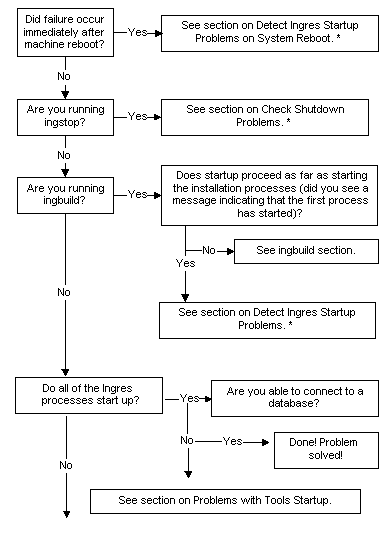
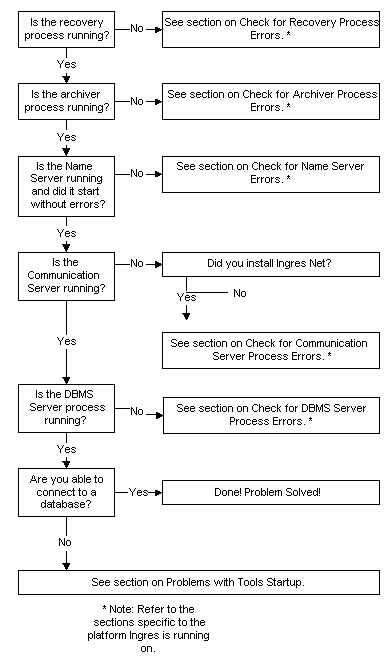
Use the following flow chart to isolate a problem with startup, shutdown or configuration of your Ingres installation:
To check if the Ingres installation is working fine, follow these steps:
echo %II_SYSTEM%
All users must have Ingres executables in their path variables. Check that everyone has the full search path to %II_SYSTEM%\ingres\bin.
The installation owner must also include %II_SYSTEM%\ingres\utility.
Ingres environment variables are only used and "seen" by Ingres and can be displayed with the following command entered at the operating system prompt:
ingprenv
If you are in doubt about the function or legal value of a particular environment variable, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals" and the appendix "Environment Variables and Logicals."
Ingres environment variables denoting installation locations (II_DATABASE, II_CHECKPOINT, II_DUMP, II_JOURNAL, II_LOG_FILE, II_SYSTEM) cannot be reset. To change these, you must unload the databases, rerun the installation program, and reload the databases, as described in Installation Location.
Only a small category of Ingres environment variables must be defined in the local user environment: those that permit you to access Ingres, and those that define values that are different for your local environment. They include TERM_INGRES and ING_EDIT.
If you trace the problem to an Ingres environment variable setting, correct the value. For procedures and scenarios for setting these environment variables, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals." If the installation does not start up, continue with this procedure.
ingstart
If startup problems persist, continue diagnostics in the ingstart section below.
To troubleshoot startup problems on Windows, follow these steps:
Name Server process
Communication Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Net)
Recovery Server process
Archiver process
DBMS Server process
Data Access Server process
Distributed Database Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Star)
ICE Server process
Remote command process
Bridge Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Bridge)
%II_SYSTEM%\ingres\files\ingstart.log
Error log files and individual component log files are listed in Logging and Locking Systems.
To check if the Ingres installation is working fine, follow these steps:
whoami
If the user ID of the installation owner is not shown, log off and log in again as this user.
echo $II_SYSTEM
/ usr/r6 (this varies by system)
All users must have Ingres executables in their path variables. Check that everyone has the full search path to $II_SYSTEM/ingres/bin.
The installation owner must also include $II_SYSTEM/ingres/utility.
Ingres environment variables are only used and "seen" by Ingres and can be displayed with the following command entered at the operating system prompt:
ingprenv
If you are in doubt about the function or legal value of a particular environment variable, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals" and the appendix "Environment Variables and Logicals."
Ingres environment variables denoting installation locations (II_DATABASE, II_CHECKPOINT, II_DUMP, II_JOURNAL, II_LOG_FILE, II_SYSTEM) cannot be reset. To change these, you must rerun the installation program, ingbuild, and on UNIX possibly unload and reload your database with unloaddb. More information is provided in Installation Locations.
