Msc-generator has the following color names defined initially: none,
white, black, red, green, blue, gray
and lgray, the first for completly transparent color, and the last for
light gray. When you specify a color by name, no quotation marks are needed.
Color names can be appended with a ‘+’ or ‘-’ sign and a number
between [0..100] to make a color lighter or darker, respectively, by the
percentage indicated. Any color +100 equals white and any color-100 equals
black. Aliases can be further appended with a comma and a value between [0..255]
(or [0..1.0] similar to RGB values). This specifly color opaqueness: 0 means
fully transparent and 255 means fully opaque.
 |
 |
You can specify colors giving the red, green and blue components separated by commas. An optional fourth value can be added for the alpha channel to control transparency. Values can be either between zero and 1.0 or between 0 and 255. If all values are less than or equal to 1, the former range is assumed[31]. If any value is negative or above 255 the definition is invalid. Note that you must not enter spaces between the color name, its lighter/darker or transparency modifier or between the RGB values.
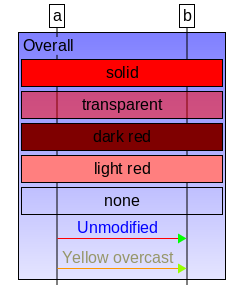
You can mark a color a overlay color by prepending the ‘++’ symbol.
An overlay color applied to an attribute is not set as the color value. Instead, it
is overlaid over and thus is combined with the existing color. (See the arrows in the
example above.) You can also assign an overlay color to a style or a color name (see
below). (This is how their weak style is implemented.)
It is possible to define your own color names using the defcolor command
as below.
defcoloralias=color definition, ... ;
Color names are case-sensitive and can only contain letters, numbers,
underscores and dots, but can not start with a number or a dot and can not end
with a dot. Aliases can also be later re-defined using the defcolor
command, by simply using an existing alias with a different color definition.
Msc-generator honors scoping. Color definitions (or re-definitions) are valid only
until the next closing brace ‘}’. This makes it possible to override
a color only for parts of the chart, returning to the default later. Note that
you can start a new scope any time by placing an opening brace. See Scoping
for more on scopes.
[31] This mechanism allows both people thinking in range [0..1] and in [0..255] to conveniently specify values. (Internally values are stored on 8 bits.)