
IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding
Version 1.0 Final Specification
 |
IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding Version 1.0 Final Specification |
Copyright © 2003 IMS Global Learning Consortium, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The IMS Logo is a trademark of IMS Global Learning Consortium, Inc.
Document Name: IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding
Revision: 03 March 2003
IPR and Distribution Notices
Recipients of this document are requested to submit, with their comments, notification of any relevant patent claims or other intellectual property rights of which they may be aware that might be infringed by any implementation of the specification set forth in this document, and to provide supporting documentation.
IMS takes no position regarding the validity or scope of any intellectual property or other rights that might be claimed to pertain to the implementation or use of the technology described in this document or the extent to which any license under such rights might or might not be available; neither does it represent that it has made any effort to identify any such rights. Information on IMS's procedures with respect to rights in IMS specifications can be found at the IMS Intellectual Property Rights web page: http://www.imsglobal.org/ipr/imsipr_policyFinal.pdf.
Copyright © 2003 IMS Global Learning Consortium. All Rights Reserved.
If you wish to copy or distribute this document, you must complete a valid Registered User license registration with IMS and receive an email from IMS granting the license to distribute the specification. To register, follow the instructions on the IMS website: http://www.imsglobal.org/specificationdownload.cfm.
This document may be copied and furnished to others by Registered Users who have registered on the IMS website provided that the above copyright notice and this paragraph are included on all such copies. However, this document itself may not be modified in any way, such as by removing the copyright notice or references to IMS, except as needed for the purpose of developing IMS specifications, under the auspices of a chartered IMS project group.
Use of this specification to develop products or services is governed by the license with IMS found on the IMS website: http://www.imsglobal.org/license.html.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will not be revoked by IMS or its successors or assigns.
THIS SPECIFICATION IS BEING OFFERED WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY WHATSOEVER, AND IN PARTICULAR, ANY WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT IS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED. ANY USE OF THIS SPECIFICATION SHALL BE MADE ENTIRELY AT THE IMPLEMENTER'S OWN RISK, AND NEITHER THE CONSORTIUM, NOR ANY OF ITS MEMBERS OR SUBMITTERS, SHALL HAVE ANY LIABILITY WHATSOEVER TO ANY IMPLEMENTER OR THIRD PARTY FOR ANY DAMAGES OF ANY NATURE WHATSOEVER, DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ARISING FROM THE USE OF THIS SPECIFICATION.
This document describes the XML Binding for the IMS Simple Sequencing Information Model. It specifies an XML Schema binding conformant with the W3C's XML Schema Recommendation of 02 May 2001.
An XML binding using the Document Type Definition (DTD) format is specifically excluded from this binding specification. Other XML binding types such as Resource Description Format (RDF) may be added in the future.
The prose copy of the Sequencing Definition Model and Tracking Information Model contained within the Simple Sequencing Information and Behavior Model document are the normative and definitive specification of IMS Simple Sequencing. All binding structures specified herein are not normative or definitive, with the exception of names for XSD structures. The XSD structure names as applied to the Sequencing Definition Model elements may not be redefined, nor may any XSD structures.
This document is the IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding v1.0 Final Specification document and is derived from the corresponding Information and Behavior Model [SS, 03a]. As such it will be used as the basis for the development of the following document:
The structure of this document is:
| CP |
Content Packaging |
| DTD |
Document Type Definition |
| RDF |
Resource Description Format |
| SS |
Simple Sequencing |
| W3C |
World Wide Web Consortium |
| XML |
Extensible Mark-up Language |
| XSD |
XML Schema |
The conceptual model for expressing sequencing definitions is a hierarchy. Hierarchical models are convenient for representing data consisting of many elements and sub-elements. XML is perfectly suited for representing hierarchical models. An XML document is a hierarchy comprised of elements that have contents and attributes.
