Scene Graph Features Overview
Introduction
Although Java Platform Standard Edition (SE) provides facilities for rendering graphics in your applications, there is no means to easily add animation or the rich visual effects required by modern graphical applications. JavaFX technology addresses this limitation by offering simple, elegant ways to create and handle visual output in your applications. With JavaFX, you can make calls to Java API and use new capacities that leverage Java.
The graphical runtime for the JavaFX Script is provided by the Scene Graph project that is being implemented as a public project on java.net.
The following figure shows how the JavaFX Script makes use of the Java API including the Scene Graph API.
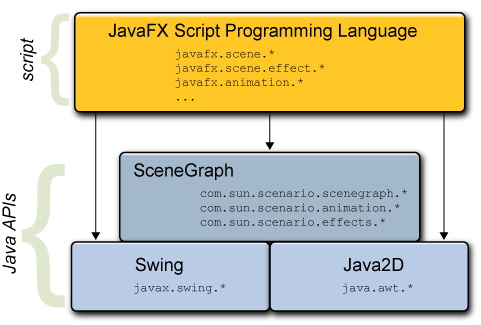
Figure 1: JavaFX Script and Underlying Libraries |
It is the scene graph that allows you to simplify creation of visual output. A scene graph provides a hierarchy of graphical objects in a scene. The scene graph underlying the JavaFX Script enables the user to transform nodes, to apply powerful effects, and to animate graphical objects and thus to create rich graphical applications. JavaFX takes advantage of the scene graph capacities and provides a new way to render a scene. You declaratively specify graphical and GUI objects, and then JavaFX renders those objects as needed. This section briefly describes the scene graph key concepts and major advantages of JavaFX Script that are available with the scenegraph functionality.
Java FX Scene Graph Key Concepts
- Nodes
- Canvas
- States
- Animation
The key concept of a scene graph is a node. You build a graphical scene with nodes. Nodes can take input and be rendered. Nodes represent visual objects such as UI components, 2-D shapes, text, and images.
Nodes can be grouped together. If you need to provide common behavior to several nodes, group them together and then apply the required behavior to the whole group.
A canvas is a container for graphical nodes. The canvas represents the scene.
There are many ways to change the state of nodes in a scene. You can transform the nodes by scaling and rotating them. You can change the node's orientation and visibility. You can also change the node's appearance by applying effects. The scene graph provides a powerful effects library that contains various effects such as dropping a shadow, blurring, and adjusting colors.
Initially designed to work with the animation framework, nodes can be easily animated. First you declaratively specify the placement of graphical objects. Then you define behaviors that change the properties of nodes over time. You can animate graphical objects by applying non-linear interpolation, repeating and reversing.
The next section provides description of the Nodes demo.