Connecting to a MySQL Database
Contributed and maintained by
Troy Giunipero
November 2007
This document demonstrates how to configure the MySQL database server on
your computer and set up a connection to it from NetBeans IDE. Once connected,
you can begin working with MySQL in the IDE's Database Explorer by creating
new databases and tables, populating tables with data, and running SQL
queries on database structures and content. This tutorial is designed for
beginners with a basic understanding of database management and application
development, who want to apply their knowledge to working with MySQL in
NetBeans IDE.
MySQL is a popular Open Source relational
database management system (RDBMS) commonly used in web applications due to
its speed, flexibility and reliability. MySQL employs SQL, or Structured
Query Language, for accessing and processing data contained in databases.
In order to work through this tutorial, you need to have the following
software installed on your computer:
- NetBeans IDE 6.0
- Java SE Development Kit (JDK™) version 5.0 or higher*
- MySQL server
(download)
*Note: You need to install
the Java SE Development Kit (JDK™) in order to install and run NetBeans
IDE. The JDK includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), as well as various
tools and API's necessary for development in Java.
Expected duration: 25 minutes

The following topics are covered below:
Installing and Configuring MySQL
If you already have the MySQL database set up and running on your computer,
skip ahead to Registering the Database in NetBeans
IDE. By way of example, this tutorial demonstrates how to install the
MySQL Community Server on both Windows XP and
Unix-based systems.
Unix
- Run sudo apt-get install mysql-server in a terminal window.
MySQL is automatically downloaded and installed.
- Start the MySQL server by running sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start.
- Run mysqladmin -u root password nbuser. This allows you to
set a new password for the root user, which is initially blank. For
purposes of this tutorial, use nbuser.
Windows XP
- Run the self-extracting file. The MySQL Setup Wizard opens to guide
you through the installation process. Accept all default settings.
- Upon completing installation, allow the MySQL wizard to immediately
configure the server by making sure the Configure the MySQL Server
Now checkbox is selected. This will allow an instance of the server
to be created, which will run as a Windows service on your computer.
- In the MySQL Server Instance Configuration wizard, select Standard
Configuration. Click Next. When you arrive at the step allowing you
to set Windows options, select the Include Bin Directory in Windows
PATH checkbox. This will later allow you to perform a simple check
to make sure the MySQL service is up and running:
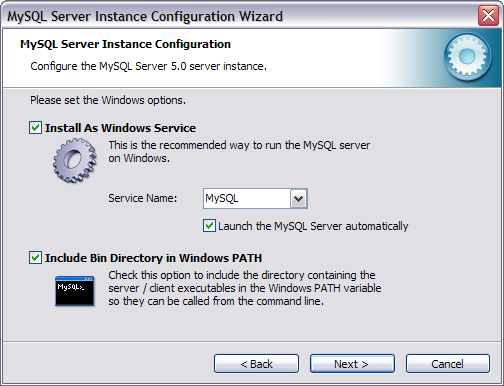
- For purposes of this tutorial, set the root password to: nbuser.
Finally, click Execute to allow the wizard to generate the server
instance on your computer. If you encounter any problems, refer to
the MySQL Reference Manual included in your installation or the
online documentation.
Before continuing further, it is important to understand the components found
in MySQL's root directory:
- The bin subdirectory contains the scripts for
executing utilities and setting up the environment.
- The data subdirectory contains all database
instances, including their data.
- The Docs subdirectory contains the MySQL Reference Manual.
- The share subdirectory contains localization
files, including character sets and language packages.
- The my.ini file is the configuration file that was
generated by the Configuration wizard, and contains information such as
the port being listened on, path to installation directory, path to
database root, and default character set.
Connecting to MySQL from NetBeans IDE
Connections to databases are managed using database drivers, which
enable applications written in different programming languages to interact
with the database management system. NetBeans IDE 6.0 comes bundled with
the MySQL Connector/J
driver, which is a pure Java implementation of the
JDBC API, and
communicates directly with the MySQL server using the MySQL protocol.
Begin by examining the functionality offered by the Database Explorer located
in the IDE's Services window (Ctrl-5). The Database Explorer is represented
by the Databases node ( ). From this interface you can connect to database
servers, view current connections, add database drivers, as well as create,
browse or edit database structures.
). From this interface you can connect to database
servers, view current connections, add database drivers, as well as create,
browse or edit database structures.