An element is a component of a document that has been identified in a way a computer can understand. Each element has a tag name. When a tag name is shown as "<TAGNAME>", with less-than and greater-than symbols before and after the tag name, it serves as the start-tag to mark the beginning of an element. When that same tag name has a forward slash "/" added, it serves as an end-tag such as "</TAGNAME>". An element may have contents between its start and end-tags, and may have one or more attributes. When an XML element has a start and end-tag (also called an opening and closing tag) with a common name, it is considered to be "well-formed" XML. The contents of an element are placed between the start and end-tags as shown below:
<TAGNAME>contents</TAGNAME>
An element may contain other elements, Parsed Character Data (PCDATA), Character Data (CDATA), or a mixture of PCDATA and elements. The allowable contents of an element are its content model. XML parsers treat PCDATA with their special or reserved meaning unless they are specifically marked (or "escaped"). In contrast, CDATA can use special or reserved characters without having to escape them, as CDATA is not read by XML parsers.
An attribute provides additional information about an element. Attributes are a way of attaching characteristics or properties to the elements of a document. An element may have more than one attribute. Attributes are contained within the start tag of an element. Attributes are represented by an attribute name followed by an equal sign and the attribute value in quotation marks:
<timeframe> <begin restrict="1"> 1999-07-23 </begin> </timeframe>
In this example, the timeframe element contains another element: the begin element. The begin element has one attribute "restrict", with the value "1". The value for the element BEGIN is "1999-07-23". These two elements then make up a timeframe begin date.
Each element has a unique name, referred to as the tag name. XML is case-sensitive in its processing of tag names. The IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding Specification adheres to the following tag name rules:
The tag name, content model, and attributes of elements were historically defined in a Document Type Definition (DTD) statement. A DTD is a kind of schema. It may exist as an external file or a block of text internal to an XML document. However, the DTD schema was developed before object-oriented programming concepts became prevalent within software development communities and before the use of entities drawn from multiple namespaces became a requirement. Those communities began working on other schema representations to provide more object-like structures and procedures and to support the flexible use of multiple namespaces than could be realized within the constraints of the DTD schema for describing and structuring the contents of XML documents. One such schema language has become today's preferred representation language: XML Schema produced by the Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C).
A schema is a formal specification of element names that indicates which elements are allowed in an XML instance, and in which combinations. New schema languages, such as those defined in the XML-Schemas Working Group, provide the same baseline functionality as a DTD. However, because these schema languages are extensible, developers can augment them with additional information, such as data types, inheritance, and presentation rules. This makes schema languages far more powerful than DTDs. For more information about XML schemas, visit http://www.w3.org/TR/smlschema-0/.
This specification defines a W3C XML Schema (imsss_bindv1p0.xsd) as a non-normative reference. Some XML editors may make use of these schemas to help guide the developer in creating the proper elements at the proper locations in an XML file. Other developers will make use of the schemas to validate their XML instances and/or to define extensions to the IMS Meta-Data Binding. Details of the construction of schemas are outside the scope of this document.
An IMS Sequencing definition instance must use UTF-8 encoding of the character sets as defined in ISO 10646. See the XML Version 1.0 for more details on the specification of well-formed XML.
This section of the specification uses a series of graph segments, accompanied by simple narrative, to describe the XML format of the XML Schema definition (XSD) binding for the Sequencing Definition Model. XSD documents that implement this abstract format are referenced as non-normative parts of this specification.
These data elements and their relationships from the information model are expressed in XML Schema by means structuring entities called elements, attributes, and groups. These structuring entities are further typified as complex types or simple types. The XML Schema structuring entities comprise a binding of an information model when expressed in a special instance of an XML document - an XSD.
The Sequencing Definition Model also defines values or vocabulary terms required by certain data model elements. These controlled lists of terms or values can be expressed in XML Schema as restrictions placed on the values that may be declared for a given structuring element.
It is often necessary for bindings to create structuring entities with names that are not present in an information or data model that is being expressed in XML Schema. These special structuring entities enable the grouping and use of elements as defined in a data model.
