The target audience for this guide is the JOnAS server administrator.
JOnAS provides the following two tools for performing some administration tasks on a running JOnAS Server:
jonas admin, a
command line toolJonasAdmin, a
graphical tool based on the Struts framework and the JMX technology
These tools also allow administration of several JOnAS Servers. Each JOnAS
Server is identified by a name, which is the value of the -n
option used in the jonas start command (the default name is
jonas).
Begining with JOnAS 4, we also provide the
J2EE Management EJB component (MEJB), as specified by the
J2EE Management Specification which defines the J2EE Management Model.
jonas admin is described in the JOnAS Commands chapter.
This chapter provides information about installing, configuring, and using the JonasAdmin administration console.
JonasAdmin is the new administration tool for JOnAS and replaces the deprecated Jadmin tool.
JonasAdmin was developed using the Struts framework; it uses standard technologies such as Java Servlets and JavaServer Pages. JonasAdmin is more ergonomic than Jadmin and provides integrated administration facilities for a Tomcat server running embedded in JOnAS.
Designed as a web application, JonasAdmin is packed in a WAR and installed
under the JONAS_ROOT/webapps/autoload/ directory. This WAR can
be installed in JONAS_BASE/webapps/autoload if a JONAS_BASE
variable has been defined in the environment. When installed in the
autoload directory, JonasAdmin is deployed when starting the
JOnAS server, thus the administration console is automatically accessible.
As with any web application, JonasAdmin requires a servlet server to be
installed. Additionally, the JOnAS server running JonasAdmin must have the
web container service present in the list of services defined in the
jonas.properties configuration file.
When accessing JonasAdmin, the administrator must provide identification
and authentication.
The jonas-realm.xml configuration file contains a memory realm
definition named memrlm_1, which is referenced in both
server.xml (for Tomcat) and jetty.xml (for Jetty) configuration files. The
default user name (jonas) and
password (jonas) corresponding to the admin
role can be modified here.
Once started, JonasAdmin can administer the JOnAS server in which it is
running, as well as other JOnAS servers with which it shares the same
registry. Typically, this is used to administer JOnAS servers running without
the WEB container service.
Note that the administered JOnAS servers can be running on the same host or
on different hosts. Also, if Tomcat is used as the WEB container service
implementation, it can be administered using JonasAdmin.
Ensure that the web service is listed in the
jonas.services property in the jonas.properties
configuration file. If you are not using a jonas-tomcat or jonas-jetty
package, depending on the Servlet container being used, the
CATALINA_HOME or the JETTY_HOME environment
variable must have been previously set. Note that when running the Servlet
container on top of Unix, the DISPLAY environment variable must
be set in order to use the JOnAS server monitoring feature of JonasAdmin.
Once JOnAS is launched, JonasAdmin must be loaded if it was not installed
in the autoload directory. The administration console is
accessible at the URL:
http://<hostname>:<portnumber>/jonasAdmin/
using any web browser.
<hostname> is the name of the host where the Servlet container is running and <portnumber> is the http port number (default is 9000).
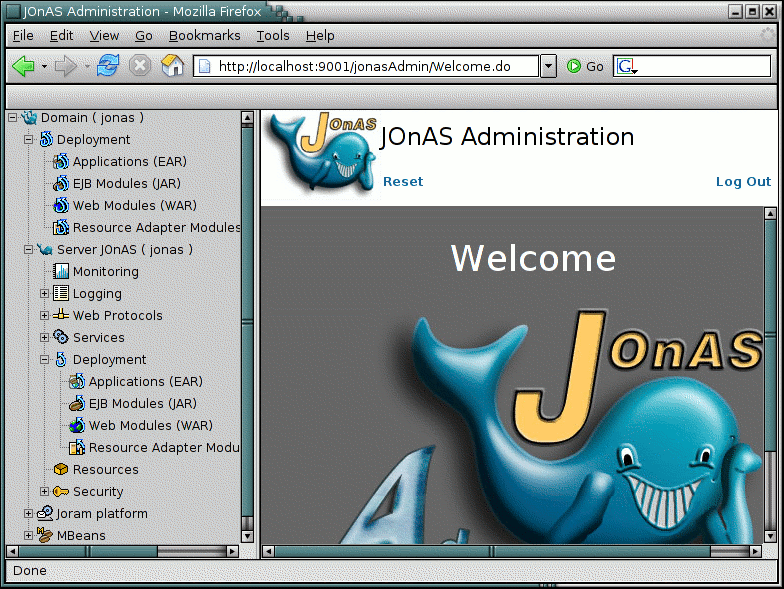
After logging in, the left-hand frame in the Welcome page displays the
management tree associated with the JOnAS server running JonasAdmin.
Starting with JOnAS 4.6, the management tree's root is Domain, which
corresponds to the new domain management facilities.
In the image below, JonasAdmin is running on the master server named jonas
within a domain also named jonas. It is immediately apparent that this is a
master server, as we have a Deployment sub-tree under the Domain
root node.

