Dynamic Sensor Backend Registration
Static Backend Registration
Sensor backends are generally registered statically. The registration happens when the sensors library is first used and the registration remains in effect while the program runs.
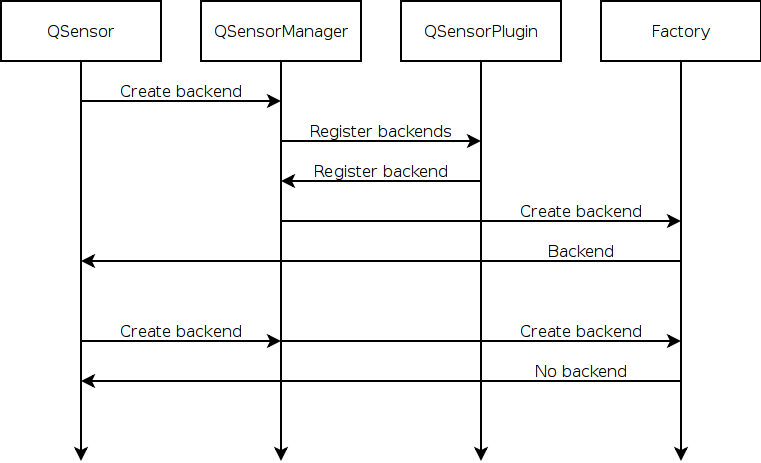
Statically registered backends may still exhibit some dynamic behaviour as the QSensorBackendFactory is free to return 0 to indicate that a backend cannot be created.
Dynamic Backend Registration
Although static registration is fine for most backends, there are some situations where this is problematic.
The clearest example is backends that represent non-fixed hardware. For example, a game controller that is connected via Bluetooth. As there may be more than one game controller in range of the phone, the program wants to record that a specific game controller should be used. If the backend had been registered statically there would have been no unique information about the controller. Instead, the registration is delayed until the controller is seen.
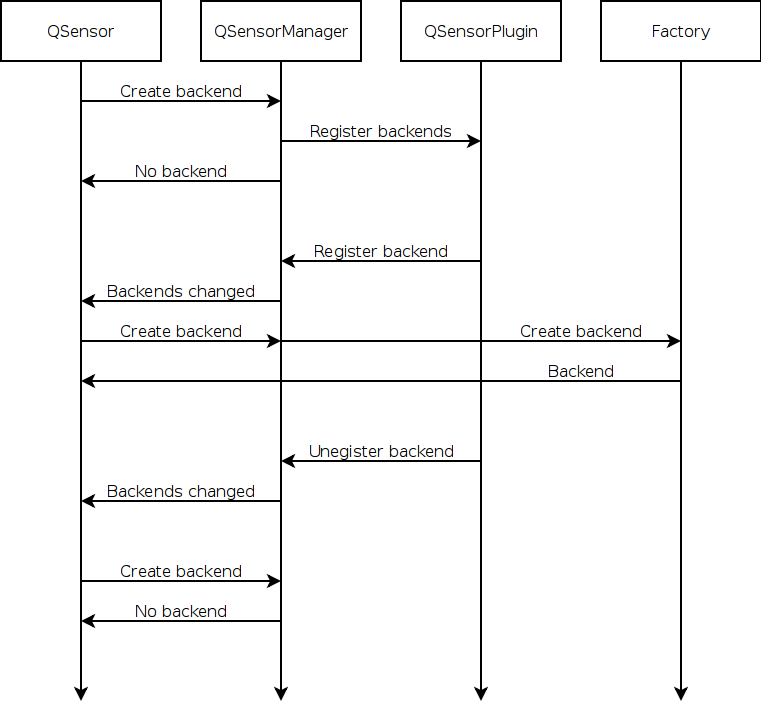
Suggested Registration Policy
A backend for fixed hardware should be registered immediately. Applications can see that the sensor can be used.
A backend for remote hardware should not be registered immediately. Applications can see that the sensor cannot be used. When the remote hardware becomes available, the backend should be registered. Applications can see that the sensor is available now.
If it is necessary to return 0 from a factory for a backend that was registered, the backend should be unregistered. Applications can see that the sensor is no longer available. If the factory can create the backend again, it should be re- gistered. Applications can see that the sensor is available again.
When the underlying hardware is no longer available, the backend should be unregistered. Existing instances of the backend should report error states to the application but should handle the situation gracefully.
© 2015 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
