 |  |  |  |  |
A splitter is a type of router that splits an incoming message
into a series of outgoing messages. Each of the outgoing messages contains a piece of the
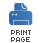
original message. In FUSE Mediation Router, the splitter pattern, shown in Figure 5.4, is implemented by the
splitter() Java DSL command, which takes a list of message pieces as its sole
argument.
Each outgoing message includes a copy of all of the original headers from the incoming message. In addition, the splitter processor adds the headers descibed in Table 5.1 to each outgoing message.
Table 5.1. Splitter Headers
| Header Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
org.apache.camel.splitSize | Integer | The total number of parts into which the original message is split. |
org.apache.camel.splitCounter | Integer | Index of the current message part (starting at 0). |
The following example defines a route from seda:a to seda:b
that splits messages by converting each line of an incoming message into a separate outgoing
message:
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("seda:a").splitter(bodyAs(String.class).tokenize("\n")).to("seda:b");
}
};The splitter can use any expression language, so you can split messages using any of
the supported scripting languages, such as XPath, XQuery, or SQL (see Languages for Expressions and Predicates in bar elements from an incoming message and insert them into separate outgoing
messages:
from("activemq:my.queue").splitter(xpath("//foo/bar")).to("file://some/directory")The following example shows how to configure a splitter route in XML, using the XPath scripting language:
<camelContext id="buildSplitter" xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/camel/schema/spring">
<route>
<from uri="seda:a"/>
<splitter>
<xpath>//foo/bar</xpath>
<to uri="seda:b"/>
</splitter>
</route>
</camelContext>