Using Enterprise Media Beans with JOnAS
This guide provides explanations for using Enterprise Media Beans with JOnAS.
Table of Contents:
What are Enterprise Media Beans (EMB)
Enterprise Media Beans provide a framework to integrate rich media data (i.e. audio, video, or image) into applications based on EJB Entity Beans within the J2EE application development model.
Architecture
Enterprise Media Beans target the seamless integration of rich media data into applications based on the J2EE programming model. Because such applications come in two basic shapes as described above, the Enterprise Media Beans architecture is separated into two components:
- Media Foundation Beans require only basic Java 2TM technology and can be used in any kind of J2EE application.
- Media Entity Beans rely on EJB entity beans and are therefore of interest only for applications based on the Enterprise JavaBeans architecture.
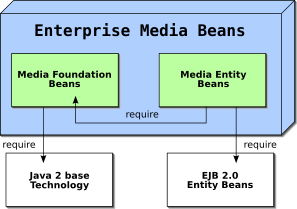
EMB components Dependencies
Media Entity Beans
Media Entity Beans (MEB) integrate the services provided by Media Foundation Beans into the Enterprise JavaBeans architecture, adding additional services that require media persistence. This means that MEBs could participate in relationships with Entity Beans in a transparent "CMP-style" way.
Media Foundation Beans
Media Foundation Beans (MFB) allow media to be represented independently of its type. MFB represents media in a uniform way, allowing programming based on interfaces that represent the media and its metadata (width, height, color dept, frame rate, etc.), instead of programming based on a particular media format (GIF or MPEG video for example).
Media Foundation Beans can be used to transcode from one format to another, for example to convert GIF files to PNG (due to patent problems) when serving them from a Servlet. Media can be resized to certain required dimensions, or digital watermarks can be added to stock photographs that are sold online. All these media transformations are represented with interfaces, allowing any type of transformation chain to be implemented, from any media to any media.
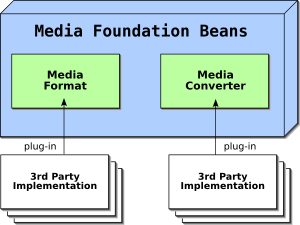
MFB plug-in architecture
For more information about architecture, refer to the brief chapter about EMB specification Architecture (Chapter 3): JSR 086
EMB in JOnAS
What JOnAS provides for using EMB
The JOnAS EMB implementation provides:
- an MEB implementation to manage media persistense and access,
- a basic MFB implementation to manipulate some basic media formats (i.e. images),
- a sample application,
- an API to add a new way for accessing media (Publisher Plugins API),
- an API to exend MFB and provide some new features (MFB Plugins API),
- serveral easy-to-use plugin samples.
This schema provides an overview of all components that can be used with EMB in JOnAS.
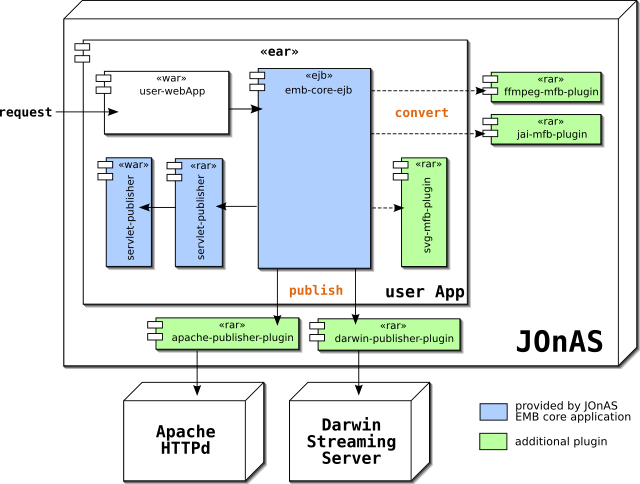
EMB components in JOnAS EMB implementation
Enterprise Media Beans Sample Application
The Enterprise Media Beans Sample Application is located in JONAS_EXAMPLES/emb-sample.
