A data source configuration is a collection of information that identifies the database you want to access using the ODBC driver. You must configure a data source before connecting to a database through ODBC.
To configure a new data source on UNIX and VMS
The ODBC Administrator Main Menu form is displayed. This form lists all currently configured data sources.
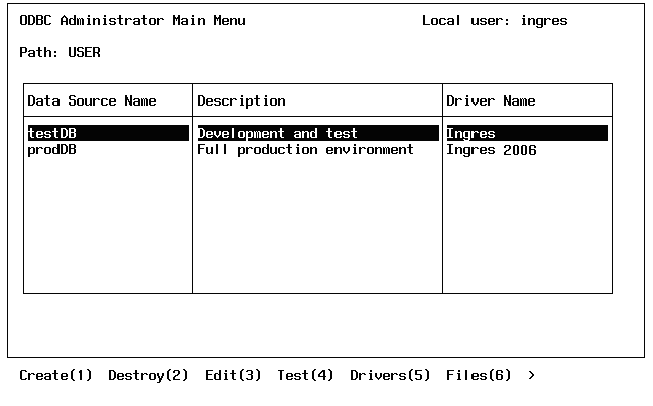
The following form is displayed:
A pop-up menu is displayed with a list of available installed drivers:

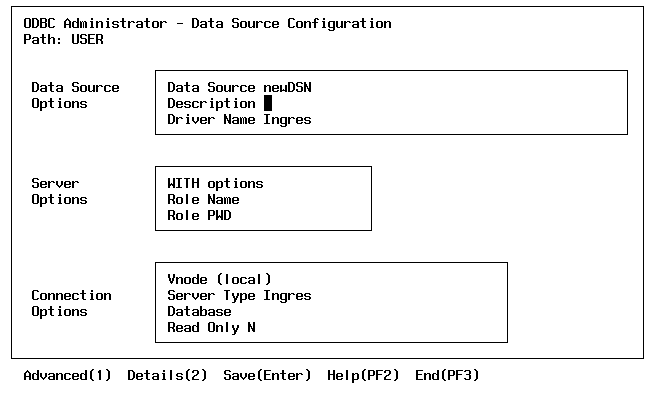
The Data Source Configuration Page is displayed:
The Advanced Configuration Options form is displayed:

