Custom Chart Example
This example shows how to customize the appearance of the different elements on a chart.
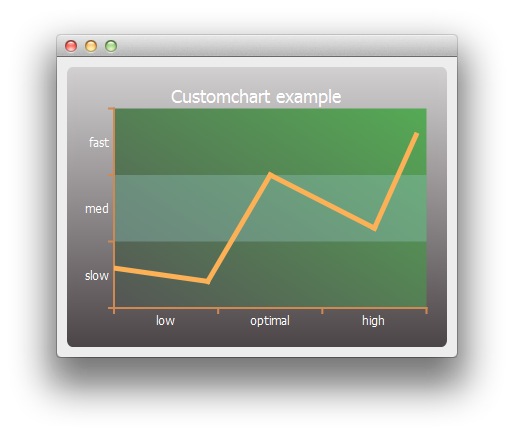
Running the Example
To run the example from Qt Creator, open the Welcome mode and select the example from Examples. For more information, visit Building and Running an Example.
Customizing Charts
We begin by creating a simple line series and a chart object.
QLineSeries *series = new QLineSeries(); *series << QPointF(0, 6) << QPointF(9, 4) << QPointF(15, 20) << QPointF(25, 12) << QPointF(29, 26); QChart *chart = new QChart(); chart->legend()->hide(); chart->addSeries(series);
First we customize the series and the chart's title and background.
// Customize series QPen pen(QRgb(0xfdb157)); pen.setWidth(5); series->setPen(pen); // Customize chart title QFont font; font.setPixelSize(18); chart->setTitleFont(font); chart->setTitleBrush(QBrush(Qt::white)); chart->setTitle("Customchart example"); // Customize chart background QLinearGradient backgroundGradient; backgroundGradient.setStart(QPointF(0, 0)); backgroundGradient.setFinalStop(QPointF(0, 1)); backgroundGradient.setColorAt(0.0, QRgb(0xd2d0d1)); backgroundGradient.setColorAt(1.0, QRgb(0x4c4547)); backgroundGradient.setCoordinateMode(QGradient::ObjectBoundingMode); chart->setBackgroundBrush(backgroundGradient); // Customize plot area background QLinearGradient plotAreaGradient; plotAreaGradient.setStart(QPointF(0, 1)); plotAreaGradient.setFinalStop(QPointF(1, 0)); plotAreaGradient.setColorAt(0.0, QRgb(0x555555)); plotAreaGradient.setColorAt(1.0, QRgb(0x55aa55)); plotAreaGradient.setCoordinateMode(QGradient::ObjectBoundingMode); chart->setPlotAreaBackgroundBrush(plotAreaGradient); chart->setPlotAreaBackgroundVisible(true);
Then we customize the axes.
QCategoryAxis *axisX = new QCategoryAxis(); QCategoryAxis *axisY = new QCategoryAxis(); // Customize axis label font QFont labelsFont; labelsFont.setPixelSize(12); axisX->setLabelsFont(labelsFont); axisY->setLabelsFont(labelsFont); // Customize axis colors QPen axisPen(QRgb(0xd18952)); axisPen.setWidth(2); axisX->setLinePen(axisPen); axisY->setLinePen(axisPen); // Customize axis label colors QBrush axisBrush(Qt::white); axisX->setLabelsBrush(axisBrush); axisY->setLabelsBrush(axisBrush); // Customize grid lines and shades axisX->setGridLineVisible(false); axisY->setGridLineVisible(false); axisY->setShadesPen(Qt::NoPen); axisY->setShadesBrush(QBrush(QColor(0x99, 0xcc, 0xcc, 0x55))); axisY->setShadesVisible(true);
Then the axis label values and ranges. Once the axes are ready, we set them to be used by the chart.
axisX->append("low", 10); axisX->append("optimal", 20); axisX->append("high", 30); axisX->setRange(0, 30); axisY->append("slow", 10); axisY->append("med", 20); axisY->append("fast", 30); axisY->setRange(0, 30); chart->addAxis(axisX, Qt::AlignBottom); chart->addAxis(axisY, Qt::AlignLeft); series->attachAxis(axisX); series->attachAxis(axisY);
Finally, we create a view containing the chart.
QChartView *chartView = new QChartView(chart); chartView->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
Now we are ready to show the chart on a main window.
QMainWindow window; window.setCentralWidget(chartView); window.resize(400, 300); window.show();
© 2023 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.