It is a simple webapp that provides an overview of the EMBs' features.
This application is based on EMB Core Application and is designed to use the additional features provided by MFB Plugins or Publisher Plugins (additional image support, svg support, video transcodage, video streaming, ...)
Enterprise Media Beans Core Application
Enterprise Media Beans Core is the minimal base of any application that uses EMB in JOnAS. This core is located in JONAS_ROOT/lib/commons/jonas/emb/emb-core.ear.
The emb-core.ear content includes:
- META-INF/application.xml, which describes the application components,
- emb-core-ejb.jar, which provides a Media Entity Beans implementation,
- emb-plugin-publisher-servlet-jonas.rar and emb-plugin-publisher-servlet-jonas.war, a Publisher plugin that provides different media and describes how to access this media through a servlet.
Media Entity Beans (emb-core-ejb.jar)
This is an EJB archive that provides a Media Entity Beans
implementation.
In order to use EMB more easily, some of the settings have been set to the default
values:
- MEB uses the default jdbc connector names, "jdbc_1". If another database will be used, this can be changed in META-INF/jonas-ejb-jar.xml.
- The maximum media size has been set to 6 MB in order to work properly with JOnAS default env. If necessary, this can be increased in META-INF/ejb-jar.xml.
The default Publisher (emb-plugin-publisher-servlet-jonas.rar and emb-plugin-publisher-servlet-jonas.war)
This publisher describes and provides a way to access different types of media
through a Servlet.
In order to use EMB more easily, some of the settings have been set to the default
values:
- By default, the Publisher provides access on localhost using the default port (http://localhost:9000/...). This can be changed to access media from outside the computer. To do this, change the property in ra.xml named servletAccessURL(ex: http://yourname:8080/servletContext). Note that the servlet context must be consistent with application.xml.
- Other settings are explained in EMB advanced settings.
Additional EMB plugins
The JOnAS EMB implementation provides some plugins that show how
capabilities can be extended.
These plugins are based on resource Adaptators (.rar) and, therefore, are able to dynamically add the
new features mentioned below.
The plugin rar file can be included in an application or it can be deployed directly.
It provides the following new MFB features :
- JAI Plugin: new image-format support with Java Advanced Imaging
- SVG Batik Plugin: capabilities for converting SVG to PNG with Batik
- FFMPEG Plugin: capabilities for converting video to 3GPP to MPG with the ffmpeg command-line help
It also provides the following new Publisher features:
- Darwin Streaming Server publisher Plugin: rstp access to MP4 media
- Apache HTTPd publisher Plugin: more efficient and progressive downloading
These plugins can be downloaded from ObjectWeb CVS -> emb-jonas/emb-plugins or ObjectWeb Files -> Tools.
Additional MFB Plugins
Java Advanced Imaging Plugin
The Java Advanced Imaging Plugin provides new image-format support
with Java Advanced Imaging.
It provides mainly TIFF and JPEG2000 support and uses JAI algorithms
instead of awt algorithms.
The Java Advanced Imaging API provides a set of object-oriented
interfaces that support a simple, high-level programming model that allows images to be easily manipulated.
The source code for the jai-core project is licensed under the Java
Research License (JRL) for non-commercial use. The JRL allows users to
download, build, and modify the source code in the jai-core project for
research use, subject to the terms of the license.
The source for the jai-core project is also licensed for commercial use
under a new, no-fee Java Distribution License (JDL). The JDL allows
commercial use of Java Advanced Imaging with or without modification, as
long as compatibility with the entire API Specification is maintained.
Java Advanced Imaging and Java Advanced Imaging Image I/O must be
installed in CLASSPATH before lauching JOnAS.
JAI and JAI Image I/O can be downloaded from Sun Web Site.
If the desired platform is not supported, the "Linux CLASSPATH version" can be downloaded and each
jar files placed in JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext. In this case, the pure java implementation should be used instead of the native implementation.
