sys.write push dword 1 sys.exit align 4 global _start _start: pop eax ; argc pop eax ; program name pop ecx ; file to convert jecxz usage pop eax or eax, eax ; Too many arguments? jne usage ; Open the file push dword O_RDWR push ecx sys.open jc cantopen mov ebp, eax ; Save fd sub esp, byte stat_size mov ebx, esp ; Find file size push ebx push ebp ; fd sys.fstat jc facerr mov edx, [ebx + st_size + 4] ; File is too long if EDX != 0 ... or edx, edx jne near toolong mov ecx, [ebx + st_size] ; ... or if it is above 2 GB or ecx, ecx js near toolong ; Do nothing if the file is 0 bytes in size jecxz .quit ; Map the entire file in memory push edx push edx ; starting at offset 0 push edx ; pad push ebp ; fd push dword MAP_SHARED push dword PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE push ecx ; entire file size push edx ; let system decide on the address sys.mmap jc near memerr mov edi, eax mov esi, eax push ecx ; for SYS_munmap push edi ; Use EBX for state machine mov ebx, ordinary mov ah, 0Ah cld .loop: lodsb call ebx loop .loop cmp ebx, ordinary je .filesize ; Output final lf mov al, ah stosb inc edx .filesize: ; truncate file to new size push dword 0 ; high dword push edx ; low dword push eax ; pad push ebp sys.ftruncate ; close it (ebp still pushed) sys.close add esp, byte 16 sys.munmap .quit: push dword 0 sys.exit align 4 ordinary: cmp al, 0Dh je .cr cmp al, ah je .lf stosb inc edx ret align 4 .cr: mov ebx, cr ret align 4 .lf: mov ebx, lf ret align 4 cr: cmp al, 0Dh je .cr cmp al, ah je .lf xchg al, ah stosb inc edx xchg al, ah ; fall through .lf: stosb inc edx mov ebx, ordinary ret align 4 .cr: mov al, ah stosb inc edx ret align 4 lf: cmp al, ah je .lf cmp al, 0Dh je .cr xchg al, ah stosb inc edx xchg al, ah stosb inc edx mov ebx, ordinary ret align 4 .cr: mov ebx, ordinary mov al, ah ; fall through .lf: stosb inc edx ret
Warning:
Do not use this program on files stored on a disk formatted
by MS-DOS® or Windows®. There seems to be a
subtle bug in the FreeBSD code when using mmap
on these drives mounted under FreeBSD: If the file is over
a certain size, mmap will just fill the memory
with zeros, and then copy them to the file overwriting
its contents.
As a student of Zen, I like the idea of a one-pointed mind: Do one thing at a time, and do it well.
This, indeed, is very much how UNIX® works as well. While a typical Windows® application is attempting to do everything imaginable (and is, therefore, riddled with bugs), a typical UNIX® program does only one thing, and it does it well.
The typical UNIX® user then essentially assembles his own applications by writing a shell script which combines the various existing programs by piping the output of one program to the input of another.
When writing your own UNIX® software, it is generally a good idea to see what parts of the problem you need to solve can be handled by existing programs, and only write your own programs for that part of the problem that you do not have an existing solution for.
I will illustrate this principle with a specific real-life example I was faced with recently:
I needed to extract the 11th field of each record from a database I downloaded from a web site. The database was a CSV file, i.e., a list of comma-separated values. That is quite a standard format for sharing data among people who may be using different database software.
The first line of the file contains the list of various fields separated by commas. The rest of the file contains the data listed line by line, with values separated by commas.
I tried awk, using the comma as a separator. But because several lines contained a quoted comma, awk was extracting the wrong field from those lines.
Therefore, I needed to write my own software to extract the 11th field from the CSV file. However, going with the UNIX® spirit, I only needed to write a simple filter that would do the following:
Remove the first line from the file;
Change all unquoted commas to a different character;
Remove all quotation marks.
Strictly speaking, I could use sed to remove the first line from the file, but doing so in my own program was very easy, so I decided to do it and reduce the size of the pipeline.
At any rate, writing a program like this took me about 20 minutes. Writing a program that extracts the 11th field from the CSV file would take a lot longer, and I could not reuse it to extract some other field from some other database.
This time I decided to let it do a little more work than a typical tutorial program would:
It parses its command line for options;
It displays proper usage if it finds wrong arguments;
It produces meaningful error messages.
Here is its usage message:
Usage: csv [-t<delim>] [-c<comma>] [-p] [-o <outfile>] [-i <infile>]
All parameters are optional, and can appear in any order.
The -t parameter declares what to replace
the commas with. The tab is the default here.
For example, -t; will replace all unquoted
commas with semicolons.
I did not need the -c option, but it may
come in handy in the future. It lets me declare that I want a
character other than a comma replaced with something else.
For example, -c@ will replace all at signs
(useful if you want to split a list of email addresses
to their user names and domains).
The -p option preserves the first line, i.e.,
it does not delete it. By default, we delete the first
line because in a CSV file it contains the field
names rather than data.
The -i and -o
options let me specify the input and the output files. Defaults
are stdin and stdout,
so this is a regular UNIX® filter.
I made sure that both -i filename and
-ifilename are accepted. I also made
sure that only one input and one output files may be
specified.
To get the 11th field of each record, I can now do:
%csv '-t;'data.csv| awk '-F;' '{print $11}'
The code stores the options (except for the file descriptors)
in EDX: The comma in DH, the new
separator in DL, and the flag for
the -p option in the highest bit of
EDX, so a check for its sign will give us a
quick decision what to do.
Here is the code:
;;;;;;; csv.asm ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;
; Convert a comma-separated file to a something-else separated file.
;
; Started: 31-May-2001
; Updated: 1-Jun-2001
;
; Copyright (c) 2001 G. Adam Stanislav
; All rights reserved.
;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
%include 'system.inc'
%define BUFSIZE 2048
section .data
fd.in dd stdin
fd.out dd stdout
usg db 'Usage: csv [-t<delim>] [-c<comma>] [-p] [-o <outfile>] [-i <infile>]', 0Ah
usglen equ $-usg
iemsg db "csv: Can't open input file", 0Ah
iemlen equ $-iemsg
oemsg db "csv: Can't create output file", 0Ah
oemlen equ $-oemsg
section .bss
ibuffer resb BUFSIZE
obuffer resb BUFSIZE
section .text
align 4
ierr:
push dword iemlen
push dword iemsg
push dword stderr
sys.write
push dword 1 ; return failure
sys.exit
align 4
oerr:
push dword oemlen
push dword oemsg
push dword stderr
sys.write
push dword 2
sys.exit
align 4
usage:
push dword usglen
push dword usg
push dword stderr
sys.write
push dword 3
sys.exit
align 4
global _start
_start:
add esp, byte 8 ; discard argc and argv[0]
mov edx, (',' << 8) | 9
.arg:
pop ecx
or ecx, ecx
je near .init ; no more arguments
; ECX contains the pointer to an argument
cmp byte [ecx], '-'
jne usage
inc ecx
mov ax, [ecx]
.o:
cmp al, 'o'
jne .i
; Make sure we are not asked for the output file twice
cmp dword [fd.out], stdout
jne usage
; Find the path to output file - it is either at [ECX+1],
; i.e., -ofile --
; or in the next argument,
; i.e., -o file
inc ecx
or ah, ah
jne .openoutput
pop ecx
jecxz usage
.openoutput:
push dword 420 ; file mode (644 octal)
push dword 0200h | 0400h | 01h
; O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY
push ecx
sys.open
jc near oerr
add esp, byte 12
mov [fd.out], eax
jmp short .arg
.i:
cmp al, 'i'
jne .p
; Make sure we are not asked twice
cmp dword [fd.in], stdin
jne near usage
; Find the path to the input file
inc ecx
or ah, ah
jne .openinput
pop ecx
or ecx, ecx
je near usage
.openinput:
push dword 0 ; O_RDONLY
push ecx
sys.open
jc near ierr ; open failed
add esp, byte 8
mov [fd.in], eax
jmp .arg
.p:
cmp al, 'p'
jne .t
or ah, ah
jne near usage
or edx, 1 << 31
jmp .arg
.t:
cmp al, 't' ; redefine output delimiter
jne .c
or ah, ah
je near usage
mov dl, ah
jmp .arg
.c:
cmp al, 'c'
jne near usage
or ah, ah
je near usage
mov dh, ah
jmp .arg
align 4
.init:
sub eax, eax
sub ebx, ebx
sub ecx, ecx
mov edi, obuffer
; See if we are to preserve the first line
or edx, edx
js .loop
.firstline:
; get rid of the first line
call getchar
cmp al, 0Ah
jne .firstline
.loop:
; read a byte from stdin
call getchar
; is it a comma (or whatever the user asked for)?