Now that you have the MySQL database server installed and configured, you can
connect to it from the NetBeans IDE using the Database Explorer. Note that
you are connecting to the database server. In the next step, you
will create a database instance through this connection. Do the
following:
- In the Database Explorer, expand the Drivers node, then right-click
the MySQL (Connector/J driver) and choose Connect Using. The New Database
Connection dialog displays.
- In the Database URL field, replace the default <HOST>:<PORT>/<DB>
with a forward-slash (/) so that the entry now reads: jdbc:mysql:///.
- For User Name and Password, enter root and nbuser,
respectively. Optionally, select the Remember password option.
- Click OK, then click OK again to accept the default schema and exit the
dialog. A new Connection node displays in the Database Explorer under
the Databases node:
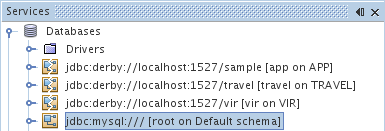
You are now connected to MyNewDatabase in the IDE. Note that the
new connection node icon appears whole ( ) when
you are connected to a database. Likewise, it appears broken
(
) when
you are connected to a database. Likewise, it appears broken
( ) when there is no connection.
) when there is no connection.
At later stages, when working with databases through the Database Explorer, you may need to
manually connect to a database. You can do so by right-clicking the broken database
connection node and choosing Connect.
Creating a Database Instance
A common way of interacting with databases is through an SQL editor. NetBeans
IDE has a built-in SQL Editor for this purpose. The SQL Editor is generally
accessible via the Execute Command option from the right-click menu of the
connection node (or of the connection node's child nodes). Now that you are
connected to the MySQL server, you can create a new database instance using
the SQL Editor. For purposes of this tutorial, create an instance called
MyNewDatabase:
- Right-click the connection node you just added and choose Execute Command.
The SQL Editor opens in the main window.
- In the SQL Editor, type:
create database MyNewDatabase;
Then, right-click anywhere within the SQL Editor and choose Run Statement.
The SQL query executes against the database. In the Output window (Ctrl-4)
you will see output similar to the following, indicating that the query
executed successfully:
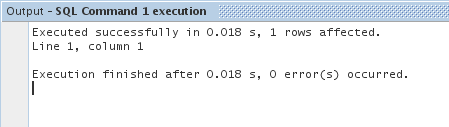
Connecting to the Database Instance
- In the Services window (Ctrl-5) choose Connect Using from the right-click
menu of the MySQL driver. The New Database Connection dialog opens.
- In the Basic Setting tab, enter the Database's URL in the corresponding
text field. The URL is used to identify the type and location of a database
server. In this example, you need to specify the host name (i.e. the
location of the server), the port number on which the database communicates,
and the name of the database instance being used. In this case you can
enter: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MyNewDatabase.
- For User Name and Password, enter root and nbuser
respectively:
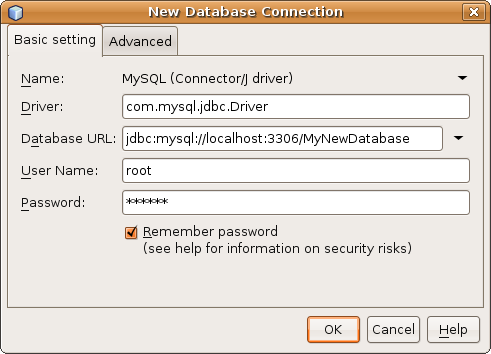
- Click OK, then click OK again to exit the dialog. A new Connection
node displays in the Database Explorer under the Databases node, just
as it did when you connected to the MySQL server.
Note: While you can now access MyNewDatabase through
your connection in the IDE, you have not yet made it available to any specific
application. At this stage, you can use the IDE to access and modify the database,
but cannot do so within the context of an application yet.
Creating Database Tables
Now that you have connected to MyNewDatabase, you can begin exploring
how to create tables, populate them with data, and modify data maintained
in tables. This allows you to take a closer look at the functionality
offered by the Database Explorer, as well as NetBeans IDE's support for
SQL files.
