Distributed computing environments, often need to deploy similar or identical servers at multiple locations. These environments include ISPs, geographically distributed sales offices, and telecommunication service providers. Servers in a distributed computing environment might provide some of the following services:
-
Router or firewall services
-
Email services
-
DNS caches
-
Usenet (Network News) servers
-
DHCP services
-
Other services best provided at a variety of locations
These small servers have several characteristics in common:
-
High-reliability requirements
-
High-availability requirements
-
Routine hardware and performance requirements
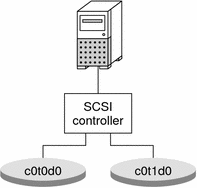
As a starting point, consider a Netra™ server with a single SCSI bus and two internal disks. This off-the-shelf configuration is a good starting point for distributed servers. Solaris Volume Manager could easily be used to mirror some or all of the slices, thus providing redundant storage to help guard against disk failure. See the following figure for an example of this small system configuration.
This configuration might include mirrors for the root (/), /usr, swap, /var, and /export file systems, plus state database replicas (one per disk). As such, a failure
of either side of any of the mirrors would not necessarily result in system failure.
Also, up to five discrete failures could possibly be tolerated. However, the system
is not sufficiently protected against disk or slice failure. A variety of potential
failures could result in a complete system failure, requiring operator intervention.
While this configuration does help provide some protection against catastrophic disk failure, it exposes key possible single points of failure:
-
The single SCSI controller represents a potential point of failure. If the controller fails, the system is down, pending replacement of the part.
-
The two disks do not provide adequate distribution of state database replicas. The majority consensus algorithm requires that half of the state database replicas be available for the system to continue to run. This algorithm also requires half plus one replica for a reboot. So, if one state database replica were on each disk and one disk or the slice that contains the replica failed, the system could not reboot. As a result a mirrored root (
/) file system would become ineffective. If two or more state database replicas were on each disk, a single slice failure would likely not be problematic. However, a disk failure would still prevent a reboot. If different number of replicas were on each disk, one disk would have more than half and one disk would have fewer than half. If the disk with fewer replicas failed, the system could reboot and continue. However, if the disk with more replicas failed, the system would immediately panic.
A “Best Practices” approach would be to modify the configuration by adding one more controller and one more hard drive. The resulting configuration would be far more resilient.