Map QML Type
The Map type displays a map. More...
| Import Statement: | import QtLocation 5.3 |
| Since: | Qt Location 5.0 |
Properties
- activeMapType : MapType
- center : coordinate
- gesture : MapGestureArea
- mapItems : list<MapItem>
- maximumZoomLevel : real
- minimumZoomLevel : real
- plugin : Plugin
- supportedMapTypes : list<MapType>
- zoomLevel : real
Methods
- addMapItem(MapItem item)
- void cameraStopped()
- void clearMapItems()
- fitViewportToGeoShape(QGeoShape shape)
- fitViewportToMapItems()
- void pan(int dx, int dy)
- void removeMapItem(MapItem item)
- toCoordinate(QPointF screenPosition)
- toScreenPosition(coordinate coordinate)
Detailed Description
The Map type is used to display a map or image of the Earth, with the capability to also display interactive objects tied to the map's surface.
There are a variety of different ways to visualize the Earth's surface in a 2-dimensional manner, but all of them involve some kind of projection: a mathematical relationship between the 3D coordinates (latitude, longitude and altitude) and 2D coordinates (X and Y in pixels) on the screen.
Different sources of map data can use different projections, and from the point of view of the Map type, we treat these as one replaceable unit: the Map plugin. A Map plugin consists of a data source, as well as all other details needed to display its data on-screen.
The current Map plugin in use is contained in the plugin property of the Map item. In order to display any image in a Map item, you will need to set this property. See the Plugin type for a description of how to retrieve an appropriate plugin for use.
The geographic region displayed in the Map item is referred to as its viewport, and this is defined by the properties center, and zoomLevel. The center property contains a coordinate specifying the center of the viewport, while zoomLevel controls the scale of the map. See each of these properties for further details about their values.
When the map is displayed, each possible geographic coordinate that is visible will map to some pixel X and Y coordinate on the screen. To perform conversions between these two, Map provides the toCoordinate and toScreenPosition functions, which are of general utility.
Map Objects
Map related objects can be declared within the body of a Map object in Qt Quick and will automatically appear on the Map. To add objects programmatically, first be sure they are created with the Map as their parent (for example in an argument to Component::createObject), and then call the addMapItem method on the Map. A corresponding removeMapItem method also exists to do the opposite and remove an object from the Map.
Moving Map objects around, resizing them or changing their shape normally does not involve any special interaction with Map itself -- changing these details about a map object will automatically update the display.
Interaction
The Map type includes support for pinch and flick gestures to control zooming and panning. These are enabled by default, and available at any time by using the gesture object. The actual GestureArea is constructed specially at startup and cannot be replaced or destroyed. Its properties can be altered, however, to control its behavior.
Performance
Maps are rendered using OpenGL (ES) and the Qt Scene Graph stack, and as a result perform quite well where GL accelerated hardware is available.
For "online" Map plugins, network bandwidth and latency can be major contributors to the user's perception of performance. Extensive caching is performed to mitigate this, but such mitigation is not always perfect. For "offline" plugins, the time spent retrieving the stored geographic data and rendering the basic map features can often play a dominant role. Some offline plugins may use hardware acceleration themselves to (partially) avert this.
In general, large and complex Map items such as polygons and polylines with large numbers of vertices can have an adverse effect on UI performance. Further, more detailed notes on this are in the documentation for each map item type.
Example Usage
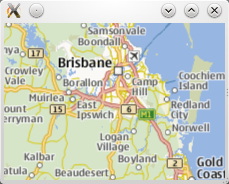
The following snippet shows a simple Map and the necessary Plugin type to use it. The map is centered near Brisbane, Australia, zoomed out to the minimum zoom level, with gesture interaction enabled.
Plugin {
id: somePlugin
// code here to choose the plugin as necessary
}
Map {
id: map
plugin: somePlugin
center {
latitude: -27
longitude: 153
}
zoomLevel: map.minimumZoomLevel
gesture.enabled: true
}
Property Documentation
activeMapType : MapType |
Access to the currently active map type.
This property can be set to change the active map type. See the supportedMapTypes property for possible values.
See also MapType.
center : coordinate |
This property holds the coordinate which occupies the center of the mapping viewport. Invalid center coordinates are ignored.
The default value is an arbitrary valid coordinate.
gesture : MapGestureArea |
Contains the MapGestureArea created with the Map. This covers pan, flick and pinch gestures. Use gesture.enabled: true to enable basic gestures, or see MapGestureArea for further details.
Returns the list of all map items in no particular order. These items include items that were declared statically as part of the type declaration, as well as dynamical items (addMapItem, MapItemView).
See also addMapItem, removeMapItem, and clearMapItems.
This property holds the maximum valid zoom level for the map.
The maximum zoom level is defined by the plugin used. If a plugin supporting mapping is not set, -1.0 is returned.
This property holds the minimum valid zoom level for the map.
The minimum zoom level is defined by the plugin used. If a plugin supporting mapping is not set, -1.0 is returned.
plugin : Plugin |
This property holds the plugin which provides the mapping functionality.
This is a write-once property. Once the map has a plugin associated with it, any attempted modifications of the plugin will be ignored.
supportedMapTypes : list<MapType> |
This read-only property holds the set of map types supported by this map.
See also activeMapType.
This property holds the zoom level for the map.
Larger values for the zoom level provide more detail. Zoom levels are always non-negative. The default value is 8.0.
Method Documentation
Adds the given item to the Map (for example MapQuickItem, MapCircle). If the object already is on the Map, it will not be added again.
As an example, consider the case where you have a MapCircle representing your current position:
import QtQuick 2.0 import QtLocation 5.3 PositionSource { id: positionSource } Map { id: map property MapCircle circle Component.onCompleted: { circle = Qt.createQmlObject('import QtLocation 5.3; MapCircle {}', page) circle.center = positionSource.position.coordinate circle.radius = 5000.0 circle.color = 'green' circle.border.width = 3 map.addMapItem(circle) } }
Note: MapItemViews cannot be added with this method.
See also mapItems, removeMapItem, and clearMapItems.
Removes all items from the map.
See also mapItems, addMapItem, and removeMapItem.
fitViewportToGeoShape(QGeoShape shape) |
Fits the current viewport to the boundary of the shape. The camera is positioned in the center of the shape, and at the largest integral zoom level possible which allows the whole shape to be visible on screen
Fits the current viewport to the boundary of all map items. The camera is positioned in the center of the map items, and at the largest integral zoom level possible which allows all map items to be visible on screen
Removes the given item from the Map (for example MapQuickItem, MapCircle). If the MapItem does not exist or was not previously added to the map, the method does nothing.
See also mapItems, addMapItem, and clearMapItems.
toCoordinate(QPointF screenPosition) |
Returns the coordinate which corresponds to the screen position screenPosition.
Returns an invalid coordinate if screenPosition is not within the current viewport.
toScreenPosition(coordinate coordinate) |
Returns the screen position which corresponds to the coordinate coordinate.
Returns an invalid QPointF if coordinate is not within the current viewport.
© 2015 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