MyNewDatabase is currently empty. In the IDE it is possible to add
a database table by either using the Create Table dialog, or by inputting
an SQL query and running it directly from the SQL Editor. Here you can
explore both methods:
- Using the SQL Editor
- Using the Create Table Dialog
Using the SQL Editor
- In the Database Explorer, expand the MyNewDatabase
connection node (
 ) and note that there are three subfolders:
Tables, Views and Procedures. Right-click the Tables node beneath the
MyNewDatabase connection node and choose Execute Command.
A blank canvas opens in the SQL Editor in the main window.
) and note that there are three subfolders:
Tables, Views and Procedures. Right-click the Tables node beneath the
MyNewDatabase connection node and choose Execute Command.
A blank canvas opens in the SQL Editor in the main window.
- In the SQL Editor, type in the following query. This is a
table definition for the Counselor table you are
about to create:
CREATE TABLE Counselor (
id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
firstName VARCHAR (50),
nickName VARCHAR (50),
lastName VARCHAR (50),
telephone VARCHAR (25),
email VARCHAR (50),
memberSince DATE DEFAULT '0000-00-00',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
Note: Queries formed in the SQL Editor are parsed in
Structured Query Language (SQL). SQL adheres to strict syntax rules
which you should be familiar with when working in the IDE's Editor.
Upon running a query, feedback from the SQL engine is generated in
the Output window indicating whether execution was successful or not.
- To execute the query, either click the Run SQL (
 )
button in the task bar at the top (Ctrl-Shift-E), or right-click within
the SQL Editor and choose Run Statement. The IDE generates the
Counselor table in the database, and you receive a message
similar to the following in the Output window:
)
button in the task bar at the top (Ctrl-Shift-E), or right-click within
the SQL Editor and choose Run Statement. The IDE generates the
Counselor table in the database, and you receive a message
similar to the following in the Output window:

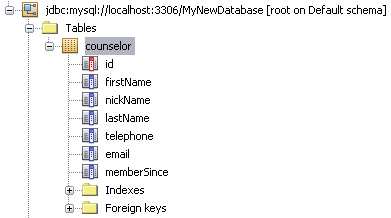
- To verify changes, right-click the Tables node in the Database Explorer
and choose Refresh. The Refresh option updates the Database Explorer's
UI component to the current status of the specified database. Note that
the new Counselor table node (
 ) now displays
under Tables in the Database explorer. If you expand the table node you
can see the columns (fields) you created, starting with the primary key
(
) now displays
under Tables in the Database explorer. If you expand the table node you
can see the columns (fields) you created, starting with the primary key
( ):
):
Using the Create Table Dialog
- In the Database Explorer, right-click the Tables node and choose
Create Table. The Create Table dialog opens.
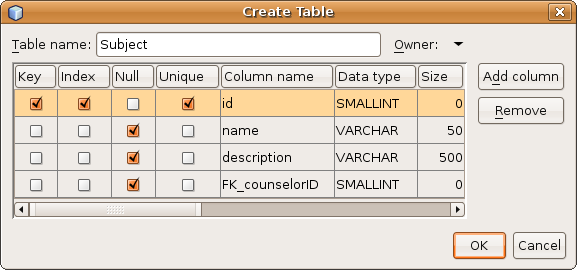
- In the Table Name text field, type Subject.
- In the first row displayed, select the Key check box. You are
specifying the primary key for your table. All tables found in
relational databases must contain a primary key. Note that when
you select the Key check box, the Index and Unique check boxes
are also automatically selected and the Null check box is deselected.
This is because primary keys are used to identify a unique row in
the database, and by default form the table index. Because all rows
need to be identified, primary keys cannot contain a Null value.
- For Column Name, enter id. For Data Type, choose
SMALLINT from the drop-down list, then click the Add
Column button.
- Repeat this procedure by specifying all remaining fields, as shown
in the table below:
| Key |
Index |
Null |
Unique |
Column Name |
Data Type |
Size |
| [checked] |
[checked] |
|
[checked] |
id |
SMALLINT |
3 |
|
|
[checked] |
|
name |
VARCHAR |
50 |
|
|
[checked] |
|
description |
VARCHAR |
500 |
|
|
[checked] |
|
FK_counselorID |
SMALLINT |
3 |
You are creating a table named Subject
that will hold data for each of the following records:
- Name: name of the subject
- Description: description of the subject
- Counselor ID: counselor ID that corresponds
to an ID from the Counselor table
Make sure that the fields in your Create Table dialog match those
shown above, then click OK. The IDE generates the Subject
table in the database, and you can see a new Subject table
node ( ) immediately display under Tables in the
Database Explorer.
