 |  |  | 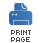 |  |
The multicast pattern, shown in Figure 5.8, is a variation of the recipient list with a fixed destination pattern, which is compatible with the InOut message exchange pattern. This is in contrast to recipient list, which is only compatible with the InOnly exchange pattern.
Whereas the multicast processor receives multiple Out messages in response to the original request (one from each of the recipients), the original caller is only expecting to receive a single reply. Thus, there is an inherent mismatch on the reply leg of the message exchange, and to overcome this mismatch, you must provide a custom aggregation strategy to the multicast processor. The aggregation strategy class is responsible for aggregating all of the Out messages into a single reply message.
Consider the example of an electronic auction service, where a seller offers an item for
sale to a list of buyers. The buyers each put in a bid for the item, and the seller
automatically selects the bid with the highest price. You can implement the logic for
distributing an offer to a fixed list of buyers using the multicast() DSL
command, as follows:
from("cxf:bean:offer").multicast(new HighestBidAggregationStrategy()).
to("cxf:bean:Buyer1", "cxf:bean:Buyer2", "cxf:bean:Buyer3");Where the seller is represented by the endpoint, cxf:bean:offer, and the
buyers are represented by the endpoints, cxf:bean:Buyer1,
cxf:bean:Buyer2, cxf:bean:Buyer3. To consolidate the
bids received from the various buyers, the multicast processor uses the aggregation
strategy, HighestBidAggregationStrategy. You can implement the
HighestBidAggregationStrategy in Java, as follows:
// Java
import org.apache.camel.processor.aggregate.AggregationStrategy;
import org.apache.camel.Exchange;
public class HighestBidAggregationStrategy implements AggregationStrategy {
public Exchange aggregate(Exchange oldExchange, Exchange newExchange) {
float oldBid = oldExchange.getOut().getHeader("Bid", Float.class);
float newBid = newExchange.getOut().getHeader("Bid", Float.class);
return (newBid > oldBid) ? newExchange : oldExchange;
}
}Where it is assumed that the buyers insert the bid price into a header named,
Bid. For more details about custom aggregation strategies, see Aggregator.
By default, the multicast processor invokes each of the recipient endpoints one after
another (in the order listed in the to() command). In some cases, this might
cause unacceptably long latency. To avoid these long latency times, you have the
option of enabling parallel processing in the multicast processor by passing the value
true as the second argument. For example, to enable parallel processing in
the electronic auction example, define the route as follows:
from("cxf:bean:offer")
.multicast(new HighestBidAggregationStrategy(), true)
.to("cxf:bean:Buyer1", "cxf:bean:Buyer2", "cxf:bean:Buyer3");Where the multicast processor now invokes the buyer endpoints, using a thread pool that has one thread for each of the endpoints.
If you want to customize the size of the thread pool that invokes the buyer endpoints,
you can invoke the setThreadPoolExecutor() method to specify your own custom
thread pool executor. For example:
from("cxf:bean:offer")
.multicast(new HighestBidAggregationStrategy(), true)
.setThreadPoolExecutor(MyExecutor)
.to("cxf:bean:Buyer1", "cxf:bean:Buyer2", "cxf:bean:Buyer3");Where MyExecutor is an instance of java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor type.
The following example shows how to configure a similar route in XML, where the route uses a custom aggregation strategy and a custom thread executor:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd
">
<camelContext id="camel" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="cxf:bean:offer"/>
<multicast strategyRef="highestBidAggregationStrategy"
parallelProcessing="true"
threadPoolRef="myThreadExcutor">
<to uri="cxf:bean:Buyer1"/>
<to uri="cxf:bean:Buyer2"/>
<to uri="cxf:bean:Buyer3"/>
</multicast>
</route>
</camelContext>
<bean id="highestBidAggregationStrategy" class="com.acme.example.HighestBidAggregationStrategy"/>
<bean id="myThreadExcutor" class="com.acme.example.MyThreadExcutor"/>
</beans>Where both the parallelProcessing attribute and the
threadPoolRef attribute are optional. It is only necessary to set them if you want
to customize the threading behavior of the multicast processor.