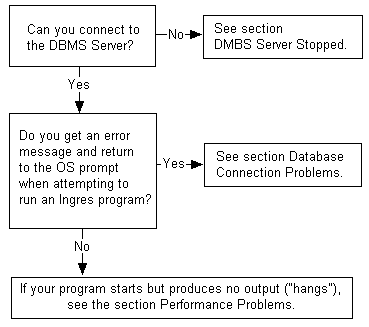
The following flow chart helps you isolate a problem when starting an Ingres tool:
Once started with ingstart, the DBMS Server process must continue running until the ingstop or iimonitor command is issued to stop it. If the DBMS Server stops running ("dies") for any other reason, report it to technical support along with the associated error log messages and, if possible, the cause of the DBMS Server stopping.
Windows:
SET II_DBMS_LOG=%II_SYSTEM%\ingres\files\dbms.log
UNIX:
C Shell:
setenv II_DBMS_LOG $II_SYSTEM/ingres/files/dbms_%p.trace
Bourne Shell:
II_DBMS_LOG = $II_SYSTEM/ingres/files/dbms_%p.trace export
II_DBMS_LOG
At startup, the %p in the II_DBMS_LOG specification is replaced by the Process Identifier (PID) of the server process. This prevents DBMS servers from clobbering each others logs (or the recovery process log)
VMS:
define /system/exec II_DBMS_LOG -
II_SYSTEM:[INGRES.FILES]DBMS.LOG (for a system level installation)
define/group/exec II_DBMS_LOG - II_SYSTEM:[INGRES.FILES]DBMS.LOG (for a group level installation)
Database connection problems occur in the following scenarios:
If you cannot connect to any database, follow these steps:
If you can connect, at the "IIMONITOR>" prompt type show sessions to examine DBMS server activity.
If you cannot connect to the DBMS Server, see How to Log System Issues.
Check the Ingres environment variable/logical II_DBMS_SERVER:
Windows:
Use ingprenv and your system's echo command to verify that II_DBMS_SERVER is not set, either in the Ingres symbol table or your local environment.
UNIX:
Use ingprenv and your system's env or printenv command to verify that II_DBMS_SERVER is not set, either in the Ingres symbol table or your local environment.
VMS:
Use II_DBMS_SERVER to bypass the Name Server process. Issue the following command at the operating system prompt:
define II_DBMS_SERVER II_DBMS_pid
If you can connect to some databases but not others:
Verify that your database still exists and is not being recovered by the recovery system.
If the database does not exist, a corresponding error message is sent.
Using VDBA: