
Table of Contents
Objective: To familiarize you with the basic features and functions of an Enterprise Content Management system through exploration of the Nuxeo EP server.
The website is down. "The sales guy" (as seen on youtube).
If you have any comments, questions, or general-purpose harassment you would like give us about this book, then please use the comment form at the bottom of each page! We promise that we will try to incorporate any feedback you give (minus the profanity, of course), will respond to your questions, and credit you appropriately.
This lesson is not long enough to have a full explanation of the meaning of Enterprise Content Management or the software that implements this function, often called an ECM system. In the preface to this volume, we have provided you with a short discussion of the basics of ECM. (It's likely you know something about ECM already, you are reading this book!) [Definition: To repeat, in a short form, an ECM system is for the creation, discovery, management, and distribution of content, especially unstructured content.]
Many organizations have found that they are unable to locate or manage the content that they have, leading to enormous wastes in resources since useful content ends up being created multiple times rather than being reused. For example, a technical writer in an organization writes a summary of a product called frobnitz that his or her employer sells; ideally, that content should be reused in product brochures about the frobnitz, published to the website on the frobnitz page, and perhaps integrated into a comparison document circulated internally about how the frobnitz compares to the competition's offering. If the tech writer were to submit the summary to the [Definition: repository, the central location where all the content is stored], of an ECM system, this content reuse could be achieved. The technical writer's document would at least be found and consulted when each of the other documents is created, and perhaps even incorporated without change into the work of other users.
Another key function of ECM systems, including Nuxeo 5, is the ability to automate organizational processes that involve content in the repository. [Definition: Automating a business process that involves multiple users and is based on documents is often called workflow.] A simple example of workflow is document review before publication: Alice writes a document and wants to publish it to the website. Alice submits the document to the repository and begins a workflow called 'Approval For External Publication' that involves her boss, Bob. Bob is notified the next time he accesses the ECM system that he has work to do. He uses the repository to find and access the document, and then uses the workflow subsystem to indicate 'Approved.' At this point, the document is automatically made available via the website by the ECM system, and the workflow is marked as completed.
This will be a brief introduction to some of the basic functions of
Nuxeo that are available in the standard system download. For a more
detailed discussion of all the capabilities that are offered to a Nuxeo 5
user, see the User's Guide at
http://doc.nuxeo.org/5.2/books/nuxeo-user-guide/html.
In the previous lesson we
showed you how to start the Nuxeo server and go to the login screen. Now,
we will take the next steps and log in to the system and use some of it's
features. A freshly installed Nuxeo system has the user name and password
"Administrator" (note the capital 'A'). Try logging in to the system with
your web browser at http://localhost:8080/nuxeo and the
Administrator account. When you have succeed, you should see a web page
like this:
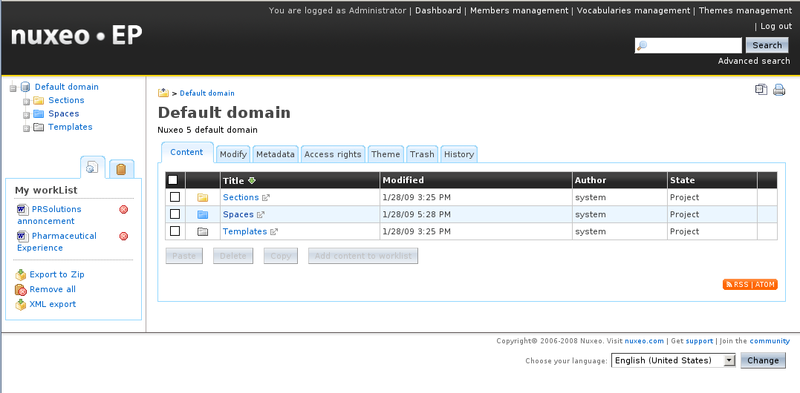
If you are new to the Nuxeo system or ECM, you will find it very illuminating to "play with" all the parts of the visible user interface. Some fun exercises to do are:
Create a two new users, Alice and Bob via the 'members management' link. Create Alice in the 'Administrators' group and Bob in the 'Members' group.
Logout as Administrator and log back in as Bob. Explore the user interface, noting the differences between what a "normal user" sees and what an administrator sees.
Upload a document as Bob and alter some of its properties. Submit the document for publication via the 'Publish' tab.
Logout as Bob and log back in as Alice. Check your dashboard and find the document Bob has submitted. Approve or reject the document and give a reason in the comment section. If you have approved the document, verify that the document has appeared in one of the Sections.
Create a new workspace 'foo' and alter the permissions so that Bob can rename of the workspace and add content to it.
Log out as Alice and log back in as Bob. Check the status of the previously submitted document and the comment made by Alice. Look at the document's history to get an overview of all the activity.
Go to workspace 'foo' and (try to) change the name to 'bar'. Create a new "Note" document in the workspace. (A 'note' has no file associated with it, just meta-data.)
Use the workflow system to set up a 'review' of the document. Put some questions from Bob to Alice in the comment sections when asked.
Look at the dashboard as Bob to see the status of the two documents that he has created. Log out and log back in as Alice to respond to the workflow...
Again, the Nuxeo User's Guide,
http://doc.nuxeo.org/5.2/books/nuxeo-user-guide/html, covers
all the features of the system in some detail.
iansmith@Photo /nuxeo $ cd /nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5/NuxeoServer/bin iansmith@Photo /nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5/NuxeoServer/bin $ ls classpath.sh* probe.bat* run.jar* shutdown.sh* wstools.bat* jboss_init_hpux.sh* probe.sh* run.sh* twiddle.bat* wstools.sh* jboss_init_redhat.sh* run.bat* shutdown.bat* twiddle.jar* jboss_init_suse.sh* run.conf* shutdown.jar* twiddle.sh*
In the
screen listing above, you can see that when you navigate to the
bin directory of the Nuxeo server, you see some files
that are associated with JBoss. In fact, all of the scripts in the
bin directory manipulate the JBoss server rather than
Nuxeo proper. Nuxeo 5 runs inside the JBoss application
server. As of Nuxeo 5.2, the version of JBoss used is 4.2.3 GA.
If you are unfamiliar with software development for or administration of
JBoss there is no need to worry. This book will cover what you need to
know about JBoss, and in truth that amount is very small.
Why is Nuxeo designed this way? Nuxeo software follows the open source software principle of "building on the work of giants." This means not rebuilding subsystems that others have already built! JBoss provides a number of key features that the Nuxeo system "rides" on. For example, JBoss provides support for interacting with databases via JDBC (Java DataBase Connectivity) and JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface). Most importantly, JBoss provides the "web connector" that allows the Nuxeo server's capabilities to be accessed via the web-as you saw when you logged in above.
If you are familiar with web application development in Java, the
Nuxeo 5 server is implemented as a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE)
application and deployed as an Enterprise Application Resource, a
.ear module. If you are not familiar with enterprise
web applications, no need to worry! You do not need to work with J2EE to
build new capabilities or applications with Nuxeo server. J2EE
is how Nuxeo is implemented, not how you will implement your
code.
The most important directory for configuring Nuxeo 5, if you
followed our instructions on installing Nuxeo in
/nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5, is
/nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5/NuxeoServer/server/default/deploy/nuxeo.ear.
This is the "exploded" version of a distribution of Nuxeo; in principle,
the entire system can be distributed as a single file-with many files
compressed inside it, but this is less convenient for most users who want
to configure the system. In configuring a Nuxeo server, most users need to
edit some of the files in this directory and its subdirectories. If you
ever have the need to upgrade or change your installation, it would be
wise to save all the files in this directory and all its
subdirectories.
Some of the key subdirectories' contents are:
config This contains the configuration
files for many parts of the Nuxeo system, including the
repository.
datasources This directory allows to
configure Nuxeo to use your particular database. By default, Nuxeo is
set to use the H2 embedded database
(http://www.h2database.com) that requires no external
programs to function. In the file
datasources/default-repository-ds.xml are some
commented out configuration examples for other databases such as
postgres and derby.
lib This directory contains third-party,
open-source libraries that Nuxeo uses.
nuxeo.war This directory contains the
html files, xhtml files,
graphic files, css style sheets, and other files that make the user
interface of Nuxeo 5 when you visit it in your web browser.
This directory is re-generated each time you start the server, so do not try changing the files in this directory as your changes will be lost. You can change the files that get placed in this directory by editing bundles (see next lesson).
plugins This is where your code is placed
when you have built an extension to Nuxeo, normally packaged as a
'bundle' which will be explained more fully in the next lesson.
Normally, this directory is empty when you have a fresh installation
of Nuxeo.
system This directory contains the
built-in, ECM features of Nuxeo 5. These are packaged as bundles also;
a fresh download contains about 125 bundles in this directory.
META-INF This directory has a number of
configuration files in it. These are used to tell JBoss information
Nuxeo and are normally not something that developers would need to be
concerned about unless they are working on the Nuxeo system
itself.
As we noted before, the Nuxeo server runs inside JBoss, using many
of its features. One of these features is logging and to configure the
logging level of Nuxeo you need to make a change to the JBoss
configuration. The JBoss configuration file for the amount of logging you
desire is in the directory
/nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5/NuxeoServer/server/default/conf
in the file jboss-log4j.xml. The output of
the logger can be found in the directory
/nuxeo/tools/NuxeoEP5/NuxeoServer/server/default/log
in the files boot.log,
nuxeo-error.log and server.log.
The boot file is the information about the startup of the JBoss server and
the last is the information about the running system, including Nuxeo. The
configuration file log4j only affects the
server.log logging. The middle one is usually empty
except in the case where Nuxeo has detected a problem.
To change the amount of logging you see, on the console or in the log files, you must change the log level or "Threshold" used by the JBoss server. This is the snippet of XML from jboss-log4j.xml that controls the output to the console window:
<!-- ============================== -->
<!-- Append messages to the console -->
<!-- ============================== -->
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<errorHandler class="org.jboss.logging.util.OnlyOnceErrorHandler"/>
<param name="Target" value="System.out"/>
<param name="Threshold" value="INFO"/>
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<!-- The default pattern: Date Priority [Category] Message\n -->
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%d{ABSOLUTE} %-5p [%c{1}] %m%n"/
>
</layout>
</appender>In this listing, you can see the
Threshold is set to print information at the INFO level
or more. To get more information, change the INFO to
DEBUG; to get less try using ERROR
or WARN. More information about the (vast number of)
log4j configuration options can be found at
http://logging.apache.org/log4j/1.2/index.html.