Odoo's tax engine is very flexible and support many different type of taxes: value added taxes (VAT), eco-taxes, federal/states/city taxes, retention, withholding taxes, etc. For most countries, your system is pre-configured with the right taxes.
Cette section décrit comment vous pouvez définir de nouvelles taxes pour des cas d'utilisation particuliers.
- Go to . From this menu, you get all the taxes you can use: sales taxes and purchase taxes.
- Choose a scope: Sales, Purchase or None (e.g. deprecated tax).
Select a computation method:
- Fixed: eco-taxes, etc.
- Percentage of Price: most common (e.g. 15% sales tax)
- Percentage of Price Tax Included: used in Brazil, etc.
Groupe de taxes : permet d'avoir une taxe composée
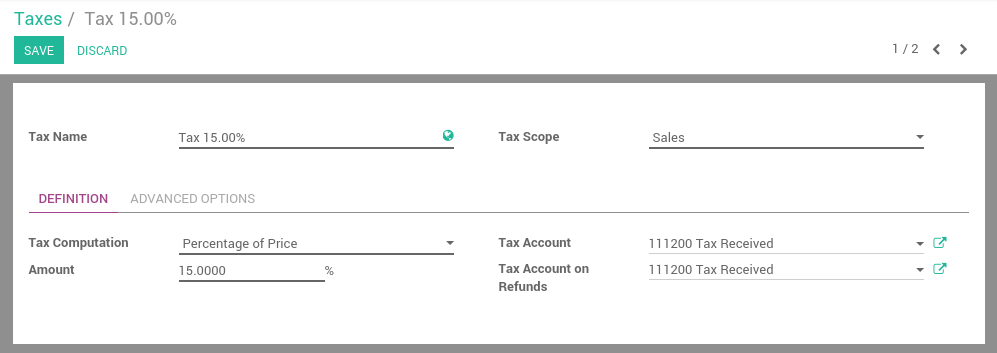
- If you use Odoo Accounting, set a tax account (i.e. where the tax journal item will be posted). This field is optional, if you keep it empty, Odoo posts the tax journal item in the income account.
Astuce
If you want to avoid using a tax, you can not delete it because the tax is probably used in several invoices. So, in order to avoid users to continue using this tax, you should set the field Tax Scope to None.
Note
If you need more advanced tax mechanism, you can install the module account_tax_python and you will be able to define new taxes with Python code.
Advanced configuration
- Label on Invoices: a short text on how you want this tax to be printed on invoice line. For example, a tax named "15% on Services" can have the following label on invoice "15%".
Groupe de taxe: définit où cette taxe est ajoutée dans le pied de page de la facture. Toutes les TVA appartenant au même groupe de taxe seront regroupées sur le pied de page de la facture. Des exemples de groupe de taxe : TVA, rétention.
Inclure dans le coût analytique : la taxe est comptabilisée comme un coût et, par conséquent, génére une entrée analytique si votre facture utilise des comptes analytiques.
- Tags: are used for custom reports. Usually, you can keep this field empty.