cmp al, dh
jne .quote
; Replace the comma with a tab (or whatever the user wants)
mov al, dl
.put:
call putchar
jmp short .loop
.quote:
cmp al, '"'
jne .put
; Print everything until you get another quote or EOL. If it
; is a quote, skip it. If it is EOL, print it.
.qloop:
call getchar
cmp al, '"'
je .loop
cmp al, 0Ah
je .put
call putchar
jmp short .qloop
align 4
getchar:
or ebx, ebx
jne .fetch
call read
.fetch:
lodsb
dec ebx
ret
read:
jecxz .read
call write
.read:
push dword BUFSIZE
mov esi, ibuffer
push esi
push dword [fd.in]
sys.read
add esp, byte 12
mov ebx, eax
or eax, eax
je .done
sub eax, eax
ret
align 4
.done:
call write ; flush output buffer
; close files
push dword [fd.in]
sys.close
push dword [fd.out]
sys.close
; return success
push dword 0
sys.exit
align 4
putchar:
stosb
inc ecx
cmp ecx, BUFSIZE
je write
ret
align 4
write:
jecxz .ret ; nothing to write
sub edi, ecx ; start of buffer
push ecx
push edi
push dword [fd.out]
sys.write
add esp, byte 12
sub eax, eax
sub ecx, ecx ; buffer is empty now
.ret:
ret
Much of it is taken from hex.asm above. But there
is one important difference: I no longer call write
whenever I am outputting a line feed. Yet, the code can be
used interactively.
I have found a better solution for the interactive problem since I first started writing this chapter. I wanted to make sure each line is printed out separately only when needed. After all, there is no need to flush out every line when used non-interactively.
The new solution I use now is to call write every
time I find the input buffer empty. That way, when running in
the interactive mode, the program reads one line from the user's
keyboard, processes it, and sees its input buffer is empty. It
flushes its output and reads the next line.
This change prevents a mysterious lockup in a very specific case. I refer to it as the dark side of buffering, mostly because it presents a danger that is not quite obvious.
It is unlikely to happen with a program like the csv above, so let us consider yet another filter: In this case we expect our input to be raw data representing color values, such as the red, green, and blue intensities of a pixel. Our output will be the negative of our input.
Such a filter would be very simple to write. Most of it would look just like all the other filters we have written so far, so I am only going to show you its inner loop:
.loop: call getchar not al ; Create a negative call putchar jmp short .loop
Because this filter works with raw data, it is unlikely to be used interactively.
But it could be called by image manipulation software.
And, unless it calls write before each call
to read, chances are it will lock up.
Here is what might happen:
The image editor will load our filter using the C function
popen().It will read the first row of pixels from a bitmap or pixmap.
It will write the first row of pixels to the pipe leading to the
fd.inof our filter.Our filter will read each pixel from its input, turn it to a negative, and write it to its output buffer.
Our filter will call
getcharto fetch the next pixel.getcharwill find an empty input buffer, so it will callread.readwill call theSYS_readsystem call.The kernel will suspend our filter until the image editor sends more data to the pipe.
The image editor will read from the other pipe, connected to the
fd.outof our filter so it can set the first row of the output image before it sends us the second row of the input.The kernel suspends the image editor until it receives some output from our filter, so it can pass it on to the image editor.
At this point our filter waits for the image editor to send it more data to process, while the image editor is waiting for our filter to send it the result of the processing of the first row. But the result sits in our output buffer.
The filter and the image editor will continue waiting for each other forever (or, at least, until they are killed). Our software has just entered a race condition.
This problem does not exist if our filter flushes its output buffer before asking the kernel for more input data.
Strangely enough, most of assembly language literature does not even mention the existence of the FPU, or floating point unit, let alone discuss programming it.
Yet, never does assembly language shine more than when we create highly optimized FPU code by doing things that can be done only in assembly language.
The FPU consists of 8 80–bit floating–point registers.
These are organized in a stack fashion—you can
push a value on TOS
(top of stack) and you can
pop it.
That said, the assembly language op codes are not push
and pop because those are already taken.
You can push a value on TOS
by using fld, fild,
and fbld. Several other op codes
let you push many common
constants—such as pi—on
the TOS.
Similarly, you can pop a value by
using fst, fstp,
fist, fistp, and
fbstp. Actually, only the op
codes that end with a p will
literally pop the value,
the rest will store it
somewhere else without removing it from
the TOS.
We can transfer the data between the TOS and the computer memory either as a 32–bit, 64–bit, or 80–bit real, a 16–bit, 32–bit, or 64–bit integer, or an 80–bit packed decimal.
The 80–bit packed decimal is a special case of binary coded decimal which is very convenient when converting between the ASCII representation of data and the internal data of the FPU. It allows us to use 18 significant digits.
No matter how we represent data in the memory, the FPU always stores it in the 80–bit real format in its registers.
Its internal precision is at least 19 decimal digits, so even if we choose to display results as ASCII in the full 18–digit precision, we are still showing correct results.
We can perform mathematical operations on the TOS: We can calculate its sine, we can scale it (i.e., we can multiply or divide it by a power of 2), we can calculate its base–2 logarithm, and many other things.
We can also multiply or divide it by, add it to, or subtract it from, any of the FPU registers (including itself).
The official Intel op code for the
TOS is st, and
for the registers
st(0)–st(7).
st and st(0), then,
refer to the same register.
For whatever reasons, the original author of
nasm has decided to use
different op codes, namely
st0–st7.
In other words, there are no parentheses,
and the TOS is always
st0, never just st.
The packed decimal format uses 10 bytes (80 bits) of memory to represent 18 digits. The number represented there is always an integer.
Tip:
You can use it to get decimal places by multiplying the TOS by a power of 10 first.
The highest bit of the highest byte (byte 9) is the sign bit: If it is set, the number is negative, otherwise, it is positive. The rest of the bits of this byte are unused/ignored.
The remaining 9 bytes store the 18 digits of the number: 2 digits per byte.
The more significant digit is stored in the high nibble (4 bits), the less significant digit in the low nibble.
That said, you might think that -1234567
would be stored in the memory like this (using
hexadecimal notation):
80 00 00 00 00 00 01 23 45 67
Alas it is not! As with everything else of Intel make, even the packed decimal is little–endian.