BSD:
printenv | grep II
printenv | grep ING
System V:
env | grep II
env | grep ING
Only a small category of Ingres environment variables must be defined in the local user environment: those that permit you to access Ingres, and those that define values that are different for your local environment. They include TERM_INGRES and ING_EDIT.
If you trace the problem to an Ingres environment variable setting, correct the value. For procedures and scenarios for setting these environment variables, see "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals." If the installation does not start up, continue with this procedure.
ingprenv | grep II_INSTALLATION
The two-letter installation code is displayed (for example, the following code R6):
II_INSTALLATION=R6
Take note of your installation code: ______.
ingstart
The executable script ingbuild performs all the steps necessary to set up an installation. It checks system resources, installs shared memory and semaphores, configures DBMS server parameters, configures the logging and locking system, and starts all the required processes.
The ingbuild program is located in $II_SYSTEM/ingres/utility. It makes use of numerous shell commands as well as the following Ingres binary and shell executables:
One of the last things ingbuild does is call the ingstart script to actually start installation processes. When ingstart is called, it displays the message "Starting the Name Server process (iigcn)." If there are startup problems after this message has displayed, see Ingstart on UNIX.
Before you can diagnose a problem with ingbuild, you must identify which subroutine is failing. If you know which routine is failing and it is ingstart or one of the main installation processes (iigcn, iigcc, II_IUSV_nnn, dmfacp or iidbms), see the section below that addresses that executable.
Details on tracing are described in Bourne Shell -x Option.
To diagnose Ingres problems, use the following procedure.
The csreport utility is described in Operating System Utilities and the ps command is described in UNIX Operating System Utilities.
Name Server process
Communications Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Net)
Recovery Server process
Data Access Server process
Archiver process
DBMS Server process
DBMS Server asynchronous write daemons—these processes are created at the time of the first database write operation (only present on sites where Ingres does not use OS threads or asynchronous I/O)
Distributed Database Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Star)
ICE Server process
Bridge Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Bridge)
Note: If the command ingprenv | grep II_CLIENT shows "II_CLIENT = true", you need to run only the Name Server and Communications Server processes.
In a few special cases Ingres can be run without the Communications Server process. This includes releases that use the streams device driver for interprocess communications. If you are not sure if your release uses the streams device driver, see your Readme file.
The problem is with ingstart. The ingstart script fails due to results of the checks it makes for sufficient resources and installation settings. If this is the reason for startup failure, correct the deficiency.
A process failed to start. If a process failed to start, continue on to the details sections on startup problems for that specific process.
It is recommended that you first make the following basic installation checks:
show process
If the ISA is not shown, log off and log in again as the ISA. The ISA is typically ingres if there is only a single installation per machine. For multiple installations, there is a different ISA for each installation.
show logical II_SYSTEM
Ingres symbols are defined in the following files:
If you are in doubt about the function or legal value of a particular logical, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals" and the appendix "Environment Variables and Logicals".
Ingres logicals denoting installation locations (II_DATABASE, II_CHECKPOINT, II_DUMP, II_JOURNAL, II_LOG_FILE, II_SYSTEM) can not be reset. To change these, you must edit II_CONFIG:config.dat, update the existing definition, and execute @ii_system:[ingres]ingsysdef.com. For additional details, see Installation Locations.
show logical *II*, *ING*
This shows which ones have been set at process, job, or group level, overriding the system-level definitions.
Only a small category of Ingres logicals are defined in the local user environment: those that permit you to access Ingres, and those that define values that are different for your local environment. They can include TERM_INGRES and ING_EDIT.
If you trace the problem to an Ingres logical setting, correct the value. For procedures and scenarios for setting these logicals, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables and Logicals." If the installation does not start up, continue with this procedure.
show logical II_INSTALLATION
The two-letter installation code is displayed. For example:
II_INSTALLATION=R6
If this is a system-wide Ingres installation, there is no definition for II_INSTALLATION. The installation code is used to distinguish which processes belong to which installation at sites with more than one Ingres installation on the same machine:
ingstart
The executable script vmsinstal performs all the steps necessary to set up an installation. It checks system resources, installs shared images, configures DBMS server parameters, configures the logging and locking system, and starts all the required processes.
