
 |
Home · All Namespaces · All Classes · Main Classes · Grouped Classes · Modules · Functions |
The QDesktopWidget class provides access to screen information on multi-head systems. More...
#include <QDesktopWidget>
Inherits QWidget.
The QDesktopWidget class provides access to screen information on multi-head systems.
QApplication::desktop() function should be used to get an instance of the QDesktopWidget.
Systems with more than one graphics card and monitor can manage the physical screen space available either as multiple desktops, or as a large virtual desktop, which usually has the size of the bounding rectangle of all the screens (see isVirtualDesktop()). For an application, one of the available screens is the primary screen, i.e. the screen where the main widget resides (see primaryScreen()). All windows opened in the context of the application should be constrained to the boundaries of the primary screen; for example, it would be inconvenient if a dialog box popped up on a different screen, or split over two screens.
The QDesktopWidget provides information about the geometry of the available screens with screenGeometry(). The number of screens available is returned by numScreens(). The screen number that a particular point or widget is located in is returned by screenNumber().
Widgets provided by Qt use this class, for example, to place tooltips, menus and dialog boxes according to the parent or application widget.
Applications can use this class to save window positions, or to place child widgets on one screen.
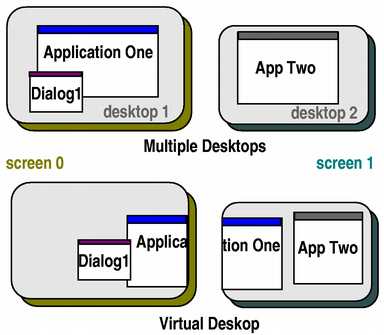
In the illustration above, Application One's primary screen is screen 0, and App Two's primary screen is screen 1.
Note: QDesktopWidget inherits the QWidget properties, width() and height(), which specify the size of the desktop. However, for desktops with multiple screens, the size of the desktop is the union of all the screen sizes, so width() and height() should not be used for computing the size of a widget to be placed on one of the screens. The correct width and height values are obtained using availableGeometry() or screenGeometry() for a particular screen.
See also QApplication, QApplication::desktop(), and QX11Info::appRootWindow().
Returns the available geometry of the screen with index screen. What is available will be subrect of screenGeometry() based on what the platform decides is available (for example excludes the dock and menu bar on Mac OS X, or the task bar on Windows). The default screen is used if screen is -1.
See also screenNumber() and screenGeometry().
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the available geometry of the screen which contains widget.
See also screenGeometry().
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the available geometry of the screen which contains p.
See also screenGeometry().
Returns true if the system manages the available screens in a virtual desktop; otherwise returns false.
For virtual desktops, screen() will always return the same widget. The size of the virtual desktop is the size of this desktop widget.
Returns the number of available screens.
See also primaryScreen().
Returns the index of the primary screen.
See also numScreens().
This signal is emitted when the size of screen changes.
Returns a widget that represents the screen with index screen (a value of -1 means the default screen).
If the system uses a virtual desktop, the returned widget will have the geometry of the entire virtual desktop; i.e., bounding every screen.
See also primaryScreen(), numScreens(), and isVirtualDesktop().
Returns the geometry of the screen with index screen. The default screen is used if screen is -1.
See also screenNumber().
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the geometry of the screen which contains widget.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the geometry of the screen which contains p.
Returns the index of the screen that contains the largest part of widget, or -1 if the widget not on a screen.
See also primaryScreen().
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the index of the screen that contains the point, or the screen which is the shortest distance from the point.
See also primaryScreen().
This signal is emitted when the work area available on screen changes.
| Copyright © 2009 Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies) | Trademarks | Qt 4.5.1 |