That means our -1234567
is stored like this:
67 45 23 01 00 00 00 00 00 80
Remember that, or you will be pulling your hair out in desperation!
Note:
The book to read—if you can find it—is Richard Startz' 8087/80287/80387 for the IBM PC & Compatibles. Though it does seem to take the fact about the little–endian storage of the packed decimal for granted. I kid you not about the desperation of trying to figure out what was wrong with the filter I show below before it occurred to me I should try the little–endian order even for this type of data.
To write meaningful software, we must not only understand our programming tools, but also the field we are creating software for.
Our next filter will help us whenever we want to build a pinhole camera, so, we need some background in pinhole photography before we can continue.
The easiest way to describe any camera ever built is as some empty space enclosed in some lightproof material, with a small hole in the enclosure.
The enclosure is usually sturdy (e.g., a box), though sometimes it is flexible (the bellows). It is quite dark inside the camera. However, the hole lets light rays in through a single point (though in some cases there may be several). These light rays form an image, a representation of whatever is outside the camera, in front of the hole.
If some light sensitive material (such as film) is placed inside the camera, it can capture the image.
The hole often contains a lens, or a lens assembly, often called the objective.
But, strictly speaking, the lens is not necessary: The original cameras did not use a lens but a pinhole. Even today, pinholes are used, both as a tool to study how cameras work, and to achieve a special kind of image.
The image produced by the pinhole is all equally sharp. Or blurred. There is an ideal size for a pinhole: If it is either larger or smaller, the image loses its sharpness.
This ideal pinhole diameter is a function of the square root of focal length, which is the distance of the pinhole from the film.
D = PC * sqrt(FL)
In here, D is the
ideal diameter of the pinhole,
FL is the focal length,
and PC is a pinhole
constant. According to Jay Bender,
its value is 0.04, while
Kenneth Connors has determined it to
be 0.037. Others have
proposed other values. Plus, this
value is for the daylight only: Other types
of light will require a different constant,
whose value can only be determined by
experimentation.
The f–number is a very useful measure of how much light reaches the film. A light meter can determine that, for example, to expose a film of specific sensitivity with f5.6 may require the exposure to last 1/1000 sec.
It does not matter whether it is a 35–mm camera, or a 6x9cm camera, etc. As long as we know the f–number, we can determine the proper exposure.
The f–number is easy to calculate:
F = FL / D
In other words, the f–number equals the focal length divided by the diameter of the pinhole. It also means a higher f–number either implies a smaller pinhole or a larger focal distance, or both. That, in turn, implies, the higher the f–number, the longer the exposure has to be.
Furthermore, while pinhole diameter and focal
distance are one–dimensional measurements,
both, the film and the pinhole, are two–dimensional.
That means that
if you have measured the exposure at f–number
A as t, then the exposure
at f–number B is:
t * (B / A)²
While many modern cameras can change the diameter of their pinhole, and thus their f–number, quite smoothly and gradually, such was not always the case.
To allow for different f–numbers, cameras typically contained a metal plate with several holes of different sizes drilled to them.
Their sizes were chosen according to the above formula in such a way that the resultant f–number was one of standard f–numbers used on all cameras everywhere. For example, a very old Kodak Duaflex IV camera in my possession has three such holes for f–numbers 8, 11, and 16.
A more recently made camera may offer f–numbers of 2.8, 4, 5.6, 8, 11, 16, 22, and 32 (as well as others). These numbers were not chosen arbitrarily: They all are powers of the square root of 2, though they may be rounded somewhat.
A typical camera is designed in such a way that setting any of the normalized f–numbers changes the feel of the dial. It will naturally stop in that position. Because of that, these positions of the dial are called f–stops.
Since the f–numbers at each stop are powers of the square root of 2, moving the dial by 1 stop will double the amount of light required for proper exposure. Moving it by 2 stops will quadruple the required exposure. Moving the dial by 3 stops will require the increase in exposure 8 times, etc.
We are now ready to decide what exactly we want our pinhole software to do.
Since its main purpose is to help us design a working pinhole camera, we will use the focal length as the input to the program. This is something we can determine without software: Proper focal length is determined by the size of the film and by the need to shoot "regular" pictures, wide angle pictures, or telephoto pictures.
Most of the programs we have written so far worked with individual characters, or bytes, as their input: The hex program converted individual bytes into a hexadecimal number, the csv program either let a character through, or deleted it, or changed it to a different character, etc.
One program, ftuc used the state machine to consider at most two input bytes at a time.
But our pinhole program cannot just work with individual characters, it has to deal with larger syntactic units.
For example, if we want the program to calculate the
pinhole diameter (and other values we will discuss
later) at the focal lengths of 100 mm,
150 mm, and 210 mm, we may want
to enter something like this:
100, 150, 210
Our program needs to consider more than a single byte of
input at a time. When it sees the first 1,
it must understand it is seeing the first digit of a
decimal number. When it sees the 0 and
the other 0, it must know it is seeing
more digits of the same number.
When it encounters the first comma, it must know it is
no longer receiving the digits of the first number.
It must be able to convert the digits of the first number
into the value of 100. And the digits of the
second number into the value of 150. And,
of course, the digits of the third number into the
numeric value of 210.
We need to decide what delimiters to accept: Do the input numbers have to be separated by a comma? If so, how do we treat two numbers separated by something else?
Personally, I like to keep it simple. Something either is a number, so I process it. Or it is not a number, so I discard it. I do not like the computer complaining about me typing in an extra character when it is obvious that it is an extra character. Duh!
Plus, it allows me to break up the monotony of computing and type in a query instead of just a number:
What is the best pinhole diameter for the focal length of 150?There is no reason for the computer to spit out a number of complaints:
Syntax error: What Syntax error: is Syntax error: the Syntax error: best
Et cetera, et cetera, et cetera.
Secondly, I like the # character to denote
the start of a comment which extends to the end of the
line. This does not take too much effort to code, and
lets me treat input files for my software as executable
scripts.
In our case, we also need to decide what units the input should come in: We choose millimeters because that is how most photographers measure the focus length.
Finally, we need to decide whether to allow the use of the decimal point (in which case we must also consider the fact that much of the world uses a decimal comma).
In our case allowing for the decimal point/comma
would offer a false sense of precision: There is
little if any noticeable difference between the
focus lengths of 50 and 51,
so allowing the user to input something like
50.5 is not a good idea. This is
my opinion, mind you, but I am the one writing
this program. You can make other choices in yours,
of course.
The most important thing we need to know when building
a pinhole camera is the diameter of the pinhole. Since
we want to shoot sharp images, we will use the above
formula to calculate the pinhole diameter from focal length.
As experts are offering several different values for the
PC constant, we will need to have the choice.
It is traditional in UNIX® programming to have two main ways of choosing program parameters, plus to have a default for the time the user does not make a choice.
Why have two ways of choosing?
One is to allow a (relatively) permanent choice that applies automatically each time the software is run without us having to tell it over and over what we want it to do.
The permanent choices may be stored in a configuration
file, typically found in the user's home directory.
The file usually has the same name as the application
but is started with a dot. Often "rc"
is added to the file name. So, ours could be
~/.pinhole or ~/.pinholerc.
(The ~/ means current user's
home directory.)
The configuration file is used mostly by programs
that have many configurable parameters. Those
that have only one (or a few) often use a different
method: They expect to find the parameter in an
environment variable. In our case,
we might look at an environment variable named
PINHOLE.