During the execution of the vmsinstal script, if a problem occurs, do the following:
@sys$update:vmsinstal * device_name options L
set verify
If you are having ingstart problems, use the following procedure:
show system /out = filename
search filename "II_", "DMF"
The search command searches the user-specified filename for the process names.
Where nn is the optional two-letter installation code, and pppp is the lower two bytes of the process' process ID.
Note: If you are checking the processes on a client node, only the Name Server and Communications Server processes are displayed when issuing the $ SHOW SYSTEM command.
II_SYSTEM:[INGRES.FILES] II_CONFIG:errlog.log
For a complete list of error log files and individual component log files, see Logging and Locking Systems.
To detect Ingres startup problems on system reboot on Windows, follow these steps:
To detect Ingres startup problems on system reboot on UNIX, follow these steps:
Make sure that the following line appears in the boot script:
su userid -c "ii_system/ingres/utility/ingstart ii_system" /dev/console
where:
userid refers to the user that owns the installation
ii_system refers to the value of II_SYSTEM for your installation.
Issue the following command at the operating system prompt:
chmod g+w /dev/kmem
The user that owns the installation must be able to read /dev/kmem or the kernel resource checks in ingstart fails.
To detect Ingres startup problems on system reboot on VMS, follow these steps:
SYLOGIN.COM is run when any user logs in. The script to set up Ingres user symbols are defined here.
@II_SYSTEM:[INGRES]ingusrdef.com
If the DBA symbols are also to be known by all users, the ingdbadef.com script can be used instead.
If the system administrator symbols are also to be known by all users, the ingsysdef.com script can be used instead.
Only one script needs to be defined.
An alternative method is to include these in a user's particular login.com.
SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM is run when the system is booted. To have Ingres restarted automatically on reboot, add the following line:
@SYS$STARTUP:INGRES_STARTUP.COM
Edit the file SYS$STARTUP:INGRES_STARTUP.COM to ensure it is correct for your environment. A line is added to start each installation, but the line is commented out to prevent accidental errors.
Edit this file to meet your needs.
If the installation still does not start, contact technical support, as described in What You Need Before Contacting Technical Support.
If Ingres has problems during shutdown on Windows, follow these steps:
echo %II_SYSTEM%
echo %PATH%
If you are having problems shutting down a client installation because Ingres believes a Communications Server is running locally when there is none, remove this file:
%II_SYSTEM%\ingres\files\name\clientname\IICOMSVR_clientname
logstat | findstr RECOVER
If Ingres is recovering aborted transactions, wait for this process to finish. Continue reissuing the logstat command and examining the STATUS field. When it reads "ONLINE, ECP DONE," proceed with normal shutdown.
ingstop
You can also click the Stop toolbar button in Ingres Visual Manager to shut down the installation.
Note: All users must be logged out of Ingres (that is, no sessions running in the server) for ingstop to succeed.
ipclean
Your installation is now shut down.
Note: For information about shutting down an Ingres installation that includes an ICE Server, see the chapter "Managing and Monitoring Web Deployment Option" in the Web Deployment Option User Guide.
If Ingres has problems during shutdown on UNIX, follow these steps:
echo $II_SYSTEM
/usr/r6 (this varies system by system)
echo $PATH
ingprenv | grep II_INSTALLATION
The two-letter installation code is displayed (for example, the code here is JB):
II_INSTALLATION=JB
Take note of your installation code: ______.
ingprenv | grep II_CLIENT
If this displays "II_CLIENT=true", this is a client installation, and only two processes (iigcn, iigcc) are running on this node.
$II_SYSTEM/ingres/files/name/clientname/IICOMSVR_clientname
For troubleshooting details see the Connectivity Guide.
logstat | grep RECOVER
If Ingres is recovering aborted transactions, wait for this process to finish. Continue reissuing the logstat command and examining the STATUS field. When it says: "ONLINE, ECP DONE," proceed with normal shutdown.
ingstop
Note: All users must be logged out of Ingres (that is, no sessions running in the server) for the ingstop script to succeed.
