|
This section contains the following topics: |
To connect to Ingres from PHP, you need to download or build the PECL extension and install it. (PECL stands for PHP Extension Community Library, which is a repository for PHP extensions.)
Download the PECL extension for Windows.
Select the appropriate DLL for the PHP version you are using from the following page:
http://pecl4win.php.net/ext.php/php_ingres.dll
The PHP project provides anonymous access to the CVS server to enable users to download the code as needed. Windows users can download a compatible CVS client from http://www.cvsnt.org.
To download the Windows CVS client
cvs -d :pserver:[email protected]/repository login
When prompted for a password, enter phpfi.
cvs -d :pserver:[email protected]/repository co pecl/ingres
This creates two directories, pecl and a subdirectory of ingres. The library code is located in the ingres folder.
Note: If you want to download the source code for PHP, go to http://php.net/anoncvs.php.
After downloading the appropriate extension for your environment, you must install it.
To install the extension on Windows
extension=php_ingres.dll
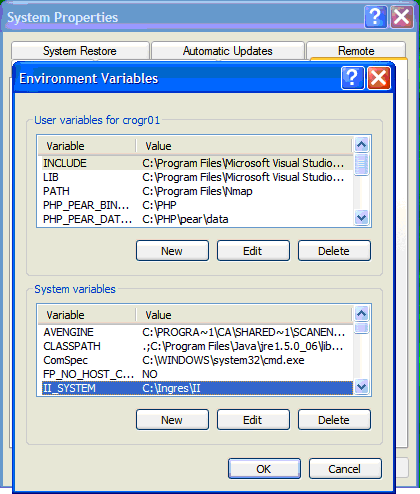
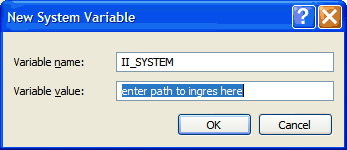
Click OK when you are finished.
IUSR_YourPCName
SYSTEM or whatever user the service runs as
<!-- file : php_setup_info.php -->
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
This will confirm that the extension has been set up and is active. For example:
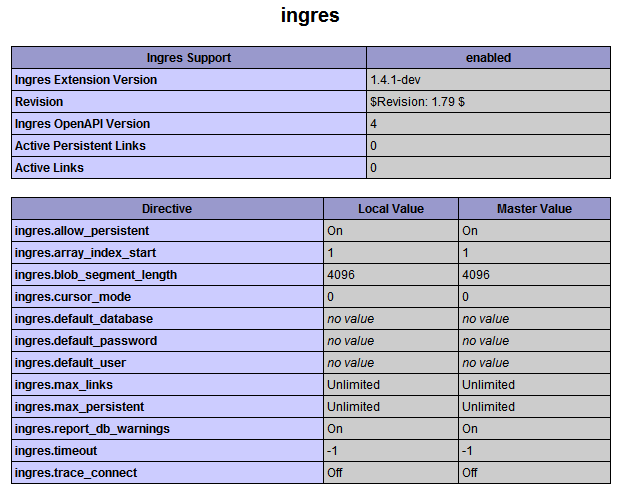
You connect to Ingres using the ingres_connect() function and disconnect using ingres_close(). ingres_connect() returns an Ingres II link resource on success, or FALSE on failure.
This function has the following syntax:
resource = ingres_connect([database[,username[,password]]])
Specifies a database with the following syntax:
[vnode_id::]dbname[/svr_class]
Specifies the virtual node name used to connect to a remote machine
Specifies the database name
Specifies the Ingres server class, which defaults to INGRES if not specified. It is used when connecting to different server classes.
Specifies an Ingres user name to use for the connection
Specifies the password for the user name
Note: If any parameters are missing, ingres_connect() uses the values in php.ini for ingres.default_database, ingres.default_user, and ingres.default_password.
Example: ingres_connect()
<?php
$link = ingres_connect("mydb", "username", "password");
or die("Could not connect");
echo "Connected successfully";
ingres_close($link);
?>
Note: You can use ingres_pconnect() function to create a persistent connection.
The following are examples of PHP code you can use for various Ingres operations.
Example: Error checking
<?php
$link = ingres_connect("mydb", "username", "password");
if (ingres_errno($link) != 0) {
echo ingres_errno($link) . " : " . ingres_error($link) . "<BR/>\n";
}
?>
Example: Simple query
<?php
$link = ingres_connect("mydb", "username", "password");
// Gives a list of the tables
$sql = "select * from iirelation order by relid asc";
$rc = ingres_query($sql,$link);
// Do some error checking...
while ( $iirelation = ingres_fetch_object($link) ) {
echo $iirelation->relid "<BR/>\n";
}
?>
Example: Query with parameters
<?php
$link = ingres_connect("iidbdb", "ingres", "ingres");
// Gives a list of the tables based on a parameter
$sql = "select * from iirelation where relowner = ? order by relid asc";
$params["owner1"] = ("usrname");
$rc = ingres_query($sql,$link,$params);
// Do some error checking...
while ( $iirelation=ingres_fetch_object($link) ) {
echo $iirelation->relid "<BR/>\n";
}
?>
Example: Loading a BLOB
<?php
// Fetch the image to be inserted
$handle = fopen ("usrname.png","r");
$login_image = stream_get_contents($handle);
fclose($handle);
// Set up the query
$sql = "insert into login_images values (?,?)";
// Type the parameters being passed
$types = "vB"; // varchar, BLOB
// Set up the parameter values
$params["login"] = "usrname";
$params["image"] = $login_image;
// Execute
$rc = ingres_query($sql,$link,$params,$types);
?>