Scrolled windows are used to create a scrollable area with another widget inside it. You may insert any type of widget into a scrolled window, and it will be accessible regardless of the size by using the scrollbars.
The following function is used to create a new scrolled window.
scrolled_window = gtk.ScrolledWindow(hadjustment=None, vadjustment=None) |
Where the first argument is the adjustment for the horizontal direction, and the second, the adjustment for the vertical direction. These are almost always set to None or not specified.
scrolled_window.set_policy(hscrollbar_policy, vscrollbar_policy) |
This method sets the policy to be used with respect to the scrollbars. The first argument sets the policy for the horizontal scrollbar, and the second, the policy for the vertical scrollbar.
The policy may be one of POLICY_AUTOMATIC or POLICY_ALWAYS. POLICY_AUTOMATIC will automatically decide whether you need scrollbars, whereas POLICY_ALWAYS will always leave the scrollbars there.
You can then place your object into the scrolled window using the following method.
scrolled_window.add_with_viewport(child) |
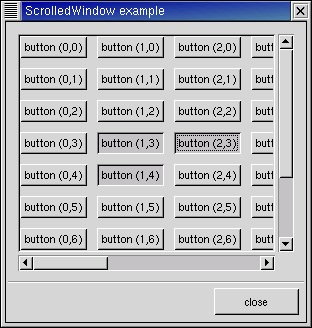
The scrolledwin.py example program packs a table with 100 toggle buttons into a scrolled window. I've only commented on the parts that may be new to you. Figure 10.7, “Scrolled Window Example” illustrates the program display:
The source code for the scrolledwin.py program is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example scrolledwin.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8
9 class ScrolledWindowExample:
10 def destroy(self, widget):
11 gtk.main_quit()
12
13 def __init__(self):
14 # Create a new dialog window for the scrolled window to be
15 # packed into.
16 window = gtk.Dialog()
17 window.connect("destroy", self.destroy)
18 window.set_title("ScrolledWindow example")
19 window.set_border_width(0)
20 window.set_size_request(300, 300)
21
22 # create a new scrolled window.
23 scrolled_window = gtk.ScrolledWindow()
24 scrolled_window.set_border_width(10)
25
26 # the policy is one of POLICY AUTOMATIC, or POLICY_ALWAYS.
27 # POLICY_AUTOMATIC will automatically decide whether you need
28 # scrollbars, whereas POLICY_ALWAYS will always leave the scrollbars
29 # there. The first one is the horizontal scrollbar, the second, the
30 # vertical.
31 scrolled_window.set_policy(gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC, gtk.POLICY_ALWAYS)
32
33 # The dialog window is created with a vbox packed into it.
34 window.vbox.pack_start(scrolled_window, True, True, 0)
35 scrolled_window.show()
36
37 # create a table of 10 by 10 squares.
38 table = gtk.Table(10, 10, False)
39
40 # set the spacing to 10 on x and 10 on y
41 table.set_row_spacings(10)
42 table.set_col_spacings(10)
43
44 # pack the table into the scrolled window
45 scrolled_window.add_with_viewport(table)
46 table.show()
47
48 # this simply creates a grid of toggle buttons on the table
49 # to demonstrate the scrolled window.
50 for i in range(10):
51 for j in range(10):
52 buffer = "button (%d,%d)" % (i, j)
53 button = gtk.ToggleButton(buffer)
54 table.attach(button, i, i+1, j, j+1)
55 button.show()
56
57 # Add a "close" button to the bottom of the dialog
58 button = gtk.Button("close")
59 button.connect_object("clicked", self.destroy, window)
60
61 # this makes it so the button is the default.
62 button.set_flags(gtk.CAN_DEFAULT)
63 window.action_area.pack_start( button, True, True, 0)
64
65 # This grabs this button to be the default button. Simply hitting
66 # the "Enter" key will cause this button to activate.
67 button.grab_default()
68 button.show()
69 window.show()
70
71 def main():
72 gtk.main()
73 return 0
74
75 if __name__ == "__main__":
76 ScrolledWindowExample()
77 main()
|
Try resizing the window. You'll notice how the scrollbars react. You may also wish to use the set_size_request() method to set the default size of the window or other widgets.