Deploying Applications to Embedded Linux Devices
You can specify settings for deploying applications to generic Linux devices in the project .pro file. You can view the settings in the Run Settings.
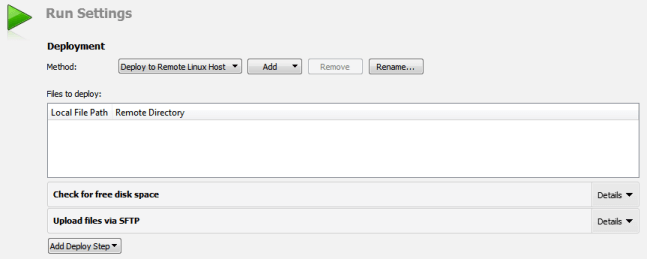
The files to be installed are listed in the Deployment step, the Files to deploy field. The Local File Path field displays the location of the file on the development PC. The Remote Directory field displays the folder where the file is installed on the device. Text in red color indicates that the information is missing. Edit the qmake INSTALLS variable in the project .pro file to add the missing files.
When you run the application, Qt Creator copies the necessary files to the device and starts the application on it.
For example, adding
target.path = /root INSTALLS += target
to the project .pro file will copy the binary of your project to /root on the remote device. Additional files can be deployed by adding them to further targets and adding those to INSTALLS as well.
Deploying on Embedded Linux
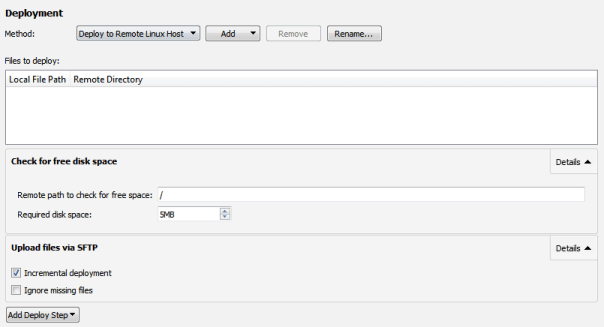
When you run the application on the Embedded Linux device, Qt Creator deploys the application as specified by the deploy steps. By default, Qt Creator copies the application files to the device by using the SSH file transfer protocol (SFTP), as specified by the Upload files via SFTP step.
If you have a lot of data to copy, select Details in the Upload Files via SFTP step, and then select the Incremental deployment check box. Qt Creator takes note of the deployment time and only copies files that have changed since the last deployment. However, when you make major changes on the device, such as removing files from the device manually or flashing a new disk image, or when you use another device with the same IP address, deselect the check box once, to have Qt Creator deploy all files again.
To only create a tarball and not copy the files to the device, select Add Deploy Step > Create tarball. Then remove all other deploy steps.
The Deploy tarball via SFTP upload step specifies that Qt Creator uploads the tarball to the device and extracts it.
The Check for free disk space step is by default the first deploy step. Use it to find out whether the remote file system has enough space left to deploy your project. Errors due to lack of disk space can otherwise be hard to detect.
Note: If the SFTP upload fails, make sure that the remote device has SFTP enabled in its SSH daemon. Some versions of Dropbear that come without SFTP support will crash when an SFTP upload is being attempted. This is not a bug in Qt Creator.
© 2016 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
