Choosing the Go operation from the StarView main frame displays the Node Status and Local Database (LDB) Types frame.
The Node Status frame also displays first if you specify the name of a distributed database as a parameter when you type starview at the operating system command line.
To connect to another distributed database, you must choose End to call up the main StarView frame and Select another distributed database.
The following figure shows the Node Status and Local Database Types frame:

The Node Status and Local Database Types frame includes the following operations. Note that both SQL and Tables selections connect to the selected distributed database:
Lists the objects in the selected distributed database.
Lists the attributes of the selected local database.
Tests whether you can connect to a node. You can test the accessibility status of a single node or all nodes.
Tests whether you can connect to a local database. You can test connections to a single database or all databases in the distributed database.
Accesses Interactive SQL (ISQL). You can enter and execute SQL statements at the interactive Terminal Monitor.
Accesses the Tables utility. You can access, create, destroy, and query all the tables in the distributed database using the forms-based Tables utility.
Standard menu operations.
The ListObj operation displays the Distributed Database Contents frame, which lists the component objects of the distributed database and the system catalogs:
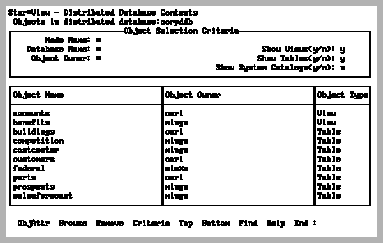
You can display all or any combination of these objects by altering the default settings.
To learn how to restrict the display of this frame to, for example, tables only, see Distributed Database Contents Frame.
The LDBAttr (local database attributes) operation displays the following frame showing the attributes of your selected local database:
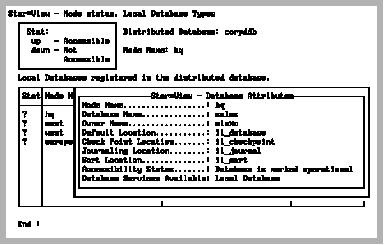
The attributes shown include name, date, checkpoints and journaling.
The Accessibility Status field displays one of the following messages:
The Database Service Available field displays either Local Database or Coordinator Database.
By choosing the SQL operation, you can use Interactive SQL (ISQL) to query your distributed databases. The following screen is displayed:
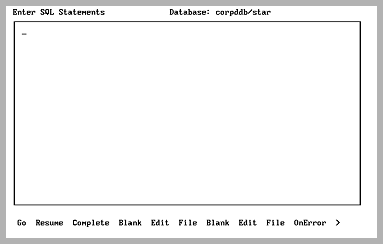
For a full explanation of ISQL, see Forms-based Application Development Tools User Guide.
By choosing the Tables operation, you can use the forms-based Tables utility to query tables in your distributed databases.
The following screen is displayed:
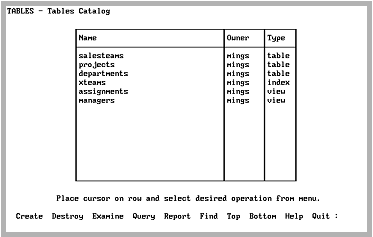
If you create any tables using the Tables utility, the underlying local tables are created in the Coordinator database.
For a full explanation of the Tables utility, see Forms-based Application Development Tools User Guide.
By choosing the TestNode operation, you can test the node connections within your distributed database. When you test a node, the Status field on the frame changes from a question mark (?) to either up (accessible) or down (not accessible).
You can test the connections to a single node or to all nodes. The following list of options is displayed:
Test a single node
Test all the nodes in the distributed database
Standard menu operations
By choosing the TestLDB operation, you can test the availability of the local databases in your distributed database. When you test a database, the Status field changes from a question mark (?) to either up (accessible) or down (not accessible).
You can test the connections to a single database or to all databases. After testing one database, you can then test another database by choosing NewLDB.
When you choose AllLDBs, StarView goes through each local database and changes the display of the status to either up or down.
The following list of options is displayed:
Test a single local database
Test all the local databases in the distributed database
Test a new local database
Standard menu operations
TestNode allows you to test whether you can connect to a node. TestLDB allows you to test whether you can connect to a local database.
If you have many local databases and only a few nodes, it is faster to test connections against the nodes rather than test every local database on the node.