Usually, a program uses one or the other of the above methods. Otherwise, if a configuration file said one thing, but an environment variable another, the program might get confused (or just too complicated).
Because we only need to choose one
such parameter, we will go with the second method
and search the environment for a variable named
PINHOLE.
The other way allows us to make ad hoc decisions: "Though I usually want you to use 0.039, this time I want 0.03872." In other words, it allows us to override the permanent choice.
This type of choice is usually done with command line parameters.
Finally, a program always needs a default. The user may not make any choices. Perhaps he does not know what to choose. Perhaps he is "just browsing." Preferably, the default will be the value most users would choose anyway. That way they do not need to choose. Or, rather, they can choose the default without an additional effort.
Given this system, the program may find conflicting options, and handle them this way:
If it finds an ad hoc choice (e.g., command line parameter), it should accept that choice. It must ignore any permanent choice and any default.
Otherwise, if it finds a permanent option (e.g., an environment variable), it should accept it, and ignore the default.
Otherwise, it should use the default.
We also need to decide what format
our PC option should have.
At first site, it seems obvious to use the
PINHOLE=0.04 format for the
environment variable, and -p0.04
for the command line.
Allowing that is actually a security risk.
The PC constant is a very small
number. Naturally, we will test our software
using various small values of PC.
But what will happen if someone runs the program
choosing a huge value?
It may crash the program because we have not designed it to handle huge numbers.
Or, we may spend more time on the program so it can handle huge numbers. We might do that if we were writing commercial software for computer illiterate audience.
Or, we might say, "Tough! The user should know better.""
Or, we just may make it impossible for the user to enter a huge number. This is the approach we will take: We will use an implied 0. prefix.
In other words, if the user wants 0.04,
we will expect him to type -p04,
or set PINHOLE=04 in his environment.
So, if he says -p9999999, we will
interpret it as 0.9999999—still
ridiculous but at least safer.
Secondly, many users will just want to go with either
Bender's constant or Connors' constant.
To make it easier on them, we will interpret
-b as identical to -p04,
and -c as identical to -p037.
We need to decide what we want our software to send to the output, and in what format.
Since our input allows for an unspecified number
of focal length entries, it makes sense to use
a traditional database–style output of showing
the result of the calculation for each
focal length on a separate line, while
separating all values on one line by a
tab character.
Optionally, we should also allow the user
to specify the use of the CSV
format we have studied earlier. In this case,
we will print out a line of comma–separated
names describing each field of every line,
then show our results as before, but substituting
a comma for the tab.
We need a command line option for the CSV
format. We cannot use -c because
that already means use Connors' constant.
For some strange reason, many web sites refer to
CSV files as "Excel
spreadsheet" (though the CSV
format predates Excel). We will, therefore, use
the -e switch to inform our software
we want the output in the CSV format.
We will start each line of the output with the focal length. This may sound repetitious at first, especially in the interactive mode: The user types in the focal length, and we are repeating it.
But the user can type several focal lengths on one line. The input can also come in from a file or from the output of another program. In that case the user does not see the input at all.
By the same token, the output can go to a file which we will want to examine later, or it could go to the printer, or become the input of another program.
So, it makes perfect sense to start each line with the focal length as entered by the user.
No, wait! Not as entered by the user. What if the user types in something like this:
00000000150Clearly, we need to strip those leading zeros.
So, we might consider reading the user input as is, converting it to binary inside the FPU, and printing it out from there.
But...
What if the user types something like this:
17459765723452353453534535353530530534563507309676764423Ha! The packed decimal FPU format lets us input 18–digit numbers. But the user has entered more than 18 digits. How do we handle that?
Well, we could modify our code to read
the first 18 digits, enter it to the FPU,
then read more, multiply what we already have on the
TOS by 10 raised to the number
of additional digits, then add to it.
Yes, we could do that. But in this program it would be ridiculous (in a different one it may be just the thing to do): Even the circumference of the Earth expressed in millimeters only takes 11 digits. Clearly, we cannot build a camera that large (not yet, anyway).
So, if the user enters such a huge number, he is either bored, or testing us, or trying to break into the system, or playing games—doing anything but designing a pinhole camera.
What will we do?
We will slap him in the face, in a manner of speaking:
17459765723452353453534535353530530534563507309676764423 ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
To achieve that, we will simply ignore any leading zeros.
Once we find a non–zero digit, we will initialize a
counter to 0 and start taking three steps:
Send the digit to the output.
Append the digit to a buffer we will use later to produce the packed decimal we can send to the FPU.
Increase the counter.
Now, while we are taking these three steps, we also need to watch out for one of two conditions:
If the counter grows above 18, we stop appending to the buffer. We continue reading the digits and sending them to the output.
If, or rather when, the next input character is not a digit, we are done inputting for now.
Incidentally, we can simply discard the non–digit, unless it is a
#, which we must return to the input stream. It starts a comment, so we must see it after we are done producing output and start looking for more input.
That still leaves one possibility uncovered: If all the user enters is a zero (or several zeros), we will never find a non–zero to display.
We can determine this has happened
whenever our counter stays at 0.
In that case we need to send 0
to the output, and perform another
"slap in the face":
0 ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
Once we have displayed the focal
length and determined it is valid
(greater than 0
but not exceeding 18 digits),
we can calculate the pinhole diameter.
It is not by coincidence that pinhole contains the word pin. Indeed, many a pinhole literally is a pin hole, a hole carefully punched with the tip of a pin.
That is because a typical pinhole is very
small. Our formula gets the result in
millimeters. We will multiply it by 1000,
so we can output the result in microns.
At this point we have yet another trap to face: Too much precision.
Yes, the FPU was designed for high precision mathematics. But we are not dealing with high precision mathematics. We are dealing with physics (optics, specifically).
Suppose we want to convert a truck into
a pinhole camera (we would not be the
first ones to do that!). Suppose its box is
12
meters long, so we have the focal length
of 12000. Well, using Bender's constant, it gives us square root of
12000 multiplied by 0.04,
which is 4.381780460 millimeters,
or 4381.780460 microns.
Put either way, the result is absurdly precise.
Our truck is not exactly 12000
millimeters long. We did not measure its length
with such a precision, so stating we need a pinhole
with the diameter of 4.381780460
millimeters is, well, deceiving. 4.4
millimeters would do just fine.
Note:
I "only" used ten digits in the above example. Imagine the absurdity of going for all 18!
We need to limit the number of significant
digits of our result. One way of doing it
is by using an integer representing microns.
So, our truck would need a pinhole with the diameter
of 4382 microns. Looking at that number, we still decide that 4400 microns,
or 4.4 millimeters is close enough.
Additionally, we can decide that no matter how big a result we get, we only want to display four significant digits (or any other number of them, of course). Alas, the FPU does not offer rounding to a specific number of digits (after all, it does not view the numbers as decimal but as binary).
We, therefore, must devise an algorithm to reduce the number of significant digits.
Here is mine (I think it is awkward—if you know a better one, please, let me know):
Initialize a counter to
0.While the number is greater than or equal to
10000, divide it by10and increase the counter.Output the result.
While the counter is greater than
0, output0and decrease the counter.
Note:
The 10000 is only good if you want
four significant digits. For any other
number of significant digits, replace
10000 with 10
raised to the number of significant digits.
We will, then, output the pinhole diameter in microns, rounded off to four significant digits.
At this point, we know the focal length and the pinhole diameter. That means we have enough information to also calculate the f–number.
We will display the f–number, rounded to four significant digits. Chances are the f–number will tell us very little. To make it more meaningful, we can find the nearest normalized f–number, i.e., the nearest power of the square root of 2.