The graphs below show individual elements encapsulated within larger structures, like complex types. Structures without child elements are not represented separately. The reader is referred to a binding document instance (.xsd) for the full lexical representation of all structures and values.
Red Branching lines = XML Schema grouping model connector
Description: This is a container for individual sequencing instructions. If used, references to the contained sequencing instructions are embedded in the IMS content package at the appropriate points. The actual sequencing details are then all collected and placed under the <sequencingCollection> element that is itself located at an agreed place within the content package.
Multiplicity: Appears as a child of the <manifest> element within an IMS content package. Occurs zero or one times within any given manifest.
The following minimal IMS CP manifest (stripped of namespace definitions for clarity) shows how an <organization> can reference sequencing information that is stored at the top level of the manifest.
<manifest identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1">
<organizations default = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<organization identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<item identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Item.1"/>
<imsss:sequencing IDRef = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1"/>
</organization>
</organizations>
<resources/>
<imsss:sequencingCollection>
<imsss:sequencing ID = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1">
<!-- Sequencing info goes here -->
</imsss:sequencing>
</imsss:sequencingCollection>
</manifest>
The following minimal IMS CP manifest (stripped of namespace definitions for clarity) shows how locally defined information overrides referenced information when using both in the same <sequencing> element.
<manifest identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1">
<organizations default = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<organization identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<item identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Item.1"/>
<imsss:sequencing IDRef = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1">
<imsss:limitConditions attemptLimit="1"/>
<!-- This element has a limit of 1 attempt, and the begin time limit is
undefined, because the inline element overrides the referenced element.
However, this element has choice and choiceExit both false, because of the
referenced element. -->
</organization>
</organizations>
<resources/>
<imsss:sequencingCollection>
<imsss:sequencing ID = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1">
<imsss:controlMode choice="false" choiceExit="false"/>
<imsss:limitConditions attemptLimit="2" beginTimeLimit="2002-10-16T12:00:00"/>
</imsss:sequencing>
</imsss:sequencingCollection>
</manifest>
Description: Sequencing information is associated with items in a hierarchical structure by associating a single <sequencing> element with the hierarchical item. In the context of IMS CP, this is done by including the <sequencing> element within either an <item> element or an <organization> element.
Sequencing information can be reused across multiple items. This is done by using the "IDRef" attribute of the <sequencing> element, and assigning the ID of the <sequencing> element to use to the "IDRef" attribute. The <sequencing> elements that are referred to using this mechanism may be stored in a <sequencingCollection> element placed at the top level of the manifest.
Note the following restrictions on the use of "IDRef" attributes. <sequencing> elements that are children of the <sequencingCollection> element may not have an "IDRef" attribute. Further, the "IDRef" attribute, when used, must reference a <sequencing> element that is a child of the <sequencingCollection> element in the same manifest.
Note that the in-line definition of sequencing information (using the various elements contained within the <sequencing> element) and the referencing of sequencing information (using the "IDRef" attribute) are not mutually exclusive for any particular element in the hierarchical structure. If a <sequencing> element uses both the "IDRef" attribute and in-line definition, any top-level element defined in-line overrides any similar element defined in the referenced element. Note that this override is for the entire top-level element, and not for individual parts of the top-level element.
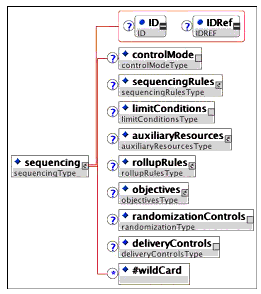
Multiplicity: Occurs once or more within the <sequencingCollection> element, if the <sequencingCollection> element is present. Occurs zero or once for each <item> or <organization> within an IMS content package.
<manifest identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1">
<organizations default = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<organization identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Org.1">
<item identifier = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Item.1"/>
<imsss:sequencing IDRef = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1">
<imsss:limitConditions attemptLimit="1"/>
<!-- This element has a limit of 1 attempt, and the begin time limit is
undefined, because the inline element overrides the referenced element.
