 |  |  |  |  |
An instance of org.apache.camel.Endpoint type encapsulates an endpoint URI,
and it also serves as a factory for Consumer, Producer, and
Exchange objects. There are three different approaches to implementing an endpoint:
Event-driven
scheduled poll
polling
These endpoint implementation patterns complement the corresponding patterns for implementing a consumer—see Implementing the Consumer Interface.
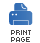
Figure 6.1 shows the relevant Java interfaces and
classes that make up the Endpoint inheritance hierarchy.
Example 6.1 shows the definition of the
org.apache.camel.Endpoint interface.
Example 6.1. Endpoint Interface
package org.apache.camel;
public interface Endpoint<E extends Exchange> {
boolean isSingleton();
String getEndpointUri();
CamelContext getCamelContext();
void setCamelContext(CamelContext context);
void configureProperties(Map options);
boolean isLenientProperties();
E createExchange();
E createExchange(ExchangePattern pattern);
E createExchange(Exchange exchange);
Producer<E> createProducer() throws Exception;
Consumer<E> createConsumer(Processor processor) throws Exception;
PollingConsumer<E> createPollingConsumer() throws Exception;
}The Endpoint interface defines the following methods:
isSingleton()—Returns true, if you want to ensure
that each URI maps to a single endpoint within a CamelContext. When this property is
true, multiple references to the identical URI within
your routes always refer to a single endpoint instance. When this
property is false, on the other hand, multiple references to the same URI
within your routes refer to distinct endpoint instances. Each time you
refer to the URI in a route, a new endpoint instance is created.
getEndpointUri()—Returns the endpoint URI of this endpoint.
getCamelContext()—return a reference to the
CamelContext instance to which this endpoint belongs.
setCamelContext()—Sets the CamelContext instance to
which this endpoint belongs.
configureProperties()—Stores a copy of the parameter map that is
used to inject parameters when creating a new Consumer instance.
isLenientProperties()—Returns true to
indicate that the URI is allowed to contain unknown parameters (that is, parameters that cannot be
injected on the Endpoint or the Consumer class).
Normally, this method should be implemented to return false.
createExchange()—An overloaded method with the
following variants:
E createExchange()—Creates a new exchange instance with a
default exchange pattern setting.
E createExchange(ExchangePattern pattern)—Creates a new
exchange instance with the specified exchange pattern.
E createExchange(Exchange exchange)—Converts the given
exchange argument to the type of exchange needed for this endpoint.
If the given exchange is not already of the correct type, this method copies it into
a new instance of the correct type. A default implementation of this method is
provided in the DefaultEndpoint class.
createProducer()—Factory method used to create new
Producer instances.
createConsumer()—Factory method to create new event-driven
consumer instances. The processor argument is a reference to the first processor in the route.
createPollingConsumer()—Factory method to create new
polling consumer instances.
In order to avoid unnecessary overhead, it is a good idea to create a
single endpoint instance for all endpoints that have the same URI
(within a CamelContext). You can enforce this condition by implementing
isSingleton() to return true.
![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
In this context, same URI means that two URIs are the same when compared using string equality. In principle, it is possible to have two URIs that are equivalent, though represented by different strings. In that case, the URIs would not be treated as the same. |