We do that by multiplying the actual f–number
by itself, which, of course, will give us
its square. We will then calculate
its base–2 logarithm, which is much
easier to do than calculating the
base–square–root–of–2 logarithm!
We will round the result to the nearest integer.
Next, we will raise 2 to the result. Actually,
the FPU gives us a good shortcut
to do that: We can use the fscale
op code to "scale" 1, which is
analogous to shifting an
integer left. Finally, we calculate the square
root of it all, and we have the nearest
normalized f–number.
If all that sounds overwhelming—or too much work, perhaps—it may become much clearer if you see the code. It takes 9 op codes altogether:
fmul st0, st0 fld1 fld st1 fyl2x frndint fld1 fscale fsqrt fstp st1
The first line, fmul st0, st0, squares
the contents of the TOS
(top of the stack, same as st,
called st0 by nasm).
The fld1 pushes 1
on the TOS.
The next line, fld st1, pushes
the square back to the TOS.
At this point the square is both in st
and st(2) (it will become
clear why we leave a second copy on the stack
in a moment). st(1) contains
1.
Next, fyl2x calculates base–2
logarithm of st multiplied by
st(1). That is why we placed 1 on st(1) before.
At this point, st contains
the logarithm we have just calculated,
st(1) contains the square
of the actual f–number we saved for later.
frndint rounds the TOS
to the nearest integer. fld1 pushes
a 1. fscale shifts the
1 we have on the TOS
by the value in st(1),
effectively raising 2 to st(1).
Finally, fsqrt calculates
the square root of the result, i.e.,
the nearest normalized f–number.
We now have the nearest normalized
f–number on the TOS,
the base–2 logarithm rounded to the
nearest integer in st(1),
and the square of the actual f–number
in st(2). We are saving
the value in st(2) for later.
But we do not need the contents of
st(1) anymore. The last
line, fstp st1, places the
contents of st to
st(1), and pops. As a
result, what was st(1)
is now st, what was st(2)
is now st(1), etc.
The new st contains the
normalized f–number. The new
st(1) contains the square
of the actual f–number we have
stored there for posterity.
At this point, we are ready to output the normalized f–number. Because it is normalized, we will not round it off to four significant digits, but will send it out in its full precision.
The normalized f-number is useful as long as it is reasonably small and can be found on our light meter. Otherwise we need a different method of determining proper exposure.
Earlier we have figured out the formula of calculating proper exposure at an arbitrary f–number from that measured at a different f–number.
Every light meter I have ever seen can determine proper exposure at f5.6. We will, therefore, calculate an "f5.6 multiplier," i.e., by how much we need to multiply the exposure measured at f5.6 to determine the proper exposure for our pinhole camera.
From the above formula we know this factor can be
calculated by dividing our f–number (the
actual one, not the normalized one) by
5.6, and squaring the result.
Mathematically, dividing the square of our
f–number by the square of 5.6
will give us the same result.
Computationally, we do not want to square two numbers when we can only square one. So, the first solution seems better at first.
But...
5.6 is a constant.
We do not have to have our FPU
waste precious cycles. We can just tell it
to divide the square of the f–number by
whatever 5.6² equals to.
Or we can divide the f–number by 5.6,
and then square the result. The two ways
now seem equal.
But, they are not!
Having studied the principles of photography
above, we remember that the 5.6
is actually square root of 2 raised to
the fifth power. An irrational
number. The square of this number is
exactly 32.
Not only is 32 an integer,
it is a power of 2. We do not need
to divide the square of the f–number by
32. We only need to use
fscale to shift it right by
five positions. In the FPU
lingo it means we will fscale it
with st(1) equal to
-5. That is much
faster than a division.
So, now it has become clear why we have saved the square of the f–number on the top of the FPU stack. The calculation of the f5.6 multiplier is the easiest calculation of this entire program! We will output it rounded to four significant digits.
There is one more useful number we can calculate: The number of stops our f–number is from f5.6. This may help us if our f–number is just outside the range of our light meter, but we have a shutter which lets us set various speeds, and this shutter uses stops.
Say, our f–number is 5 stops from f5.6, and the light meter says we should use 1/1000 sec. Then we can set our shutter speed to 1/1000 first, then move the dial by 5 stops.
This calculation is quite easy as well. All we have to do is to calculate the base-2 logarithm of the f5.6 multiplier we had just calculated (though we need its value from before we rounded it off). We then output the result rounded to the nearest integer. We do not need to worry about having more than four significant digits in this one: The result is most likely to have only one or two digits anyway.
In assembly language we can optimize the FPU code in ways impossible in high languages, including C.
Whenever a C function needs to calculate a floating–point value, it loads all necessary variables and constants into FPU registers. It then does whatever calculation is required to get the correct result. Good C compilers can optimize that part of the code really well.
It "returns" the value by leaving the result on the TOS. However, before it returns, it cleans up. Any variables and constants it used in its calculation are now gone from the FPU.
It cannot do what we just did above: We calculated the square of the f–number and kept it on the stack for later use by another function.
We knew we would need that value later on. We also knew we had enough room on the stack (which only has room for 8 numbers) to store it there.
A C compiler has no way of knowing that a value it has on the stack will be required again in the very near future.
Of course, the C programmer may know it. But the only recourse he has is to store the value in a memory variable.
That means, for one, the value will be changed from the 80-bit precision used internally by the FPU to a C double (64 bits) or even single (32 bits).
That also means that the value must be moved from the TOS into the memory, and then back again. Alas, of all FPU operations, the ones that access the computer memory are the slowest.
So, whenever programming the FPU in assembly language, look for the ways of keeping intermediate results on the FPU stack.
We can take that idea even further! In our
program we are using a constant
(the one we named PC).
It does not matter how many pinhole diameters we are calculating: 1, 10, 20, 1000, we are always using the same constant. Therefore, we can optimize our program by keeping the constant on the stack all the time.
Early on in our program, we are calculating the
value of the above constant. We need to divide
our input by 10 for every digit in the
constant.
It is much faster to multiply than to divide.
So, at the start of our program, we divide 10
into 1 to obtain 0.1, which we
then keep on the stack: Instead of dividing the
input by 10 for every digit,
we multiply it by 0.1.
By the way, we do not input 0.1 directly,
even though we could. We have a reason for that:
While 0.1 can be expressed with just one
decimal place, we do not know how many binary
places it takes. We, therefore, let the FPU
calculate its binary value to its own high precision.
We are using other constants: We multiply the pinhole
diameter by 1000 to convert it from
millimeters to microns. We compare numbers to
10000 when we are rounding them off to
four significant digits. So, we keep both, 1000
and 10000, on the stack. And, of course,
we reuse the 0.1 when rounding off numbers
to four digits.
Last but not least, we keep -5 on the stack.
We need it to scale the square of the f–number,
instead of dividing it by 32. It is not
by coincidence we load this constant last. That makes
it the top of the stack when only the constants
are on it. So, when the square of the f–number is
being scaled, the -5 is at st(1),
precisely where fscale expects it to be.
It is common to create certain constants from
scratch instead of loading them from the memory.
That is what we are doing with -5:
fld1 ; TOS = 1 fadd st0, st0 ; TOS = 2 fadd st0, st0 ; TOS = 4 fld1 ; TOS = 1 faddp st1, st0 ; TOS = 5 fchs ; TOS = -5
We can generalize all these optimizations into one rule: Keep repeat values on the stack!
