 |  |  |  |  |
An instance of org.apache.camel.Exchange type encapsulates all of the
messages belonging to a single message exchange. For example, a typical synchronous
invocation consists of an In message and an
Out message.
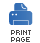
Figure 9.1
shows the inheritance hierarchy for the exchange type. You do not always need to implement a
custom exchange type for a component. In many cases, the default implementation,
DefaultExchange, is adequate.
Example 9.1 shows the definition of the
org.apache.camel.Exchange interface.
Example 9.1. Exchange Interface
package org.apache.camel;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.camel.spi.UnitOfWork;
public interface Exchange {
ExchangePattern getPattern();
Object getProperty(String name);
<T> T getProperty(String name, Class<T> type);
void setProperty(String name, Object value);
Object removeProperty(String name);
Map<String, Object> getProperties();
Message getIn();
void setIn(Message in);
Message getOut();
Message getOut(boolean lazyCreate);
void setOut(Message out);
Message getFault();
Message getFault(boolean lazyCreate);
Throwable getException();
void setException(Throwable e);
boolean isFailed();
CamelContext getContext();
Exchange newInstance();
Exchange copy();
void copyFrom(Exchange source);
UnitOfWork getUnitOfWork();
void setUnitOfWork(UnitOfWork unitOfWork);
String getExchangeId();
void setExchangeId(String id);
}The Exchange interface defines the following methods:
getPattern()—The exchange pattern can be one of the values
enumerated in org.apache.camel.ExchangePattern. The following exchange
pattern values are supported:
InOnly
RobustInOnly
InOut
InOptionalOut
OutOnly
RobustOutOnly
OutIn
OutOptionalIn
Normally, you specify the exchange pattern value in the constructor of your custom exchange class.
setProperty(), getProperty(),
getProperties(), removeProperty()—Use the property
setter and getter methods to associate named properties with the exchange instance. The
properties consist of miscellaneous metadata that you might need for your custom
exchange implementation.
setIn(), getIn()—Setter and getter methods for the
In message. These methods are used only for exchange patterns
that can have an In message.
The getIn() implementation provided by the DefaultExchange
class implements lazy creation semantics: if the In message
is null when getIn() is called, the DefaultExchange class
creates a default In message.
setOut(), getOut()—Setter and getter methods for the
Out message. These methods are used only for exchange patterns
that can have an Out message.
There are two varieties of getOut() method in the
DefaultExchange class:
getOut() with no arguments enables lazy creation of an
Out message. If the current Out
message is null, a new message is automatically created.[3]
getOut(boolean lazyCreate) with a boolean argument triggers lazy
creation. If the argument is true, it returns the current value even if the
current Out message is null.
getFault()—Getter message for the fault message. There are two
varieties of getFault() method in the DefaultExchange
class:
getFault() with no arguments enables lazy creation of a
Fault message.
getFault(boolean lazyCreate) with a boolean argument triggers lazy
creation. If the argument is true, it returns the current value even if the
current Fault message is null.
setException(), getException()—Getter and setter
methods for an exception object (of Throwable type).
isFailed()—Returns true, if the exchange failed
either due to an exception or due to a fault.
getContext()—Returns a reference to the associated
CamelContext instance.
newInstance()—Creates a new exchange instance for the purpose of
copying the current exchange object. For example, in the DefaultExchange
class, the copy() method calls newInstance() to create a new
exchange instance.
copy()—Creates a new, identical (apart from the exchange ID) copy
of the current custom exchange object. The body and headers of the
In message, the Out message (if any), and
the Fault message (if any) are also copied by this
operation.
copyFrom()—Copies the generic contents (apart from the exchange ID)
of the specified generic exchange object, exchange, into the current
exchange instance. Because this method must be able to copy from
any exchange type, it copies the generic exchange properties, but
not the custom properties. The body and headers of the In message,
the Out message (if any), and the Fault
message (if any) are also copied by this operation.
setUnitOfWork(), getUnitOfWork()—Getter and setter
methods for the org.apache.camel.spi.UnitOfWork bean property. This
property is only required for exchanges that can participate in a transaction.
setExchangeId(), getExchangeId()—Getter and setter
methods for the exchange ID. Whether or not a custom component uses and exchange ID is an implementation detail.