Table of Contents
The aggregator framework allows pluggable data sources and sinks to be written and connected together. Generally a source collects data from or about a particular grid resource, and passes it to a sink which does something interesting with it.
The aggregator sinks supplied with the toolkit implement the WS MDS Index Service and WS MDS Trigger Service. The aggregator sources supplied with the toolkit collect information using resource property queries, subscription/notification, and execution of external programs.
This document describes the programmatic interfaces to the aggregator framework. See also general Globus Toolkit coding guidelines and GT 4.0 best practices.
Features new in release GT 4.0
- Ported to use WSRF mechanisms (previously used OGSI).
- Additional sources which collect information by polling and by execution of local scripts.
- Management of aggregations is now performed over the wire through WS ServiceGroup APIs.
Other Supported Features
- Collects information from grid resources using pluggable aggregation sources.
- Delivers collected information to pluggable sinks.
- Manages creation and destruction of individual aggregation registrations.
Protocol changes since GT version 3.2
- The aggregator framework is a complete reimplementation of the MDS3 aggregator framework using WSRF rather than OGSI protocols.
- No wireside compatibility with MDS3 aggregator framework.
- Architectural similarity should make porting straightforward.
API changes since GT version 3.2
- APIs entirely rewritten, so no API compatibility.
- Architectural similarity should make porting straightforward.
Exception changes since GT version 3.2
- See API changes above.
Schema changes since GT version 3.2
- Registration interface uses WSRF rather than OGSI schemas.
- New per-source and per-sink configuration schemas.
Aggregator Framework depends on the following GT components:
- Java WS Core
Aggregator Framework depends on the following 3rd party software:
- None
By default, the aggregator sources do not use authentication credentials -- they retrieve information using anonymous SSL authentication or no authentication at all, and thus retrieve only publicly-available information. If a user or administrator changes that configuration so that a service's aggregator source uses credentials to acquire non-privileged data, then that user or administrator must configure the service's aggregator sink to limit access to authorized users.
The WS MDS Aggregator Framework is the software framework on which WS MDS services are built. The aggregator framework collects data from an aggregator source and sends that data to an aggregator sink for processing. Aggregator sources distributed with the Globus Toolkit include modules that query resource properties, acquire data through subscription/notification, and execute programs to generate data. Another way of describing the Aggregator Framework is that it is designed to facilitate the collecting of information from or about WS-Resources via plugin aggregator sources and the feeding of that information to plugin aggregator sinks, which can then perform actions such as re-publishing, logging, or archiving the information.
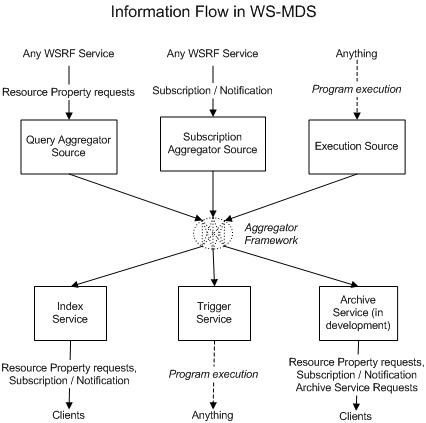
Aggregators work on a type of service group called an
AggregatorServiceGroupRP. Resources may be
registered to an AggregatorServiceGroupRP using the service
group add operation, which will cause an entry to be
added to the service group. The entry will include configuration
parameters for the aggregator source; when the registration is
made, the appropriate aggregation source and sinks will be
informed; the aggregator source will begin collecting data and
inserting it into the corresponding service group entry, and the
aggregator sink will begin processing the information in the
service group entries.
The method of collection by source and processing by the sink is dependent on the particular instantiation of the aggregator framework.
The aggregator sinks distributed with the toolkit
(org.globus.mds.aggregator.impl.ServiceGroupEntryAggregatorSink
and org.globus.mds.trigger.impl.TriggerResource) are
described in the following table.
Table 1. Standard aggregator sinks
| Aggregator Sink | Service Implemented | Description |
|---|---|---|
ServiceGroupEntryAggregatorSink | Index Service | The servicegroup sink (used by the Index Service) publishes received data as content in the AggregatingServiceGroup entry used to manage the registration. This data can therefore be retrieved by querying the index for its 'entries' resource property. |
TriggerResource | Trigger Service | The Trigger Service provides an aggregator sink which receives data, applies tests to that data, and if the tests match, runs a specified executable. See the trigger service documentation for more information. |
The aggregator sources supplied with the toolkit collect information using resource property queries (query sources), subscription/notification (subscription sources), and execution of external programs (execution sources).
The aggregator sources supplied with the Globus Toolkit are listed in the following table.
![[Note]](../../../../../docbook-images/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
All aggregator sources listed in this
table are in the |
Table 2. Standard aggregator sources
| Aggregator Source | Description |
|---|---|
| QueryAggregatorSource | The query source collects information from a registered resource by using WS-Resource Properties polling mechanisms:
Polls are made periodically, with both the period and target Resource Properties specified in the registration message. |
| SubscriptionAggregatorSource | The subscription source collects information from a registered resource using WS-Notification mechanisms. Data is delivered when property values change, rather than periodically. |
| ExecutionAggregatorSource | The execution source collects information about (not necessarily from) a registered resource by execution of a local executable, which is passed as input the identity of the registered resource. Details of the interface between the execution source and local executables are in Configuring the Execution Aggregator Source. |
The semantics and syntax of the APIs and WSDL for the component, along with descriptions of domain-specific structured interface data, can be found in the public interface guide.
The aggregator framework is used to create MDS services by linking an aggregator source (a java class that implements the AggregatorSource interface to collect data) to an aggregator sink (a java class that implements the AggregatorSink interface to process data, e.g., by providing a service interface for it). The AggregatorSource and AggregatorSink interfaces are documented in the aggregator Public Interface Guide.
Use of the index service (based on the WS MDS Aggregator Framework) is covered in the Build a Grid Service Tutorial (GlobusWORLD 2005).
See the Debug section of the Java WS Core Developer's Guide for general information on logging, including which files to edit to set logging properties.
To turn on debug logging for the Aggregator framework, add the line:
log4j.category.org.globus.mds.aggregator=DEBUG
to the appropriate properties file.
General troubleshooting information can be found in the GT 4.0 Java WS Core Developer's Guide.
Specifications for resource properties, service groups, and subscription/notification are available at http://www.globus.org/wsrf/.