For information on this form, see Advanced Data Source Configuration Options.
The Data Source Configuration form is displayed.
The new configuration is saved, and is included in the list of data sources on the Ingres ODBC Administrator Main Menu form.
The Data Source Configuration form of the Ingres ODBC Administrator has the following options:
Defines the data source name (DSN) by which an ODBC application connects to a database server. Examples include "Accounting" or "INGRES-Serv1."
Is an optional long description for a data source name. For example, "My Accounting Database" or "INGRES on Server number 1."
Specifies the predefined name of the installed driver.
Identifies a role ID and associated password that can be entered if a role identifier has been defined that associates privileges with the role.
Allows the passing of Enterprise Access or EDBC specific parameters to certain subsequent statements in a given connection. When specifying options, do not include the "WITH" keyword, and separate multiple options with a comma, (that is, keyword=value,keyword=value).
Example:
dcom_ct_option = `in area CASQLDEFAULT`
Identifies the name of the virtual node that has been defined for the local instance to identify a particular remote database server instance. Choose 'local' if the database resides on the local node.
Specifies the class of database server being accessed. The default is INGRES, which indicates a native Ingres DBMS Server. If you are accessing the database server instance through an Enterprise Access or EDBC server, specify the gateway server. If you place the cursor in this field and select List Choices, you can make a selection from a scrollable list of currently supported server types.
Identifies the name of the database that the application accesses by default. If you place the cursor in this field and select List Choices, you can make a selection from a scrollable list of available databases.
Enter "Y" if you want the Ingres ODBC driver to reject all attempts to perform database updates for the target database.
The Advanced Data Source Configuration Options form of the Ingres ODBC Administrator has the following options:
Causes either cursors or select loops to be used.
A SELECT query generated through SQLExec, ExecDirect, or the Execute method creates result sets. If multiple rows are to be fetched, the result set is traversed using a select loop or cursor loop.
Select loops generally have the best performance, especially for fetching a large number of rows. However, only one select loop can be active at a time. Select loops cannot be nested.
Cursors can be slower than select loops, but cursors place no limits on the number of active result sets. Cursor loops can be nested.
Causes the ODBC driver to convert the ownername.tablename.columnname references to tablename.columnname references. Some applications fully qualify their column-name references as ownername.tablename.columnname references. Ingres 6.4 based servers and gateways cannot handle this form of the SQL syntax.
Includes "SYS*"tables in the result set. By default, the ODBC driver filters out tables beginning with "SYS*" when the SQLTables() query is executed, as these are usually system (internal) tables.
Causes applications to receive a NULL value for empty date values. By default, the ODBC driver returns the date value of 9999-12-31 23:59:59 for empty date values.
Causes applications to receive a NULL value when fetching the "magic" date of 1582-01-01. Some MK (Manufacturing Knowledge) applications load their database with this date to indicate a default beginning date. This is meaningless, however, to other applications that use the same date.
Causes the ODBC driver to use two sessions with a separate session for ODBC catalog functions (SQLTables, SQLColumns, SQLPrimaryKeys, and so on). This behavior is used by older releases of the ODBC driver. By default, the ODBC driver uses just one database session for all ODBC functions. This option is only needed for compatibility issues where Select Loops were used and the application was relying on the separation of interleaved main and catalog function result sets. Before using this option, first try selecting the Cursor Loops option to solve any compatibility issues.
Causes the ODBC driver to ignore a numeric overflow, underflow (and so on) condition. By default, this condition is an error. This option is equivalent to the ľnumeric_overflow=ignore command line flag.
Causes ODBC applications to evaluate the II_DECIMAL variable and use a comma if so specified. If this box is not checked, or II_DECIMAL is not defined as a comma character (","), the ODBC defaults to a period character (".").
Causes the driver to return NULL for schema (owner) names for the ODBC catalog functions. The option is not safe if a user has table t1 and the DBA also has a table t1 in the database.
There is no problem if user1 has a table t1 and user2 also has a table t1. Table names returned are limited to those owned by the current user or DBA. This avoids problems between user1 and user2, but not with the DBA.
Although SQLTables work, ambiguities between user and DBA duplicate table names cause failures on calls to SQLColumns, SQLPrimaryKeys, SQLSpecialColumns, etc. when Yes is selected for this option. This option must be used with caution.
Causes ODBC catalog functions to not treat underscore characters as a wildcard
Allows applications to execute database procedures that perform updates. If No is selected, the default behavior is to reject execution of updating database procedures. This applies only to Ingres II databases and all later releases.
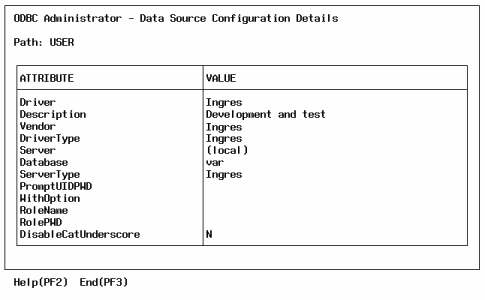
You can view detailed data source configuration information for debugging and support purposes.
To see detailed information on a data source
Select the Details menu option from the Data Source Configuration form.
The Data Source Configuration Details form, which is read-only, is displayed.
The Ingres ODBC Administrator does not allow the installation or modification of driver information, except for tracing in an ODBC environment. The driver is typically installed when Ingres is installed, or can be set up after installation by using the iisuodbc or iiodbcinst utilities.
To see information about the installed drivers
Select the Drivers menu option from the Main Menu form.
The Installed Drivers Form is displayed:
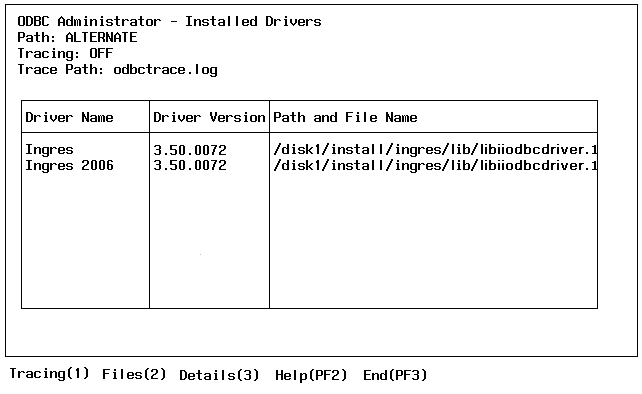
This form allows you to perform the following configuration tasks for each installed driver:
The default mode for tracing is OFF.
To enable ODBC tracing
The Select ODBC Tracing form is displayed:

The Driver Manager field displays the type of driver manager that was specified when the iiodbcinst or iisuodbc utility was executed.
You can use the default path configured for ODBC drivers, or set an alternate path.
To select a path for the driver definitions and system-level data source definitions
The Select Driver Files form is displayed:

To select the default path, place the cursor on SYSTEM and choose Select.
To select an alternate path, place the cursor on the ALTERNATE option and choose Select.
The Define Alternate Driver Path form is displayed:

The driver path is set.
Important! This alternate path remains in effect only for the duration of the current ODBC Administrator session, or until another path and file name is defined for the data sources. You can change the default path with the iisuodbc or iiodbcinst utilities.
You can use the read-only form, Driver Configuration Details, to help in debugging and support-related tasks.
To view configuration details for a particular driver
Select the driver on the Installed Drivers form and select Details.
The Driver Configuration Details form is displayed:
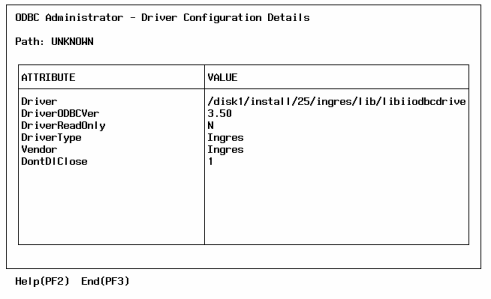
You can select the default path configured for the user-level data source definitions, or specify an alternate path.
To select a data source configuration file path
The Data Source Files form is displayed:

The default path configured for the user-level data source definitions is selected.
Note: Non-Windows environments can use any valid path for the driver configuration file, odbcinst.ini. The ODBC environment variable ODBCSYSINI defines the configuration file path. When running ODBC applications, we recommend that you define ODBCSYSINI, especially if the driver manager is CAI/PT or the Ingres ODBC CLI. Without this definition, unixODBC environments assume the driver configuration path is /usr/local/etc (SYS$SHARE on VMS). Use of the ALTERNATE path without defining ODBCSYSINI works only if the driver manager automatically uses this path.
The USER represents a private definition for the individual, logged-in user, while SYSTEM represents a global definition applicable to all users on the platform.
The Alternate Data Source Path form is displayed:
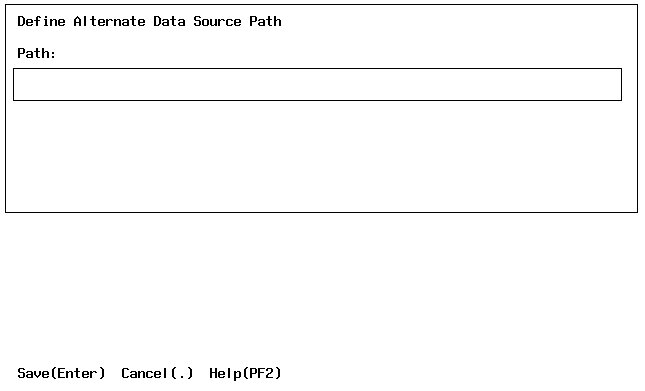
The alternate path is defined.
Important! This alternate path remains in effect only for the duration of the current ODBC Administrator session, or until another path and file name is defined for the data sources.
After a data source has been defined and any changes have been applied, you should test the current settings for the data source to insure that a proper connection can be made through ODBC.
To test the connection for a particular data source
Select the data source name on the Main Menu form and select Test.
The ODBC Administrator attempts a connection to the configured vnode for that data source and returns a message indicating whether the connection was successful.
You can configure as many data sources as you require. Once defined, a data source is available for use by any application that uses ODBC.
To modify an existing data source configuration
The Data Source Configuration form is displayed.
To remove an existing data source configuration
A prompt asks you to verify the removal of the data source configuration.
The data source definition is removed.