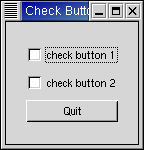
Check buttons inherit many properties and methods from the the toggle buttons above, but look a little different. Rather than being buttons with text inside them, they are small squares with the text to the right of them. These are often used for toggling options on and off in applications.
The creation method is similar to that of the normal button.
check_button = gtk.CheckButton(label=None) |
If the label argument is specified the method creates a check button with a label beside it. The label text is parsed for '_'-prefixed mnemonic characters.
Checking and setting the state of the check button are identical to that of the toggle button.
The checkbutton.py program provides an example of the use of the check buttons. Figure 6.3, “Check Button Example” illustrates the resulting window:
The source code for the checkbutton.py program is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example checkbutton.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8
9 class CheckButton:
10 # Our callback.
11 # The data passed to this method is printed to stdout
12 def callback(self, widget, data=None):
13 print "%s was toggled %s" % (data, ("OFF", "ON")[widget.get_active()])
14
15 # This callback quits the program
16 def delete_event(self, widget, event, data=None):
17 gtk.main_quit()
18 return False
19
20 def __init__(self):
21 # Create a new window
22 self.window = gtk.Window(gtk.WINDOW_TOPLEVEL)
23
24 # Set the window title
25 self.window.set_title("Check Button")
26
27 # Set a handler for delete_event that immediately
28 # exits GTK.
29 self.window.connect("delete_event", self.delete_event)
30
31 # Sets the border width of the window.
32 self.window.set_border_width(20)
33
34 # Create a vertical box
35 vbox = gtk.VBox(True, 2)
36
37 # Put the vbox in the main window
38 self.window.add(vbox)
39
40 # Create first button
41 button = gtk.CheckButton("check button 1")
42
43 # When the button is toggled, we call the "callback" method
44 # with a pointer to "button" as its argument
45 button.connect("toggled", self.callback, "check button 1")
46
47
48 # Insert button 1
49 vbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 2)
50
51 button.show()
52
53 # Create second button
54
55 button = gtk.CheckButton("check button 2")
56
57 # When the button is toggled, we call the "callback" method
58 # with a pointer to "button 2" as its argument
59 button.connect("toggled", self.callback, "check button 2")
60 # Insert button 2
61 vbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 2)
62
63 button.show()
64
65 # Create "Quit" button
66 button = gtk.Button("Quit")
67
68 # When the button is clicked, we call the mainquit function
69 # and the program exits
70 button.connect("clicked", lambda wid: gtk.main_quit())
71
72 # Insert the quit button
73 vbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 2)
74
75 button.show()
76 vbox.show()
77 self.window.show()
78
79 def main():
80 gtk.main()
81 return 0
82
83 if __name__ == "__main__":
84 CheckButton()
85 main()
|