However, this element has choice and choiceExit both false, because of the
referenced element. -->
</organization>
</organizations>
<resources/>
<imsss:sequencingCollection>
<imsss:sequencing ID = "IMSSS.TestManifest.1.Seq.1">
<imsss:controlMode choice="false" choiceExit="false"/>
<imsss:limitConditions attemptLimit="2" beginTimeLimit="2002-10-16T12:00:00"/>
</imsss:sequencing>
</imsss:sequencingCollection>
</manifest>
Description: This is the container for the sequencing control mode information including descriptions of the types of sequencing behaviors specified for an activity. Simple Sequencing processes may reference the sequencing control modes for any activity in the activity tree and the default values are used if the data is not defined for a given activity.
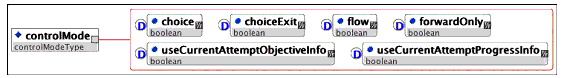
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: The container for a sequencing rule description. Each rule describes the sequencing behavior for an activity. Each activity may have an unlimited number of sequencing rules and within any grouping the rules are evaluated in the order in which they are listed.
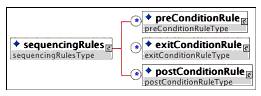
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: The container for the description of actions that control sequencing decisions and delivery of a specific activity. Rules that include such actions are used to determine if the activity will be delivered.
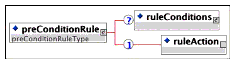
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <sequencingRules> element.
The following example shows a precondition rule that causes the associated item to be disabled if it is either completed or satisfied:
<sequencing>
<sequencingRules>
<preConditionRule>
<ruleConditions conditionCombination = "any">
<ruleCondition condition = "completed"/>
<ruleCondition condition = "satisfied"/>
</ruleConditions>
<ruleAction action = "disabled"/>
</preConditionRule>
</sequencingRules>
</sequencing>
Description: The desired sequencing behavior if the precondition rule evaluates to 'True'.

Multiplicity: Occurs once and only once within a <preConditionRule> element.
Description: The container for the description of actions that terminate an activity. Rules that include such actions are applied when a descendent of an activity exits.
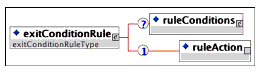
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <sequencingRules> element.
Description: The desired sequencing behavior if the exit rule evaluates to 'True'.

Multiplicity: Occurs once and only once within a <exitConditionRule> element.
Description: The container for the description of actions that control sequencing flow by issuing sequencing requests. Rules that include such actions are applied when an activity exits.
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <sequencingRules> element.
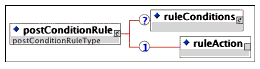
Description: The desired sequencing behavior if the postcondition rule evaluates to 'True'.

Multiplicity: Occurs once and only once within a <postConditionRule> element.
Description: The container for the set of conditions that are to be applied either the pre/post/exit condition rules.
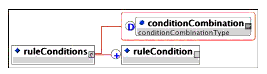
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or one times within the <preConditionRule>, <exitConditionRule>, and <postConditionRule> elements.
Description: Identification of a condition to be applied as part of the sequencing pre/post/exit rule.

Multiplicity: Occurs once or more times within the <ruleConditions> element.
Description: Defines the constraints on the access to an activity based on the time of day, time spent on the activity and number of attempts.

Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: The container for the set of references to the set of auxiliary resources. When an activity is delivered to the learner the auxiliary resources are also made available. The order in which the auxiliary resources are described is not significant.
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: The container for the information describing a single auxiliary resource.

Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <auxiliaryResources> element.
Description: The container for the set of rollup rules that are to be applied to an activity. Each activity may have an unlimited number of rollup rules and the order in which they are defined is not significant.
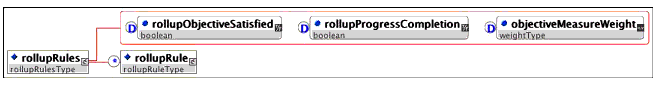
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: The container for each rollup rule that is to be applied to an activity. The general format for a rule can be expressed informally as 'If child-activity set, condition set Then action'. Multiple conditions are permitted.