BSD:
ps -aux | grep ingres
System V:
ps -ef | grep ingres
kill- QUIT process_id
where:
process_id refers to the process ID of the process to stop.
kill -9 process_id
Important! If your site has more than one Ingres installation, examine the installation code associated with the iidbms process to make sure you are stopping only the processes associated with the installation you need to shut down.
csreport
The following message indicates that shared segments have been properly removed:
!Can't map system segment
ipcclean
ipcs
Important! If your site has more than one Ingres installation, you must take care to only remove shared memory or semaphores for the installation to be shut down. If your machine contains more than one installation, enter the following command from the environment of the installation you need to target:
csreport
The csreport utility displays the shared memory and semaphore segment identifiers for this installation.
To remove the targeted segment(s), use the UNIX command:
ipcrm -mmid
or
ipcrm -ssid
where mid is the shared memory segment identifier and sid is the semaphore identifier.
$II_SYSTEM/ingres/files/memory/lockseg.mem
$II_SYSTEM/ingres/files/memory/sysseg.mem
Your installation is now shut down. Instructions on how to check and restart Ingres are described in Check Ingres Installation on UNIX.
Note: For information about shutting down an Ingres installation that includes an ICE Server, see the chapter "Managing and Monitoring Web Deployment Option" in the Web Deployment Option User Guide.
If Ingres has problems during shutdown on VMS, follow these steps:
show process
Make sure you have the WORLD and CMKRNL privileges required for stopping Ingres processes by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
show process/privilege
A privileged account must not only have the aforementioned VMS privileges but also must have the SERVER_CONTROL privilege authorized in II_CONFIG:CONFIG.DAT.
show logical II_SYSTEM
To obtain a list of running processes, use the DCL command:
show system
If you use the form show system/full, you can also see the owner of the process. This is helpful if you have group level installations.
For a group level installation the two-lettered code is displayed after the process name. In this example, the code is BE:
Pid Process Name State Pri I/O CPU Page flts Ph.Mem
236012AD II_DBMS_BE_1E3F HIB 6 86463 0 00:13:53.24 14401 8192
Important! If your site has more than one Ingres installation, examine the installation code associated with the II_DBMS_nnn process to make sure you are only shutting down processes associated with the installation you need to shut down.
IINAMU> show ingres
INGRES * II_DBMS_BE_1E3F
found.
IINAMU> show comsvr
COMSVR * II_GCC_BE_2B77
Note: Ingres can be shut down in several ways. Following are some tips on how each shutdown procedure works to enable you to make a choice as to how to shut down the installation.
When you issue the stop command from iinamu, the Name Server process is stopped. Once this command is issued, no new servers are allowed to register with the Name Server. Therefore, it makes sense to take the Name Server down first for a clean shutdown. Current, active sessions are not affected by this command.
Use iimonitor to stop the DBMS Server. The two commands you can use are:
set server shut
This causes the server to refuse further connections and shuts the server down gracefully, completing all current transactions first, including the iimonitor session.
stop server
This stops the server immediately without waiting for current connected sessions to complete. Use this command instead of the VMS command stop/id.
Take down the recovery and the archiver processes, either quickly or slowly, depending on the method you used to take down the DBMS Server in step b. Use either of the following commands at the operating system prompt:
rcpconfig/shutdown
This causes the processes to refuse all further connections and transaction processing, but allows current transactions to finish. This allows the archiver and recovery processes to shut down cleanly.
rcpconfig/imm_shutdown
This stops all pending transactions and immediately shuts down the recovery and archiver processes. This leaves open transactions in the log file, which requires rollback (and slow startup) when the system is restarted.
Alternatively, you can write a DCL script that puts the above steps in a command procedure to shut down each of the Ingres processes.
show system
Check to be sure that none of the processes listed in the Ingstart on VMS section is shown.
stop process_name
or
stop/id = pid#
Note: For serious system problems that require immediate attention, the VMS stop command can be used to stop an Ingres process. This is not recommended because it does not permit the recovery process to back out open transactions or the archiver process to flush the log file to disk.
If this is a cluster installation, remember that these Ingres processes run on each node.
Your Ingres installation is now shut down. Information about checking and restarting Ingres is described in Check Ingres Installation on VMS.
Note: For information about shutting down an Ingres installation that includes an ICE Server, see the chapter "Managing and Monitoring Web Deployment Option" in the Web Deployment Option User Guide.