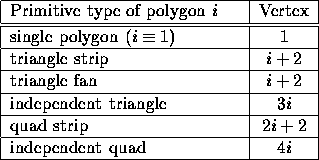



Next: 2.13.8 Color and Texture
Up: 2.13 Colors and Coloring
Previous: 2.13.6 Clamping or Masking
A primitive may be flatshaded,
meaning that all vertices of the primitive are assigned the same color.
This color is the color of the vertex that spawned the primitive.
For a point,
this is the color associated with the point.
For a line segment,
it is the color of the second (final) vertex of the segment.
For a polygon,
the selected color depends on how the polygon was generated.
Table 2.9 summarizes the possibilities.
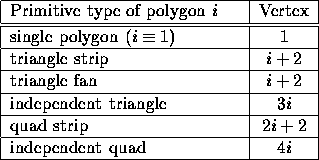
Table 2.9: Polygon flatshading color
selection.
The color used for flatshading the ith polygon generated by
the indicated Begin / End type is
the current color (if lighting is disabled) in effect
when the indicated vertex is specified.
If lighting is enabled,
the color is produced by lighting the indicated vertex.
Vertices are numbered 1 through n,
where n is the number of vertices between the Begin / End pair.
Flatshading is controlled by
void ShadeModel ( enum mode ) ;
mode value must be either of the symbolic constants SMOOTH
or FLAT.
If mode is SMOOTH (the initial state),
vertex colors are treated individually.
If mode is FLAT,
flatshading is turned on.
ShadeModel thus requires one bit of state.
David Blythe
Sat Mar 29 02:23:21 PST 1997