The management tree in this figure allows access to the following main management facilities:
Displays general information about the administered JOnAS server, including the JMX server and the WEB server, and provides the capability of listing the content of the Registry.
Presents memory usage, a count of the threads created by JOnAS, and other monitoring information concerning managed services and resources.
Allows the administrator to configure the JOnAS Logging system. Additionally, if Tomcat is used as the WEB container service implementation, it allows creation of new access log valves.
This management facility relates to the integration of Tomcat management
in JonasAdmin.
It currently presents connectors defined in the Tomcat configuration and
allows for the creation of new HTTP, HTTPS, or AJP connectors.
Note that the Protocols sub-tree is not presented if Jetty is
used as the WEB container service implementation.
All the active services have a corresponding sub-tree in the
Services tree.
Managing the various container services consists of presenting information about the components deployed in these containers. New components can be deployed using the dynamic deployment facilities presented in the next section.
Creation of a new context for WEB components to be deployed in the Tomcat server
is deprecated since JOnAS 4.6 (the New web application button is
removed).
Similarly, the services that allow management of the different types of
resources (DataSources, Resource Adapters, Jms and Mail resources) also
provide information about the resources being deployed. Additionally,
deployed resources (DataSources or MailFactories) can be reconfigured and
their new configuration made persistent by using a Save
button.
The transaction service management allows reconfiguration (possibly persistent) and presents monitoring information about transactions managed by JOnAS.
A very useful management operation is the capability of loading
stand-alone J2EE components (JAR, WAR, RAR packages) or J2EE applications
(EAR packages) in the administered server using the Deployment
sub-tree.
The administrator's task is facilitated by the display of the list of
deployable modules, the list of deployed modules, and the capability of
transferring modules from one list to another (which corresponds to
deploy/undeploy operations.
The deployable modules are files installed in directories specific to their type. For example, the
deployable JARs are un-deployed JARs installed in
JONAS_BASE/ejbjars/ or in a
JONAS_BASE/ejbjars/autoload/ directory.
The Deployment sub-tree also allows a J2EE package to be uploaded from
the local file system to the corresponding directory of the administered server
(install operation), and the opposite remove operation.
Resources sub-tree provides the capability of loading or
creating new resources managed by the active services. For example, if the
JMS service is running, the JMS sub-tree in Resources presents
the existing JMS destinations (Topics and Queues), and allows the removal of
unused destinations and the creation of new JMS destinations.Save
button, the JOnAS configuration file is updated. As in the JMS service
example, the removed topics are deleted from the list assigned to the
jonas.service.jms.topics property and the newly created topics
are added to this list.
Security sub-tree presents existing security realms and
allows the creation of new realms of different types: memory, datasource, and
ldap realms.
First recall that domain management functions are accessible only when JonasAdmin
is deployed on a master server. The Domain tree contains only one
Server sub-tree, the currently administered server, which is initially
the server hosting JonasAdmin.
Domain management principal function is to present the domain topology: list all the servers and clusters belonging to the domain. It also allows modification of the domain topology by adding new servers and clusters to the domain, removing servers and moving servers to/from clusters.
In JOnAS 4.6 there is no cluster support, and the domain topology cannot be modified. The servers presented as belonging to the domain are those that have been started with their discovery service enabled.
In JOnAS 4.7, domain management page also presents servers that are not yet started but are specified as
belonging to the domain in the new configuration file named domain.xml.
Also, a server can be added to the domain when it has been started without having the discovery service enabled.
An essential domain management function is that the administrator can switch from the master to any of the
other servers in the domain. Currently, JonasAdmin allows only one category of global domain level management
operation, the deployment operation. Using any other management operation requires switching
to the server to be administered.
Domain level deployment allows for deploying one or more J2EE packages (JARs, WARs, RARs or EARs), which
are installed in the corresponding master directory (ejbjars, webaps, rars or apps), into any running server in the domain.
A deployment operation target may be a server but also a cluster. In this case, the deployment
operation addresses all the running servers in the cluster, including servers in the embedded clusters, if any.
The deploy operation may have three semantics:
Upload and Remove operations
are only related to the master server itself.
Save operation is
related to a service or a resource reconfiguration. For example, the
administrator can reconfigure a service and a resource, but choose to save
only the new resource configuration.Save operation is global to all configuration
changes that have been performed. For example, if a new HTTP connector is
reconfigured and a new context created for a web application, both
configuration changes are saved when using the Save
button.
The MEJB component exposes the managed objects within the JOnAS platform as JMX manageable resources. It is packed in an ejb-jar file installed in the $JONAS_ROOT/ejbjars/autoload directory, and therefor it is loaded at server start-up.
The MEJB component is registered under the name
java:comp/env/ejb/MEJB.
The current implementation allows access only to the manageable resources within the current server (the server containing the MEJB's container).
The JOnAS distribution was enriched with a new example called
j2eemanagement, which shows how the MEJB can be used.
You can find details about this management application in
$JONAS_ROOT/j2eemanagement/README file.