) immediately display under Tables in the
Database Explorer.
Working with Table Data
In order to work with table data, you can make use of the SQL Editor
in NetBeans IDE. By running SQL queries on a database, you can add,
modify and delete data maintained in database structures. To add a
new record (row) to the Counselor table, do the following:
- Choose Execute Command from the Tables folder in the Database Explorer.
A blank canvas opens in the SQL Editor in the main window.
- In the SQL Editor, type in the following query:
INSERT INTO Counselor
VALUES (1, 'Ricky', '"The Dragon"', 'Steamboat','334 612-5678', '[email protected]', '1996-01-01')
- To execute the query, right-click within the SQL Editor and choose Run
Statement. In the Output window, you can see a message indicating that
the query was successfully executed.
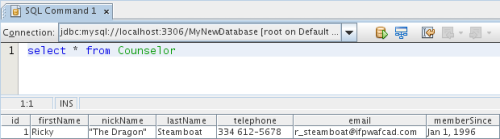
- To verify that the new record has been added to
the Counselor table, in the Database Explorer, right-click the
Counselor table node and choose View Data. A new SQL Editor pane
opens in the main window. When you choose View Data, a query to select all
the data from the table is automatically generated in the upper region of
the SQL Editor. The results of the statement are displayed in a table view
in the lower region. In this example, the Counselor table displays.
Note that a new row has been added with the data you just supplied from the
SQL query:
Running an SQL Script
Another way to manage table data in NetBeans IDE is by running an external SQL
script directly in the IDE. If you have created an SQL script elsewhere, you
can simply open it in NetBeans IDE and run it in the SQL Editor.
For demonstrative purposes, download
ifpwafcad.sql
and save it to a location on your computer. This script creates two tables similar to
what you just created above (Counselor and Subject), and
immediately populates them with data.
Because the script overwrites these tables if they already exist, delete the
Counselor and Subject tables now so it becomes obvious that
new tables are being created when the script is run. To delete tables:
- Right-click the selected table node in the Database Explorer and choose
Delete.
- In the Confirm Object Deletion dialog that displays, click Yes. Note that
the table node is automatically removed from the Database Explorer.
To run the SQL script on MyNewDatabase:
- Choose File > Open File from the IDE's main menu. In the file browser
navigate to the location where you previously saved ifpwafcad.sql
and click Open. The script automatically opens in the SQL Editor.
- Make sure your connection to MyNewDatabase is selected from
the Connection drop-down box in the toolbar at the top of the Editor:
- Click the Run SQL (
 ) button in the SQL Editor's task bar. The script is
executed against the selected database, and any feedback is generated in
the Output window.
) button in the SQL Editor's task bar. The script is
executed against the selected database, and any feedback is generated in
the Output window.
- To verify changes, right-click the MyNewDatabase connection node
in the Runtime window and choose Refresh. The Refresh option updates the
Database Explorer's UI component to the current status of the specified
database. Note that the two new tables from the SQL script now display as
a table nodes under MyNewDatabase in the Database Explorer.
- Choose View Data from the right-click menu of a selected table node to
see the data contained in the new tables. In this manner, you can compare
the tabular data with the data contained in the SQL script to see that
they match.
Next Steps
This concludes the Connecting to a MySQL Database tutorial. This document
demonstrated how to configure MySQL on your computer and set up a connection
to the database server from NetBeans IDE. It also described how to work with
MySQL in the IDE's Database Explorer by creating new database instances and
tables, populating tables with data, and running SQL queries.
For related and more advanced tutorials, see the following resources:
top



 ) when there is no connection.
) when there is no connection.

 )
button in the task bar at the top (Ctrl-Shift-E), or right-click within
the SQL Editor and choose Run Statement. The IDE generates the
Counselor table in the database, and you receive a message
similar to the following in the Output window:
)
button in the task bar at the top (Ctrl-Shift-E), or right-click within
the SQL Editor and choose Run Statement. The IDE generates the
Counselor table in the database, and you receive a message
similar to the following in the Output window:

 ) now displays
under Tables in the Database explorer. If you expand the table node you
can see the columns (fields) you created, starting with the primary key
(
) now displays
under Tables in the Database explorer. If you expand the table node you
can see the columns (fields) you created, starting with the primary key
(


