 |  |  | 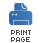 |  |
A content-based router, shown in Figure 5.1, enables you to route messages to the appropriate destination based on the message contents.
The following example shows how to route a request from an input,
seda:a, endpoint to either seda:b,
queue:c, or seda:d depending on the evaluation of
various predicate expressions:
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("seda:a").choice()
.when(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b")
.when(header("foo").isEqualTo("cheese")).to("seda:c")
.otherwise().to("seda:d");
}
};The following example shows how to configure the same route in XML:
<camelContext id="buildSimpleRouteWithChoice" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="seda:a"/>
<choice>
<when>
<xpath>$foo = 'bar'</xpath>
<to uri="seda:b"/>
</when>
<when>
<xpath>$foo = 'cheese'</xpath>
<to uri="seda:c"/>
</when>
<otherwise>
<to uri="seda:d"/>
</otherwise>
</choice>
</route>
</camelContext>