Tip:
PostScript® is a stack–oriented programming language. There are many more books available about PostScript® than about the FPU assembly language: Mastering PostScript® will help you master the FPU.
;;;;;;; pinhole.asm ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; ; Find various parameters of a pinhole camera construction and use ; ; Started: 9-Jun-2001 ; Updated: 10-Jun-2001 ; ; Copyright (c) 2001 G. Adam Stanislav ; All rights reserved. ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; %include 'system.inc' %define BUFSIZE 2048 section .data align 4 ten dd 10 thousand dd 1000 tthou dd 10000 fd.in dd stdin fd.out dd stdout envar db 'PINHOLE=' ; Exactly 8 bytes, or 2 dwords long pinhole db '04,', ; Bender's constant (0.04) connors db '037', 0Ah ; Connors' constant usg db 'Usage: pinhole [-b] [-c] [-e] [-p <value>] [-o <outfile>] [-i <infile>]', 0Ah usglen equ $-usg iemsg db "pinhole: Can't open input file", 0Ah iemlen equ $-iemsg oemsg db "pinhole: Can't create output file", 0Ah oemlen equ $-oemsg pinmsg db "pinhole: The PINHOLE constant must not be 0", 0Ah pinlen equ $-pinmsg toobig db "pinhole: The PINHOLE constant may not exceed 18 decimal places", 0Ah biglen equ $-toobig huhmsg db 9, '???' separ db 9, '???' sep2 db 9, '???' sep3 db 9, '???' sep4 db 9, '???', 0Ah huhlen equ $-huhmsg header db 'focal length in millimeters,pinhole diameter in microns,' db 'F-number,normalized F-number,F-5.6 multiplier,stops ' db 'from F-5.6', 0Ah headlen equ $-header section .bss ibuffer resb BUFSIZE obuffer resb BUFSIZE dbuffer resb 20 ; decimal input buffer bbuffer resb 10 ; BCD buffer section .text align 4 huh: call write push dword huhlen push dword huhmsg push dword [fd.out] sys.write add esp, byte 12 ret align 4 perr: push dword pinlen push dword pinmsg push dword stderr sys.write push dword 4 ; return failure sys.exit align 4 consttoobig: push dword biglen push dword toobig push dword stderr sys.write push dword 5 ; return failure sys.exit align 4 ierr: push dword iemlen push dword iemsg push dword stderr sys.write push dword 1 ; return failure sys.exit align 4 oerr: push dword oemlen push dword oemsg push dword stderr sys.write push dword 2 sys.exit align 4 usage: push dword usglen push dword usg push dword stderr sys.write push dword 3 sys.exit align 4 global _start _start: add esp, byte 8 ; discard argc and argv[0] sub esi, esi .arg: pop ecx or ecx, ecx je near .getenv ; no more arguments ; ECX contains the pointer to an argument cmp byte [ecx], '-' jne usage inc ecx mov ax, [ecx] inc ecx .o: cmp al, 'o' jne .i ; Make sure we are not asked for the output file twice cmp dword [fd.out], stdout jne usage ; Find the path to output file - it is either at [ECX+1], ; i.e., -ofile -- ; or in the next argument, ; i.e., -o file or ah, ah jne .openoutput pop ecx jecxz usage .openoutput: push dword 420 ; file mode (644 octal) push dword 0200h | 0400h | 01h ; O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY push ecx sys.open jc near oerr add esp, byte 12 mov [fd.out], eax jmp short .arg .i: cmp al, 'i' jne .p ; Make sure we are not asked twice cmp dword [fd.in], stdin jne near usage ; Find the path to the input file or ah, ah jne .openinput pop ecx or ecx, ecx je near usage .openinput: push dword 0 ; O_RDONLY push ecx sys.open jc near ierr ; open failed add esp, byte 8 mov [fd.in], eax jmp .arg .p: cmp al, 'p' jne .c or ah, ah jne .pcheck pop ecx or ecx, ecx je near usage mov ah, [ecx] .pcheck: cmp ah, '0' jl near usage cmp ah, '9' ja near usage mov esi, ecx jmp .arg .c: cmp al, 'c' jne .b or ah, ah jne near usage mov esi, connors jmp .arg .b: cmp al, 'b' jne .e or ah, ah jne near usage mov esi, pinhole jmp .arg .e: cmp al, 'e' jne near usage or ah, ah jne near usage mov al, ',' mov [huhmsg], al mov [separ], al mov [sep2], al mov [sep3], al mov [sep4], al jmp .arg align 4 .getenv: ; If ESI = 0, we did not have a -p argument, ; and need to check the environment for "PINHOLE=" or esi, esi jne .init sub ecx, ecx .nextenv: pop esi or esi, esi je .default ; no PINHOLE envar found ; check if this envar starts with 'PINHOLE=' mov edi, envar mov cl, 2 ; 'PINHOLE=' is 2 dwords long rep cmpsd jne .nextenv ; Check if it is followed by a digit mov al, [esi] cmp al, '0' jl .default cmp al, '9' jbe .init ; fall through align 4 .default: ; We got here because we had no -p argument, ; and did not find the PINHOLE envar. mov esi, pinhole ; fall through align 4 .init: sub eax, eax sub ebx, ebx sub ecx, ecx sub edx, edx mov edi, dbuffer+1 mov byte [dbuffer], '0' ; Convert the pinhole constant to real .constloop: lodsb cmp al, '9' ja .setconst cmp al, '0' je .processconst jb .setconst inc dl .processconst: inc cl cmp cl, 18 ja near consttoobig stosb jmp short .constloop align 4 .setconst: or dl, dl je near perr finit fild dword [tthou] fld1 fild dword [ten] fdivp st1, st0 fild dword [thousand] mov edi, obuffer mov ebp, ecx call bcdload .constdiv: fmul st0, st2 loop .constdiv fld1 fadd st0, st0 fadd st0, st0 fld1 faddp st1, st0 fchs ; If we are creating a CSV file, ; print header cmp byte [separ], ',' jne .bigloop push dword headlen push dword header push dword [fd.out] sys.write .bigloop: call getchar jc near done ; Skip to the end of the line if you got '#' cmp al, '#' jne .num call skiptoeol jmp short .bigloop .num: ; See if you got a number cmp al, '0' jl .bigloop cmp al, '9' ja .bigloop ; Yes, we have a number sub ebp, ebp sub edx, edx .number: cmp al, '0' je .number0 mov dl, 1 .number0: or dl, dl ; Skip leading 0's je .nextnumber push eax call putchar pop eax inc ebp cmp ebp, 19 jae .nextnumber mov [dbuffer+ebp], al .nextnumber: call getchar jc .work cmp al, '#' je .ungetc cmp al, '0' jl .work cmp al, '9' ja .work jmp short .number .ungetc: dec esi inc ebx .work: ; Now, do all the work or dl, dl je near .work0 cmp ebp, 19 jae near .toobig call bcdload ; Calculate pinhole diameter fld st0 ; save it fsqrt fmul st0, st3 fld st0 fmul st5 sub ebp, ebp ; Round off to 4 significant digits .diameter: fcom st0, st7 fstsw ax sahf jb .printdiameter fmul st0, st6 inc ebp jmp short .diameter .printdiameter: call printnumber ; pinhole diameter ; Calculate F-number fdivp st1, st0 fld st0 sub ebp, ebp .fnumber: fcom st0, st6 fstsw ax sahf jb .printfnumber fmul st0, st5 inc ebp jmp short .fnumber .printfnumber: call printnumber ; F number ; Calculate normalized F-number fmul st0, st0 fld1 fld st1 fyl2x frndint fld1 fscale fsqrt fstp st1 sub ebp, ebp call printnumber ; Calculate time multiplier from F-5.6 fscale fld st0 ; Round off to 4 significant digits .fmul: fcom st0, st6 fstsw ax sahf jb .printfmul inc ebp fmul st0, st5 jmp short .fmul .printfmul: call printnumber ; F multiplier ; Calculate F-stops from 5.6 fld1 fxch st1 fyl2x sub ebp, ebp call printnumber mov al, 0Ah call putchar jmp .bigloop .work0: mov al, '0' call putchar align 4 .toobig: call huh jmp .bigloop align 4 done: call write ; flush output buffer ; close files push dword [fd.in] sys.close push dword [fd.out] sys.close finit ; return success push dword 0 sys.exit align 4 skiptoeol: ; Keep reading until you come to cr, lf, or eof call getchar jc done cmp al, 0Ah jne .cr ret .cr: cmp al, 0Dh jne skiptoeol ret