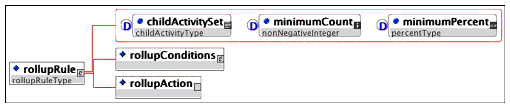
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <rollupRules> element.
The following rollup rule, if attached to an item, states that the item is satisfied if at least three of its children are either satisfied or completed.
<sequencing>
<rollupRules>
<rollupRule childActivitySet = "atLeastCount" minimumCount = "3">
<rollupConditions conditionCombination = "any">
<rollupCondition condition = "satisfied"/>
<rollupCondition condition = "completed"/>
</rollupConditions>
<rollupAction action = "satisfied"/>
</rollupRule>
</rollupRules>
</sequencing>
Description: The container for the set of conditions that are applied within a single rollup rule.
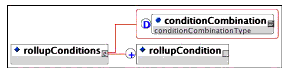
Multiplicity: Occurs once in the <rollupRule> element.
Description: Identification of a condition to be applied in the rollup rule.
Multiplicity: Occurs once or more in the <rollupConditions> element.
Description: The action that is to be undertaken if the rollup rule is declared as 'True'.
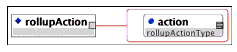
Multiplicity: Occurs once in the <rollupRule> element.
Description: The container for the set of objectives that are to be associated with an activity. Each activity must have at least one primary objective and may have an unlimited number of objectives.
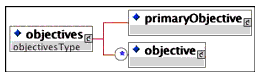
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: Identifies the objective that contributes to the rollup associated with the activity.
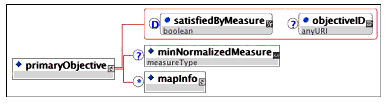
Multiplicity: Occurs once in the <objectives> element.
Description: Identifies objectives that do not contribute to rollup associated with the activity.
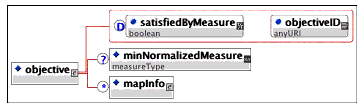
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <objectives> element.
Description: Defines the minimum satisfaction measure for the objective normalized between -1 and 1. If the objective value of 'Objective Normalized Measure' exceeds this value, the objective value of 'Objective Data Status' is set to 'true' and the objective value of 'Objective Satisfied Status' is set to 'true'. It has a real number in the range -1.0000 to 1.000 with a precision of at least four decimal places and has a default value of 1.0000.
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once on the <primaryObjective> and <objective> elements.
Description: The container for the objective map description. This defines the mapping of an activity's local objective information to and from a shared global objective. Each activity may have an unlimited number of objective maps.
Note that the information model defines constraints on how objectives may be mapped to and from global objectives, to assure that there is never an indeterminate state on any objective. While the XSD document does not enforce these constraints, they are still normative on all binding instances.
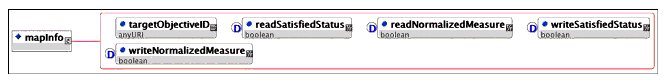
Multiplicity: Occurs zero, once, or an unlimited number of times on the <primaryObjective> and <objective> elements.
Description: The container for the descriptions of how children of an activity should be ordered during the sequence process. Simple Sequencing processes may reference the randomization control data for any activity in the activity tree and when this is absent the default values should be used.
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: This contains the description of the actions and controls used when an activity is delivered. Simple Sequencing processes may reference the delivery control data for any activity in the activity tree. The delivery controls are optional and if these are absent then the default values must be used.

Multiplicity: Occurs zero or once in the <sequencing> element.
Description: This is the Simple Sequencing Binding extension facility.
Multiplicity: Occurs zero or more times in the <sequencing> element.
This section contains several tables. Table 4.1 maps a Sequencing Definition element by its number and name as listed in the Simple Sequencing Information Model specification to the XML Schema entity used to represent it in the XML Schema binding. The Schema entity's name, kind of structure, and type are provided.