SVG Batik Plugin
The SVG Batik Plugin provides svg-format and SVG-to-PNG conversion support.
Batik is a Java(tm)-technology-based toolkit for applications or
applets that want to use images in the Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
format for various purposes, such as viewing, generating, or
manipulating.
More information is provided at Batik Web Site.
FFMPEG Plugin
The FFMPEG Plugin provides 3GPP-format support and conversion for
any format supported by FFMPEG.
Batik lib is included with the plugin.
FFmpeg is an extremely fast video and audio converter.
The command-line interface is designed to be intuitive, in the sense
that ffmpeg tries to determine all the parameters, when possible.
FFmpeg can convert from any sample rate to any other rate. It also resizes
video automatically with a high-quality polyphase filter.
More information is provided at FFMPEG Web Site.
Warning: in order to provide 3GPP and MP4 features:
- The ffmpeg command must be in the path.
- It must be compiled using at least the following options: --enable-amr_nb --enable-amr_wb --enable-faac --enable-faad. See FFMPEG doc for information about building the ffmpeg command. (Build options are listed at the top of each ffmpeg call.)
Additional Publisher Plugins
Darwin Streaming Server publisher Plugin
The Darwin Streaming Server publisher Plugin provides real streaming capabilites for MOV, MP4 and 3GPP media.
Darwin Streaming Server, the open source version of Apple's QuickTime
Streaming Server technology, allows streaming media to be sent to
clients across the Internet using the industry-standard RTP and RTSP
protocols. Based on the same code base as QuickTime Streaming Server,
Darwin Streaming Server provides a high level of customizability and
runs on a variety of platforms, allowing the code to be manipulated to
fit specific needs.
More information is provided at Darwin
Streaming Server Web Site.
Plugin settings:
- The DSS document root and DSS access URL must be set. This can be done in ra.xml by changing the properties named publishTargetDirectory(i.e. /var/www/), publishAccessURL(i.e. rtsp://localhost:554/), and publishAccessURL.
- Other settings are explained in EMB advanced settings.
A known issue is that to access media through DSS, the media must be
"hinted". (see DSS doc)
To date, there are two open-source solutions to hint MP4 media (MP4 Box and MPEG4IP), but they have not
been integrated into the JOnAS EMB implementaion
Apache HTTPd publisher Plugin
The Apache publisher Plugin provides efficient and progressive downloading.
The Apache HTTP Server Project is an effort to develop and maintain
an open-source HTTP server for current operating systems, including UNIX
and Windows NT. The goal of this project is to offer a secure,
efficient and extensible server that provides HTTP services synchronized with
the current HTTP standards.
More information is provided at Apache HTTPd Web Site.
Plugin settings:
- The apache document root and apache access URL must be set. This can be done in ra.xml by changing the properties named publishTargetDirectory(i.e. /var/www/) and publishAccessURL(i.e. http://localhost:80/)
- Other settings are explained in EMB advanced settings.
EMB Advanced Settings
Publisher Advanced Settings
The Publisher plugins provide advanced settings for optimal customization of media access.
Priority
The publisher is selected from the publisher registry by matching requirements.
If more than one publisher matches the requirements, the priority of the Publisher will determine the most appropriate to choose.
The priority must be between 0 and 100. The lower the number, the higher the priority.
There is no default value.
LRU cache
LRU cache is used to optimize media publishing. It must be sized to accommodate the resource and application needs.
The cache size must be at least equal to the number of times
different MediaBeans or MediaEntityBeans are accessed simultaneously.
The required free disk space to store the full
cache must also be available.
Warning: If there are usually serveral publisher with there own cache, sufficient free space must be available.
The default value is 100.
Auto Clean
When a media is published, it may be desirable to make the resulting link permanant. Due to cache issues and disk allocation issues, this is not the default setting. The autoclean setting must be turned off to have permanant published media.
Warning: If there are usually serveral publisher, sufficient free space must be available.
The default value is true.
Delete on exit
Published media is deleted when JOnAS server is turned off properly.
The default value is true.