

 |
Previous | Content | Next |  |
| Installation | Architecture | |||
It's recommended that ralasafe data and application data are stored separately. What's jdbc url, jdbc username and jdbc password of ralasafe/application datasource? These can be configured in WEB-INF/ralasafe/datasources.xml.
It's recommended ralasafe privilege data is separated from your application/business data with different database schema or instance.
Ralasafe supports three datasource configurations:
Security policies(non-structural data) are stored in filesystem. It's very easy to migrate them. Other privilege data is stored in database. Ralasafe supports major databases such as oracle, db2, mysql, sql server, etc.
Security policy repository dir can be specified in web.xml, org.ralasafe.servlet.StartupServlet's repositoryDir parameter.
Systems which need access control, would be logined by user. But each system's user fields and field types are different. Ralasafe uses metadata xml to describe them. Take ralasafe demo application for example:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <user> <table ds="app" name="mainTable" sqlName="UserView" uniqueFields="loginName"> <field name="id" columnName="id" sqlType="int" javaType="java.lang.Integer" /> <field name="name" columnName="name" sqlType="varchar(40)" javaType="java.lang.String" displayName="Name" show="true" /> <field name="companyName" columnName="companyName" sqlType="varchar(100)" javaType="java.lang.String" displayName="Company" show="true" /> <field name="loginName" columnName="loginName" sqlType="varchar(40)" javaType="java.lang.String" /> <field name="password" columnName="password" sqlType="varchar(40)" javaType="java.lang.String" /> <field name="isManager" columnName="isManager" sqlType="int" javaType="java.lang.Boolean" /> <field name="companyId" columnName="companyId" sqlType="int" javaType="java.lang.Integer" /> <field name="departmentId" columnName="departmentId" sqlType="int" javaType="java.lang.Integer" /> <field name="companyLevel" columnName="companyLevel" sqlType="int" javaType="java.lang.Integer" /> </table> </user>
In this example, user info comes from a table/view named UserView. This table can be found in app datasource. User contains id(required),name, companyName, loginName, password, isManager, companyId, departmentId and companyLevel fields, and loginName field is unique. Multiple unique fields are sepaerated by ','. Id field is primary key field.
Name attribute of field element means the attribute of user, while columnName attribute of field element means the sql table's columnName. User field information can be retrieved through the following API:
package org.back;
public class User {
public Object get( String fieldName );
......
}
Let's take a further look at displayName and show attributes of field element. As seen in the ralasafe demo, name and companyName fields will be shown in ralasafe designer as follows:
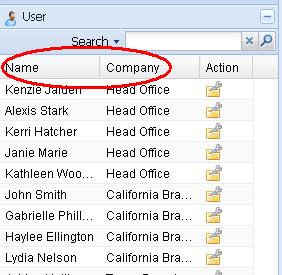
When usermetadata config file is ready, you can install it into ralasafe through url: http://localhost:8080/{your web app}/ralasafe/userTypeMng
As we mentioned before, ralasafe controls access from two directions. They correspond to these APIs:
| 1) query data from system | Query methods in Ralasafe/WebRalasafe Ralasafe.query(int privilegeId, User user,...) |
| 2) commit data to system | Permit methods in Ralasafe/WebRalasafe Ralasafe.permit((int privilegeId, User user,
Object businessData,...) |
You can wrap them into your code or aspect. Privilege ids can be exported by ralasafe gui. On the privilege panel, click the export button  on the right .
on the right .
See org.ralasafe.Ralasafe, org.ralasafe.WebRalasafe javadoc for details.
 |
Previous | Content | Next |  |
| Installation | Architecture | |||