The Sequencing Definition and Tracking Definition Models identify data elements in a dot-delimited enumeration and by a name. The dot-delimited enumeration typifies the relationship of elements to each other, where elements with a numeral following a dot are subordinate to elements who share the same numeric value to the left of a dot. The enumeration within a table is separated from the enumeration of the table by a colon character; thus, element 2.1 in table SM.2 is identified as "SM.2:2.1". The enumeration typically does not imply a strict sequence or order of occurrence. It merely implies a group relationship.
In some cases, two Information Model elements map to the same XML Schema entity. Unless otherwise noted, the following rules apply:
Table 4.1 also includes references to additional XML Schema structures used to properly express the relationships or controlled lists of Sequencing Definition element values. These additional XML Schema structures are inserted into Table 4.1 in proximity to the Sequencing Definition elements they describe.
XSD elements of type complexType and simpleType may be nested. Table 4.1 does not show this nesting. Separate tables in this section provide the further details for nested elements defined as complexType or simpleType. In those tables, the element number from the Sequencing Definition or Tracking Definition model and the XML Schema element name are used to associate a nested Schema structuring entity with the appropriate element from the Sequencing Definition model.
The XML Binding has been released as a set of XSDs. The binding is implemented as a series of files which are linked using the XML XSD 'include' statement; the hierarchical relationship is shown in Figure 5.1. The XSD files created to realize the binding are:
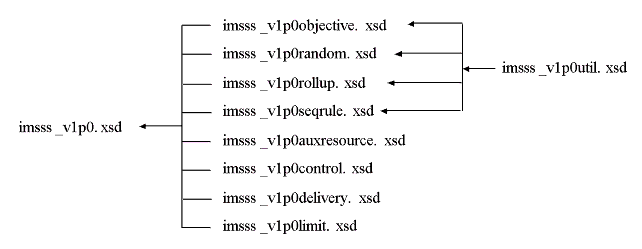
Conformant with IMS file naming conventions, an IMS Simple Sequencing XML Schema binding instance shall be named according to this syntactical model: imsss_vmpn[pr[ps]].xsd, where
Non-normative examples of XML Schema file names for IMS SS:
The namespace URI for IMS Simple Sequencing shall be: http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss/
The .xsd file found at http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss/ shall be the current XML Schema binding instance of the IMS Simple Sequencing Information Model normative elements and values. This file will change.
Versioned instances of each binding for IMS Simple Sequencing, including all major or minor release instances of that version's binding, can be found at http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss/vmpn/, where "vmpn" is a folder named for a versioned instance of the specification. These instances will not change.
For example, the non-normative examples of XML Schema files named for various binding instances of IMS Simple Sequencing v1.0 would be held at this location: http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss/v1p0/ .
The namespace Name used as the prefix of an XML Namespace Qualified Name instance of an IMS Simple Sequencing binding instance used in other XML documents shall be imsss.
For example, when declaring the IMS SS namespace URI in an IMS manifest, this attribute representation would be used:
xmlns:imsss="http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss"
An element of the IMS Simple Sequencing declared in an XML document where the imsss namespace is declared would appear like this:
<imsss:sequencing></imsss:sequencing>
A binding version of the IMS Simple Sequencing Specification shall always reflect the current version number of the IMS Simple Sequencing specification, whether or not binding structures change across specification instances. That is, the file name of the current binding instance shall share the same major and minor version number of the IMS Simple Sequencing specification.
A change to binding structures without a related change to a specification version shall result in an increment of the major or minor revision level component of a binding's file name.
Changes to binding structures without a related change in a specification shall result in an increment of the major revision level.
Changes to structure names or values without changes in structures themselves or the meaning associated with a value shall result in an increment of the minor revision level.
All versioning and revisioning shall be reflected in a binding's file name and complete version information. This new binding shall become the current binding found at http://www.imsglobal.org/xsd/imsss/. The obsolete binding shall be moved to its place within the imsss file path structure based on the value of its version level component, excluding the revision level component.