align 4 getchar: or ebx, ebx jne .fetch call read .fetch: lodsb dec ebx clc ret read: jecxz .read call write .read: push dword BUFSIZE mov esi, ibuffer push esi push dword [fd.in] sys.read add esp, byte 12 mov ebx, eax or eax, eax je .empty sub eax, eax ret align 4 .empty: add esp, byte 4 stc ret align 4 putchar: stosb inc ecx cmp ecx, BUFSIZE je write ret align 4 write: jecxz .ret ; nothing to write sub edi, ecx ; start of buffer push ecx push edi push dword [fd.out] sys.write add esp, byte 12 sub eax, eax sub ecx, ecx ; buffer is empty now .ret: ret align 4 bcdload: ; EBP contains the number of chars in dbuffer push ecx push esi push edi lea ecx, [ebp+1] lea esi, [dbuffer+ebp-1] shr ecx, 1 std mov edi, bbuffer sub eax, eax mov [edi], eax mov [edi+4], eax mov [edi+2], ax .loop: lodsw sub ax, 3030h shl al, 4 or al, ah mov [edi], al inc edi loop .loop fbld [bbuffer] cld pop edi pop esi pop ecx sub eax, eax ret align 4 printnumber: push ebp mov al, [separ] call putchar ; Print the integer at the TOS mov ebp, bbuffer+9 fbstp [bbuffer] ; Check the sign mov al, [ebp] dec ebp or al, al jns .leading ; We got a negative number (should never happen) mov al, '-' call putchar .leading: ; Skip leading zeros mov al, [ebp] dec ebp or al, al jne .first cmp ebp, bbuffer jae .leading ; We are here because the result was 0. ; Print '0' and return mov al, '0' jmp putchar .first: ; We have found the first non-zero. ; But it is still packed test al, 0F0h jz .second push eax shr al, 4 add al, '0' call putchar pop eax and al, 0Fh .second: add al, '0' call putchar .next: cmp ebp, bbuffer jb .done mov al, [ebp] push eax shr al, 4 add al, '0' call putchar pop eax and al, 0Fh add al, '0' call putchar dec ebp jmp short .next .done: pop ebp or ebp, ebp je .ret .zeros: mov al, '0' call putchar dec ebp jne .zeros .ret: ret
The code follows the same format as all the other filters we have seen before, with one subtle exception:
We are no longer assuming that the end of input implies the end of things to do, something we took for granted in the character–oriented filters.
This filter does not process characters. It processes a language (albeit a very simple one, consisting only of numbers).
When we have no more input, it can mean one of two things:
We are done and can quit. This is the same as before.
The last character we have read was a digit. We have stored it at the end of our ASCII–to–float conversion buffer. We now need to convert the contents of that buffer into a number and write the last line of our output.
For that reason, we have modified our
getcharand ourreadroutines to return with thecarry flagclear whenever we are fetching another character from the input, or thecarry flagset whenever there is no more input.Of course, we are still using assembly language magic to do that! Take a good look at
getchar. It always returns with thecarry flagclear.Yet, our main code relies on the
carry flagto tell it when to quit—and it works.The magic is in
read. Whenever it receives more input from the system, it just returns togetchar, which fetches a character from the input buffer, clears thecarry flagand returns.But when
readreceives no more input from the system, it does not return togetcharat all. Instead, theadd esp, byte 4op code adds4toESP, sets thecarry flag, and returns.So, where does it return to? Whenever a program uses the
callop code, the microprocessorpushes the return address, i.e., it stores it on the top of the stack (not the FPU stack, the system stack, which is in the memory). When a program uses theretop code, the microprocessorpops the return value from the stack, and jumps to the address that was stored there.But since we added
4toESP(which is the stack pointer register), we have effectively given the microprocessor a minor case of amnesia: It no longer remembers it wasgetcharthatcalledread.And since
getcharneverpushed anything beforecallingread, the top of the stack now contains the return address to whatever or whoevercalledgetchar. As far as that caller is concerned, hecalledgetchar, whichreturned with thecarry flagset!
Other than that, the bcdload
routine is caught up in the middle of a
Lilliputian conflict between the Big–Endians
and the Little–Endians.
It is converting the text representation of a number into that number: The text is stored in the big–endian order, but the packed decimal is little–endian.
To solve the conflict, we use the std
op code early on. We cancel it with cld
later on: It is quite important we do not
call anything that may depend on
the default setting of the direction
flag while std is active.
Everything else in this code should be quite clear, providing you have read the entire chapter that precedes it.
It is a classical example of the adage that programming requires a lot of thought and only a little coding. Once we have thought through every tiny detail, the code almost writes itself.
Because we have decided to make the program ignore any input except for numbers (and even those inside a comment), we can actually perform textual queries. We do not have to, but we can.
In my humble opinion, forming a textual query, instead of having to follow a very strict syntax, makes software much more user friendly.
Suppose we want to build a pinhole camera to use the 4x5 inch film. The standard focal length for that film is about 150mm. We want to fine–tune our focal length so the pinhole diameter is as round a number as possible. Let us also suppose we are quite comfortable with cameras but somewhat intimidated by computers. Rather than just have to type in a bunch of numbers, we want to ask a couple of questions.
Our session might look like this:
%pinhole Computer, What size pinhole do I need for the focal length of 150?150 490 306 362 2930 12Hmmm... How about 160?160 506 316 362 3125 12Let's make it 155, please.155 498 311 362 3027 12Ah, let's try 157...157 501 313 362 3066 12156?156 500 312 362 3047 12That's it! Perfect! Thank you very much! ^D
We have found that while for the focal length of 150, our pinhole diameter should be 490 microns, or 0.49 mm, if we go with the almost identical focal length of 156 mm, we can get away with a pinhole diameter of exactly one half of a millimeter.
Because we have chosen the #
character to denote the start of a comment,
we can treat our pinhole
software as a scripting language.
You have probably seen shell scripts that start with:
#! /bin/sh
...or...
#!/bin/sh
...because the blank space after the #!
is optional.
Whenever UNIX® is asked to run an executable
file which starts with the #!,
it assumes the file is a script. It adds the
command to the rest of the first line of the
script, and tries to execute that.
Suppose now that we have installed pinhole in /usr/local/bin/, we can now write a script to calculate various pinhole diameters suitable for various focal lengths commonly used with the 120 film.
The script might look something like this:
#! /usr/local/bin/pinhole -b -i # Find the best pinhole diameter # for the 120 film ### Standard 80 ### Wide angle 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 ### Telephoto 100, 120, 140
Because 120 is a medium size film, we may name this file medium.
