 |  |  | 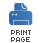 |  |
The routing slip pattern, shown in Figure 5.7, enables you to route a message consecutively through a series of processing steps, where the sequence of steps is not known at design time and can vary for each message. The list of endpoints through which the message should pass is stored in a header field (the slip), which FUSE Mediation Router reads at run time to construct a pipeline on the fly.
By default, the routing slip appears in a header named routingSlipHeader,
where the header value is a comma-separated list of endpoint URIs. For example, a routing
slip that specifies a sequence of security tasks—decrypting, authenticating, and
de-duplicating a message—might look like the following:
cxf:bean:decrypt,cxf:bean:authenticate,cxf:bean:dedup
The following route takes messages from the direct:a endpoint and passes
them into the routing slip pattern:
from("direct:a").routingSlip();You can customize the name of the routing slip header by passing a string argument to
the routingSlip() command, as follows:
from("direct:b").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader");You can also customize the URI delimiter using the two-argument form of
routingSlip(). The following example defines a route that customizes the routing slip header to be
aRoutingSlipHeader and, to specify # as the URI delimiter:
from("direct:c").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader", "#");The following example shows how to configure the same route in XML:
<camelContext id="buildRoutingSlip" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="direct:c"/>
<routingSlip headerName="aRoutingSlipHeader" uriDelimiter="#"/>
</route>
</camelContext>