An IMS Simple Sequencing binding's structure names and values shall be represented as depicted in the Tables within Section 3 of this document. This will ensure machine-level interoperability of sequencing information.
US English annotations and comment strings within an IMS binding shall occur in all binding instances of an IMS Simple Sequencing binding. Localized annotations and comments may be added to the US English annotations and comment strings within an IMS binding as deemed necessary by IMS stakeholders. Such localization activity in a binding shall promote a binding instance to the next increment in minor revision level.
This binding document may be rendered into different lingual representations except for the US English representations of:
Localization of this document shall not cause any change in specification version numbering or binding revision instance numbering.
The IMS Simple Sequencing Binding provides one and only one mechanism for extending binding instances: the "wildcard" element contained in the top level of the "sequencing" element. All other extensions to binding instances are prohibited. This means:
The IMS Simple Sequencing XML Schema Definition file enforces these restrictions by defining block="#all" on all elements in the IMS Simple Sequencing namespace.
Further, extensions to the IMS Simple Sequencing namespace are prohibited. This means:
The IMS Simple Sequencing XML Schema Definition file enforces this restriction by defining namespace="##other" on the wildcard element defined within the sequencing element in the IMS Simple Sequencing namespace.
As a potential aid to implementers, the types defined in the IMS Simple Sequencing XML Schema Definition file may be imported into other namespaces and reused within those other namespaces. However, any such reuse shall be consistent with the restrictions defined in the IMS Simple Sequencing Specification document.
| Title |
IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding |
| Editors |
Mark Norton (IMS), Brendon Towle (Thomson NETg), Colin Smythe (IMS) |
| Team Co-Leads |
Ron Ball (ADL), Brandt Dargue (Boeing) |
| Version |
1.0 |
| Version Date |
03 March 2003 |
| Status |
Final Specification |
| Summary |
This document describes the XML binding definition model for the IMS Simple Sequencing Specification. |
| Purpose |
Defines the IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding. |
| Document Location |
http://www.imsglobal.org/simplesequencing/ssv1p0/imsss_bindv1p0.html |
The following individuals contributed to the development of this document:
A
Absolute Duration 1
Activity 1, 2, 3
Attempt 1, 2, 3, 4
Auxiliary Resource 1
objectiveMeasureWeight 1, 2, 3
satisfiedByMeasure 1, 2, 3
Elements
limitConditions 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
minNormalizedMeasure 1, 2, 3, 4
randomizationControls 1, 2, 3, 4
ruleCondition 1
sequencing 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19
sequencingCollection 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
C
CDATA 1
conditionCombination 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Content Package 1, 2
E
Experienced Duration 1
Extensibility 1
I
IMS Specifications
Content Packaging 1
L
Limit Conditions 1
M
Model 1, 2, 3, 4
Sequencing Definition 1, 2
O
Objective 1, 2, 3, 4
Objective Map 1
P
PCDATA 1
Progress Information 1
R
Randomization Controls 1
Resource 1, 2
Rollup Controls 1
Rollup Rule 1
S
Selection Controls 1
Sequencing 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
Sequencing Control 1
Sequencing Definition Model 1, 2
Sequencing Rule 1
X
XML 1
XSD 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
IMS Global Learning Consortium, Inc. ("IMS") is publishing the information contained in this IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding ("Specification") for purposes of scientific, experimental, and scholarly collaboration only.
IMS makes no warranty or representation regarding the accuracy or completeness of the Specification.
This material is provided on an "As Is" and "As Available" basis.
The Specification is at all times subject to change and revision without notice.
It is your sole responsibility to evaluate the usefulness, accuracy, and completeness of the Specification as it relates to you.
IMS would appreciate receiving your comments and suggestions.
Please contact IMS through our website at http://www.imsglobal.org
Please refer to Document Name: IMS Simple Sequencing XML Binding Revision: 03 March 2003