We can set its permissions to execute, and run it as if it were a program:
%chmod 755 medium%./medium
UNIX® will interpret that last command as:
%/usr/local/bin/pinhole -b -i ./medium
It will run that command and display:
80 358 224 256 1562 11 30 219 137 128 586 9 40 253 158 181 781 10 50 283 177 181 977 10 60 310 194 181 1172 10 70 335 209 181 1367 10 100 400 250 256 1953 11 120 438 274 256 2344 11 140 473 296 256 2734 11
Now, let us enter:
%./medium -c
UNIX® will treat that as:
%/usr/local/bin/pinhole -b -i ./medium -c
That gives it two conflicting options:
-b and -c
(Use Bender's constant and use Connors'
constant). We have programmed it so
later options override early ones—our
program will calculate everything
using Connors' constant:
80 331 242 256 1826 11 30 203 148 128 685 9 40 234 171 181 913 10 50 262 191 181 1141 10 60 287 209 181 1370 10 70 310 226 256 1598 11 100 370 270 256 2283 11 120 405 296 256 2739 11 140 438 320 362 3196 12
We decide we want to go with Bender's constant after all. We want to save its values as a comma–separated file:
%./medium -b -e > bender%cat benderfocal length in millimeters,pinhole diameter in microns,F-number,normalized F-number,F-5.6 multiplier,stops from F-5.6 80,358,224,256,1562,11 30,219,137,128,586,9 40,253,158,181,781,10 50,283,177,181,977,10 60,310,194,181,1172,10 70,335,209,181,1367,10 100,400,250,256,1953,11 120,438,274,256,2344,11 140,473,296,256,2734,11%
Assembly language programmers who "grew up" under MS-DOS® and Windows® often tend to take shortcuts. Reading the keyboard scan codes and writing directly to video memory are two classical examples of practices which, under MS-DOS® are not frowned upon but considered the right thing to do.
The reason? Both the PC BIOS and MS-DOS® are notoriously slow when performing these operations.
You may be tempted to continue similar practices in the UNIX® environment. For example, I have seen a web site which explains how to access the keyboard scan codes on a popular UNIX® clone.
That is generally a very bad idea in UNIX® environment! Let me explain why.
For one thing, it may simply not be possible. UNIX® runs in protected mode. Only the kernel and device drivers are allowed to access hardware directly. Perhaps a particular UNIX® clone will let you read the keyboard scan codes, but chances are a real UNIX® operating system will not. And even if one version may let you do it, the next one may not, so your carefully crafted software may become a dinosaur overnight.
But there is a much more important reason not to try accessing the hardware directly (unless, of course, you are writing a device driver), even on the UNIX® like systems that let you do it:
UNIX® is an abstraction!
There is a major difference in the philosophy of design between MS-DOS® and UNIX®. MS-DOS® was designed as a single-user system. It is run on a computer with a keyboard and a video screen attached directly to that computer. User input is almost guaranteed to come from that keyboard. Your program's output virtually always ends up on that screen.
This is NEVER guaranteed under UNIX®. It is quite common for a UNIX® user to pipe and redirect program input and output:
%program1 | program2 | program3 > file1
If you have written program2, your input
does not come from the keyboard but from the output of
program1. Similarly, your output does not
go to the screen but becomes the input for
program3 whose output, in turn,
goes to file1.
But there is more! Even if you made sure that your input comes from, and your output goes to, the terminal, there is no guarantee the terminal is a PC: It may not have its video memory where you expect it, nor may its keyboard be producing PC-style scan codes. It may be a Macintosh®, or any other computer.
Now you may be shaking your head: My software is in PC assembly language, how can it run on a Macintosh®? But I did not say your software would be running on a Macintosh®, only that its terminal may be a Macintosh®.
Under UNIX®, the terminal does not have to be directly attached to the computer that runs your software, it can even be on another continent, or, for that matter, on another planet. It is perfectly possible that a Macintosh® user in Australia connects to a UNIX® system in North America (or anywhere else) via telnet. The software then runs on one computer, while the terminal is on a different computer: If you try to read the scan codes, you will get the wrong input!
Same holds true about any other hardware: A file you are reading may be on a disk you have no direct access to. A camera you are reading images from may be on a space shuttle, connected to you via satellites.
That is why under UNIX® you must never make any assumptions about where your data is coming from and going to. Always let the system handle the physical access to the hardware.
Note:
These are caveats, not absolute rules. Exceptions are possible. For example, if a text editor has determined it is running on a local machine, it may want to read the scan codes directly for improved control. I am not mentioning these caveats to tell you what to do or what not to do, just to make you aware of certain pitfalls that await you if you have just arrived to UNIX® form MS-DOS®. Of course, creative people often break rules, and it is OK as long as they know they are breaking them and why.
This tutorial would never have been possible without the help of many experienced FreeBSD programmers from the FreeBSD technical discussions mailing list, many of whom have patiently answered my questions, and pointed me in the right direction in my attempts to explore the inner workings of UNIX® system programming in general and FreeBSD in particular.
Thomas M. Sommers opened the door for me. His How do I write "Hello, world" in FreeBSD assembler? web page was my first encounter with an example of assembly language programming under FreeBSD.
Jake Burkholder has kept the door open by willingly answering all of my questions and supplying me with example assembly language source code.
Copyright © 2000-2001 G. Adam Stanislav. All rights reserved.
[1] Copyright © 1998 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc.. 1-55860-428-6. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc.. Computer Organization and Design. The Hardware / Software Interface. 1-2.
[2] Copyright © 1993 Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.. 0-201-56317-7. Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.. Advanced Programming in the Unix Environment. 1-2.
A
- arguments, Buffer Overflows
B
- bounds checking
- compiler-based, Compiler based run-time bounds checking
- library-based, Library based run-time bounds checking
- buffer overflow, Buffer Overflows, Compiler based run-time bounds checking
C
- chroot(), Limiting your program's environment
- contributed software, Contributed Software
- core team, Encumbered Files
D
- data validation, Trust
F
- frame pointer, Buffer Overflows
J
L
- LIFO, Buffer Overflows
M
- Morris Internet worm, Buffer Overflows
N
- NUL termination, Avoiding Buffer Overflows
P
- Perl, Perl and Python
- Perl Taint mode, Trust
- ports maintainer, MAINTAINER on Makefiles
- positive filtering, Trust
- POSIX.1e Process Capabilities, POSIX®.1e Process Capabilities
- process image
- frame pointer, Buffer Overflows
- stack pointer, Buffer Overflows
- ProPolice, Compiler based run-time bounds checking
- Python, Perl and Python
R
- race conditions
- access checks, Race Conditions
- file opens, Race Conditions
- signals, Race Conditions
- release engineering, Encumbered Files
- return address, Buffer Overflows
S
- seteuid, SetUID issues
- stack, Buffer Overflows
- stack frame, Buffer Overflows
- stack pointer, Buffer Overflows
- stack-overflow, Buffer Overflows
- StackGuard, Compiler based run-time bounds checking
- string copy functions
- strlcat, Avoiding Buffer Overflows
- strlcpy, Avoiding Buffer Overflows
- strncat, Avoiding Buffer Overflows
- strncpy, Avoiding Buffer Overflows
- style, Style Guidelines
T
- TrustedBSD, POSIX®.1e Process Capabilities
U
- user IDs
- effective user ID, SetUID issues
- real user ID, SetUID issues
V
- Von-Neuman, Buffer Overflows